C2 Knowledge PowerPoint
... The different compounds have different attractions to the material in the column and therefore travel at different speeds. Different compounds are detected at different times, we say they have different retention times. A gas chromatograph is produced as seen on the right. This chromatograph shows t ...
... The different compounds have different attractions to the material in the column and therefore travel at different speeds. Different compounds are detected at different times, we say they have different retention times. A gas chromatograph is produced as seen on the right. This chromatograph shows t ...
Syllabus of the International Chemistry Olympiad
... calculation of rate constant for second and third order reactions ...
... calculation of rate constant for second and third order reactions ...
Chapter 13
... 2H2O(l) 2H2(g) + O2(g) K = [H2]2[O2] and Kp=(P2H2)(PO2) Water is not included in either equilibrium expression because it is a pure liquid. However, if water is a gas rather than a liquid, 2H2O(g) 2H2(g) + O2(g) ...
... 2H2O(l) 2H2(g) + O2(g) K = [H2]2[O2] and Kp=(P2H2)(PO2) Water is not included in either equilibrium expression because it is a pure liquid. However, if water is a gas rather than a liquid, 2H2O(g) 2H2(g) + O2(g) ...
Honors Midterm - Stamford High School
... 4. Write numbers (coefficients) in front of each of the boxes until the inventory for each element is the same both before and after the reaction. Whenever you change a number, make sure to update the inventory - otherwise, you run the risk of balancing it incorrectly. When all the numbers in the in ...
... 4. Write numbers (coefficients) in front of each of the boxes until the inventory for each element is the same both before and after the reaction. Whenever you change a number, make sure to update the inventory - otherwise, you run the risk of balancing it incorrectly. When all the numbers in the in ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... b. Identify any reaction intermediates in this mechanism. c. Write the rate equation for the rate determining step. d. Show how the rate equation in c. can be used to obtain the rate law for the overall reaction. e. If the concentrations of the reactants are doubled, by what ratio does the reaction ...
... b. Identify any reaction intermediates in this mechanism. c. Write the rate equation for the rate determining step. d. Show how the rate equation in c. can be used to obtain the rate law for the overall reaction. e. If the concentrations of the reactants are doubled, by what ratio does the reaction ...
1999 Advanced Placement Chemistry Exam Section I: Multiple
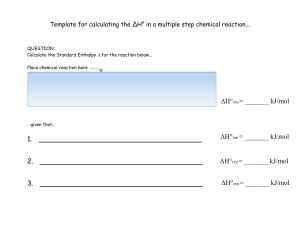
... the reaction of X with a large excess of Y to yield ∆H is -1,323 kJ. What is the value of ∆H if the Z. The concentrations of X and Y were measured combustion produced liquid water H2O(l), rather over a period of time. According to the results, than water vapor H2O(g) ? (∆H for the phase which of the ...
... the reaction of X with a large excess of Y to yield ∆H is -1,323 kJ. What is the value of ∆H if the Z. The concentrations of X and Y were measured combustion produced liquid water H2O(l), rather over a period of time. According to the results, than water vapor H2O(g) ? (∆H for the phase which of the ...
Unit 1: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
... Temperature = degree of hotness or coldness of an object, which is a measure of average kinetic energy of the molecules Heat = the energy transferred from one body to another because of the temp. difference Heat is a form of energy; temp. in NOT! There is more heat in a large iceberg than in a cup ...
... Temperature = degree of hotness or coldness of an object, which is a measure of average kinetic energy of the molecules Heat = the energy transferred from one body to another because of the temp. difference Heat is a form of energy; temp. in NOT! There is more heat in a large iceberg than in a cup ...
CHEMISTRY 102 Spring 2012 Hour Exam III Page 20 1. For the
... After equilibrium is reached, which of the following statements (a-d) regarding these experiments is true? a) In experiment 1, the rate of the forward reaction at equilibrium will be greater than the rate of the reverse reaction at equilibrium. b) Equilibrium cannot be reached in experiment 2 becaus ...
... After equilibrium is reached, which of the following statements (a-d) regarding these experiments is true? a) In experiment 1, the rate of the forward reaction at equilibrium will be greater than the rate of the reverse reaction at equilibrium. b) Equilibrium cannot be reached in experiment 2 becaus ...
Describing Chemical Reactions
... Chemical equations use chemical formulas and other symbols instead of words to summarize a reaction. All chemical equations have a common structure. A chemical equation tells you the substances you start with in a reaction and the substances you get at the end. The substances you have at the beginni ...
... Chemical equations use chemical formulas and other symbols instead of words to summarize a reaction. All chemical equations have a common structure. A chemical equation tells you the substances you start with in a reaction and the substances you get at the end. The substances you have at the beginni ...
Ch. 3 Sections 3.9-3.10 Notes
... • The coefficients tell us that to make 1 mol of Na3PO4 from 1 mol of H3PO4, we must also use 3 mol of NaOH. • We don’t however, have to carry out the reaction with these actual numbers of moles. • Whatever quantities we choose must be in the proportions set by the coefficients. • Regardless of the ...
... • The coefficients tell us that to make 1 mol of Na3PO4 from 1 mol of H3PO4, we must also use 3 mol of NaOH. • We don’t however, have to carry out the reaction with these actual numbers of moles. • Whatever quantities we choose must be in the proportions set by the coefficients. • Regardless of the ...
Chemistry 20H
... Note that the only way to increase the number of iodine atoms on the reactant side is to add another NaI molecule, thus increasing both the number of sodium and iodine atoms. This causes the number of sodium atoms to become unbalanced, so the number of sodium atoms on the product side must be increa ...
... Note that the only way to increase the number of iodine atoms on the reactant side is to add another NaI molecule, thus increasing both the number of sodium and iodine atoms. This causes the number of sodium atoms to become unbalanced, so the number of sodium atoms on the product side must be increa ...
1) Which of the following correctly lists the atoms in order of
... 10) A sample of gas is in a closed container of constant volume and at constant temperature. You may add 0.100 mol of any of the following gases: NH3, H2, CO2, or N2. a) The pressure increases least for the addition of 0.100 mol H2. b) The pressure increases more for the addition of 0.100 mol CO2 th ...
... 10) A sample of gas is in a closed container of constant volume and at constant temperature. You may add 0.100 mol of any of the following gases: NH3, H2, CO2, or N2. a) The pressure increases least for the addition of 0.100 mol H2. b) The pressure increases more for the addition of 0.100 mol CO2 th ...
Lesson 9 Review Teacher`s Copy
... 3.2.i. Oxidation numbers (states) can be assigned to atoms and ions. Changes in oxidation numbers indicate that oxidation and reduction have occurred. (5) 3.2.j. An electrochemical cell can be either voltaic or electrolytic. In an electrochemical cell, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction at ...
... 3.2.i. Oxidation numbers (states) can be assigned to atoms and ions. Changes in oxidation numbers indicate that oxidation and reduction have occurred. (5) 3.2.j. An electrochemical cell can be either voltaic or electrolytic. In an electrochemical cell, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction at ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.