AP CHEMISTRY PROBLEMS ENTHALPY, ENTROPY, AND FREE
... respectively. What is the value of ΔG° at 298 K? Assuming that ΔH° and ΔS° do not depend on temperature, at what temperature is ΔG°=O? Is ΔG° negative above or below this temperature? ...
... respectively. What is the value of ΔG° at 298 K? Assuming that ΔH° and ΔS° do not depend on temperature, at what temperature is ΔG°=O? Is ΔG° negative above or below this temperature? ...
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE
... F. Concentration Cells Since an electrode potential, E°, depends upon the concentration of the solutions used in the electrode, a cell may be constructed from two half-cells composed of the same materials but differing in concentration of ions. The spontaneous reaction occurs in the direction that ...
... F. Concentration Cells Since an electrode potential, E°, depends upon the concentration of the solutions used in the electrode, a cell may be constructed from two half-cells composed of the same materials but differing in concentration of ions. The spontaneous reaction occurs in the direction that ...
equilibrium
... 2. What is the significance of double arrows in an equation? 3. How is the term equilibrium used to describe an aqueous solution which is ...
... 2. What is the significance of double arrows in an equation? 3. How is the term equilibrium used to describe an aqueous solution which is ...
- Dr.Divan Fard
... State functions are properties that are determined by the state of the system, regardless of how that condition was achieved. ...
... State functions are properties that are determined by the state of the system, regardless of how that condition was achieved. ...
Activation of Carbon Chlorine Bonds Using Palladium (II) Catalysts
... (2) was active in chlorobenzene, producing benzene. In the presence of paradichlorobenzene and meta-dichlorobenzene, no benzene was produced. In both reactions hydrogen gas was consumed, and a solid was produced, but no benzene was detected. It is possible that the para-dichlorobenzene and metadichl ...
... (2) was active in chlorobenzene, producing benzene. In the presence of paradichlorobenzene and meta-dichlorobenzene, no benzene was produced. In both reactions hydrogen gas was consumed, and a solid was produced, but no benzene was detected. It is possible that the para-dichlorobenzene and metadichl ...
Final Review
... Calculate enthalpy, entropy and Gibb’s Free Energy (using the chart) Determine whether a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous (using Gibb’s Free Energy) Solutions Express and calculate concentrations of solutions in molarity Explain freezing point depression and boiling point elevation ...
... Calculate enthalpy, entropy and Gibb’s Free Energy (using the chart) Determine whether a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous (using Gibb’s Free Energy) Solutions Express and calculate concentrations of solutions in molarity Explain freezing point depression and boiling point elevation ...
- Wiley Online Library
... The reaction was initiated by mixing PTA with TBAF in methanol and then injecting the mixture into an IR cavity that was either tuned to (ON resonance) or detuned from (OFF resonance) the C@Si stretching mode. The detuned case serves as a control experiment for the kinetics in the absence of VSC. An ...
... The reaction was initiated by mixing PTA with TBAF in methanol and then injecting the mixture into an IR cavity that was either tuned to (ON resonance) or detuned from (OFF resonance) the C@Si stretching mode. The detuned case serves as a control experiment for the kinetics in the absence of VSC. An ...
8.5DF: Chemical Formulas and Equations
... reacting with water to produce carbon dioxide gas. This gas produces the “holes” in the cake that give the cake its light, fluffy texture. A similar type of reaction occurs when baking soda is mixed with vinegar. Work with your child to investigate, either online or via textbook, the chemical formul ...
... reacting with water to produce carbon dioxide gas. This gas produces the “holes” in the cake that give the cake its light, fluffy texture. A similar type of reaction occurs when baking soda is mixed with vinegar. Work with your child to investigate, either online or via textbook, the chemical formul ...
SAT Practice Test 3
... d. i and iii only e. i, ii, and iii 83. Which of the following statements is not true regarding the kinetic molecular theory? a. The volume that gas molecules occupy is negligible compared to the volume within which the gas is contained b. There are no forces present between gas molecules c. Collisi ...
... d. i and iii only e. i, ii, and iii 83. Which of the following statements is not true regarding the kinetic molecular theory? a. The volume that gas molecules occupy is negligible compared to the volume within which the gas is contained b. There are no forces present between gas molecules c. Collisi ...
2015 Academic Challenge CHEMISTRY TEST – STATE
... Most nitrates are soluble Most salts containing Group 1 ions or ammonium (NH4+) are soluble Most chloride, bromide, and iodide salts are soluble except those of Ag+, Pb2+, and Hg22+. Most sulfates are soluble with the exception of Ba2+, Pb2+, Hg22+, and Ca2+ Most hydroxide salts are only slightly so ...
... Most nitrates are soluble Most salts containing Group 1 ions or ammonium (NH4+) are soluble Most chloride, bromide, and iodide salts are soluble except those of Ag+, Pb2+, and Hg22+. Most sulfates are soluble with the exception of Ba2+, Pb2+, Hg22+, and Ca2+ Most hydroxide salts are only slightly so ...
Electrochemical Fundamentals
... British physical chemist who was the first to connect the kinetic electrochemistry built up in the second half of the twentieth century with the thermodynamic electrochemistry that dominated the first half. He had to his credit, not only the first exponential relation between current and potential ( ...
... British physical chemist who was the first to connect the kinetic electrochemistry built up in the second half of the twentieth century with the thermodynamic electrochemistry that dominated the first half. He had to his credit, not only the first exponential relation between current and potential ( ...
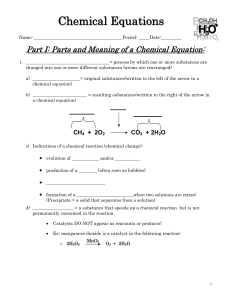
Chemical Equations
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
- Gondwana University, Gadchiroli
... (A) Second law of thermodynamics : Need for second law of thermodynamics, statements of second law of thermodynamics, concept of entropy, entropy as a state function of V & T,P&T, entropy change in phase change for ideal gas, entropy as criteria of spontaneity & equilibrium. [4L] (B) Free energy fun ...
... (A) Second law of thermodynamics : Need for second law of thermodynamics, statements of second law of thermodynamics, concept of entropy, entropy as a state function of V & T,P&T, entropy change in phase change for ideal gas, entropy as criteria of spontaneity & equilibrium. [4L] (B) Free energy fun ...
Final Exam Practice-2017
... 92. What is the element that is reduced in the following reaction? Br2 (g) + 2HI (aq) 2HBr (aq) + I2 (l) a) Br b) H c) I 93. Which of the following is the correct balanced half reaction for I2O5 I2 in a basic solution? a) 10H+ + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 5H2O c) 5H2O + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 10 OHb) 10H+ + I ...
... 92. What is the element that is reduced in the following reaction? Br2 (g) + 2HI (aq) 2HBr (aq) + I2 (l) a) Br b) H c) I 93. Which of the following is the correct balanced half reaction for I2O5 I2 in a basic solution? a) 10H+ + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 5H2O c) 5H2O + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 10 OHb) 10H+ + I ...
_______1. solution a. capable of being dissolved _______2. solute
... 118. List three ways to increase the rate at which a reactions proceeds: _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 119. If a reaction takes place very slowly, the bonds that are broken and ref ...
... 118. List three ways to increase the rate at which a reactions proceeds: _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 119. If a reaction takes place very slowly, the bonds that are broken and ref ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.