lecture #7 ppt
... Engineering Organic-to-Semiconductor Heterojunctions February 13 | 4-5 p.m. | Pitzer Auditorium, 120 Latimer Hall Professor Thomas F. Kuech, Dept. of Chemical & Biological Engineering, University of Wisconsin - Madison ...
... Engineering Organic-to-Semiconductor Heterojunctions February 13 | 4-5 p.m. | Pitzer Auditorium, 120 Latimer Hall Professor Thomas F. Kuech, Dept. of Chemical & Biological Engineering, University of Wisconsin - Madison ...
Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement
... 2. Greek philosophers – observations and logic to study matter nature composed of 4 elements air, fire, water, and earth that have 4 properties – hotness, coldness, dryness, wetness (no atoms) 3. alchemists – furthered chemistry by trying to turn other metals into gold – discovered new compounds and ...
... 2. Greek philosophers – observations and logic to study matter nature composed of 4 elements air, fire, water, and earth that have 4 properties – hotness, coldness, dryness, wetness (no atoms) 3. alchemists – furthered chemistry by trying to turn other metals into gold – discovered new compounds and ...
Reactions Homework Packet
... no reaction, write NO REACTION. For the following assume all compounds are aqueous (dissolved in water). ...
... no reaction, write NO REACTION. For the following assume all compounds are aqueous (dissolved in water). ...
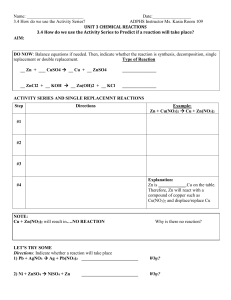
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... o Protons, electrons and neutrons make up an atom o Atoms make up molecules, all matter is made of atoms o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are buzzing outside the nucleus around the nucleus in orbitals o # of protons defines an element, # of protons = atomic # o # of neutrons ...
... o Protons, electrons and neutrons make up an atom o Atoms make up molecules, all matter is made of atoms o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are buzzing outside the nucleus around the nucleus in orbitals o # of protons defines an element, # of protons = atomic # o # of neutrons ...
Thermochemistry: study of the relationships between chemistry and
... The heat exchanged in a specific experiment is qP and its related state function for a general process is ΔH : change in enthalpy. Since ΔH only involves the heat given off or absorbed, it has the same sign conventions as q: Endothermic reaction: heat is transferred from surroundings to system (inwa ...
... The heat exchanged in a specific experiment is qP and its related state function for a general process is ΔH : change in enthalpy. Since ΔH only involves the heat given off or absorbed, it has the same sign conventions as q: Endothermic reaction: heat is transferred from surroundings to system (inwa ...
Learning Outcomes for CHEM1001 in 2015
... use the ideal gas law to relate the number of moles, pressure, volume and temperature of a gas relate gas density and molar mass convert between the common units of pressure (atm, Pa and mmHg use the appropriate value of the gas constant, R ...
... use the ideal gas law to relate the number of moles, pressure, volume and temperature of a gas relate gas density and molar mass convert between the common units of pressure (atm, Pa and mmHg use the appropriate value of the gas constant, R ...
3_2: More Chemical Changes
... Investigate: Chemical Reactions • In today’s lab, you will be looking at chemical reactions that occur between 8 different solid materials. The solids have been dissolved in water to make solutions. ...
... Investigate: Chemical Reactions • In today’s lab, you will be looking at chemical reactions that occur between 8 different solid materials. The solids have been dissolved in water to make solutions. ...
2008 local exam - American Chemical Society
... Not valid for use as an ACS Olympiad Local Section Exam after March 29, 2008. STOCK CODE OL08 Distributed by the ACS DivCHED Examinations Institute, University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. ...
... Not valid for use as an ACS Olympiad Local Section Exam after March 29, 2008. STOCK CODE OL08 Distributed by the ACS DivCHED Examinations Institute, University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. ...
Catalyst Notes - University of Idaho
... increase reaction rates to the same extent in both the forward and reverse directions do not modify the Gibbs free energy change are not consumed in the reaction concentration cancels out in the calculation of the equilibrium constant a small amount of catalyst affects the rate of reaction for a lar ...
... increase reaction rates to the same extent in both the forward and reverse directions do not modify the Gibbs free energy change are not consumed in the reaction concentration cancels out in the calculation of the equilibrium constant a small amount of catalyst affects the rate of reaction for a lar ...
Hydrogen Production by Splitting Water in an Electrolyzer
... Studies of reacting systems - whether small scale reactions in a laboratory or large scale processes, all focus on obtaining a basic description of the individual steps involved in the reaction, and the characteristic rate of each step. In most studies, this information is obtained by experimental a ...
... Studies of reacting systems - whether small scale reactions in a laboratory or large scale processes, all focus on obtaining a basic description of the individual steps involved in the reaction, and the characteristic rate of each step. In most studies, this information is obtained by experimental a ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.