AP Chapter 6 Review
... Which of the following statements is CORRECT? a. If a reaction occurs at constant pressure, w = E. b. If a reaction occurs at constant pressure, q = H. c. If a reaction occurs at constant pressure, q = E. d. If a reaction occurs at constant volume, E > H. e. If a reaction occurs at constant vol ...
... Which of the following statements is CORRECT? a. If a reaction occurs at constant pressure, w = E. b. If a reaction occurs at constant pressure, q = H. c. If a reaction occurs at constant pressure, q = E. d. If a reaction occurs at constant volume, E > H. e. If a reaction occurs at constant vol ...
Document
... As for spectrochemical analysis, two analysis methods will be held. First method will be held is a simple and basic technique, which involves only the calculation of Δo by using the longest wavelength band. This method allows us to create a ranking between ligands, however, it does not yield accurat ...
... As for spectrochemical analysis, two analysis methods will be held. First method will be held is a simple and basic technique, which involves only the calculation of Δo by using the longest wavelength band. This method allows us to create a ranking between ligands, however, it does not yield accurat ...
File
... Lesson 2.4: Combustion Reactions In some areas of the Arctic, large amounts of methane, CH4 (g) are entering the atmosphere. Where is it coming from? As the climate becomes warmer and the ground thaws bacteria produce methane from the remains of dead plants and animals. How do scientists find the me ...
... Lesson 2.4: Combustion Reactions In some areas of the Arctic, large amounts of methane, CH4 (g) are entering the atmosphere. Where is it coming from? As the climate becomes warmer and the ground thaws bacteria produce methane from the remains of dead plants and animals. How do scientists find the me ...
Electrochemistry
... Balancing Redox Equations Redox reactions are often quite complicated and difficult to balance. For this reason, you’ll learn a step-by-step method for balancing these types of reactions, when they occur in acidic or in basic solutions. The procedure is called the “Half-Reactions Method” of balanci ...
... Balancing Redox Equations Redox reactions are often quite complicated and difficult to balance. For this reason, you’ll learn a step-by-step method for balancing these types of reactions, when they occur in acidic or in basic solutions. The procedure is called the “Half-Reactions Method” of balanci ...
Solubility Product Constants We have been looking at how
... We have been looking at how equilibrium constants can be used in chemical reactions. The concept of equilibrium also applies to saturated solutions of ionic solids. A saturated solution is one that is holding the maximum amount of solute possible at a given temperature. Even though a solution is sat ...
... We have been looking at how equilibrium constants can be used in chemical reactions. The concept of equilibrium also applies to saturated solutions of ionic solids. A saturated solution is one that is holding the maximum amount of solute possible at a given temperature. Even though a solution is sat ...
Unit 4 - Calculations and Chemical Reactions
... decomposition, single replacement and double replacement reactions. I) Combination Reactions In a combination reaction, two or more substances react to form a single product. The general form of this reaction is (A + B → AB). Some examples are shown below: 2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s) 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → ...
... decomposition, single replacement and double replacement reactions. I) Combination Reactions In a combination reaction, two or more substances react to form a single product. The general form of this reaction is (A + B → AB). Some examples are shown below: 2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s) 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → ...
1985 Free Response Answers
... a) thre points Points on ordinate take into account the initial amounts of the three substances, and PCl5 line rises while others fall. Lines curved at start and flat after equilibrium. ...
... a) thre points Points on ordinate take into account the initial amounts of the three substances, and PCl5 line rises while others fall. Lines curved at start and flat after equilibrium. ...
Subject Materials for Chemistry
... 2HI(g) are as follows: [HI] = 0.490M. [H2] =0.080M and [I2] = 0.060M Calculate the equilibrium constant at this temperature Ans. P ...
... 2HI(g) are as follows: [HI] = 0.490M. [H2] =0.080M and [I2] = 0.060M Calculate the equilibrium constant at this temperature Ans. P ...
Hydrocarbon ions in fuel-rich, CH4-C2H2-0, flames
... The ion chemistry is discussed for fuel-rich, nearly sooting, methane-oxygen flames at atmospheric pressure with added acetylene. Different types of ion-molecule reactions, both positive and negative, which can contribute through chemical ionization (CI) processes are summarized including their depe ...
... The ion chemistry is discussed for fuel-rich, nearly sooting, methane-oxygen flames at atmospheric pressure with added acetylene. Different types of ion-molecule reactions, both positive and negative, which can contribute through chemical ionization (CI) processes are summarized including their depe ...
File - Mr Weng`s IB Chemistry
... So sodium hydroxide is the limiting reagent. n(NaOH) = CV = 2M x 0.02dm3 = 0.0400 moles (so the enthalpy PER MOLE can be determined) H(NaOH) = Q/n = 2.51kJ/0.04moles = 62.7 kJ/mol The energy is evolved, exothermic, so H(NaOH) = -62.7 kJ/mol ...
... So sodium hydroxide is the limiting reagent. n(NaOH) = CV = 2M x 0.02dm3 = 0.0400 moles (so the enthalpy PER MOLE can be determined) H(NaOH) = Q/n = 2.51kJ/0.04moles = 62.7 kJ/mol The energy is evolved, exothermic, so H(NaOH) = -62.7 kJ/mol ...
CHEM 230: Principles of Physical Chemistry
... 1. Gases consist of large numbers of molecules that are in continuous, random motion. 2. The combined volume of all the molecules of the gas is negligible relative to the total volume in which the gas is contained. ...
... 1. Gases consist of large numbers of molecules that are in continuous, random motion. 2. The combined volume of all the molecules of the gas is negligible relative to the total volume in which the gas is contained. ...
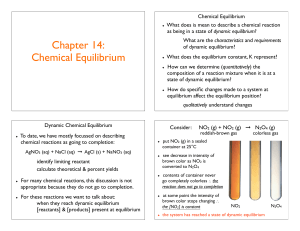
Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium
... What does the equilibrium constant, K represent? How can we determine (quantitatively) the composition of a reaction mixture when it is at a state of dynamic equilibrium? How do specific changes made to a system at equilibrium affect the equilibrium position? qualitatively understand changes ...
... What does the equilibrium constant, K represent? How can we determine (quantitatively) the composition of a reaction mixture when it is at a state of dynamic equilibrium? How do specific changes made to a system at equilibrium affect the equilibrium position? qualitatively understand changes ...
Why Study Chemistry
... – flows from hot objects to cold objects – is absorbed/released by an object resulting in its change in temperature ...
... – flows from hot objects to cold objects – is absorbed/released by an object resulting in its change in temperature ...
Chem 1B Fa2015 FinalExam Review
... [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] is a tetrahedral complex, which is a weak-field complex, and with 3d8 electron configuration for Ni2+, the complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] would be paramagnetic. In addition, a tetrahedral complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] will not exhibit isomerism. (Show d8 configuration in tetrahedral crystal field diagr ...
... [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] is a tetrahedral complex, which is a weak-field complex, and with 3d8 electron configuration for Ni2+, the complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] would be paramagnetic. In addition, a tetrahedral complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] will not exhibit isomerism. (Show d8 configuration in tetrahedral crystal field diagr ...
Chem152
... B) atomic number C) atomic mass D) mass number E) none of the above 9. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of silver-107? A) 47 B) 60 C) 107 D) 154 E) none of the above 10. What is the term for an atom (or group of atoms) that bears a charge as the result of gaining or losing valence ele ...
... B) atomic number C) atomic mass D) mass number E) none of the above 9. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of silver-107? A) 47 B) 60 C) 107 D) 154 E) none of the above 10. What is the term for an atom (or group of atoms) that bears a charge as the result of gaining or losing valence ele ...
Oxidation-Reduction Processes in Natural Waters
... Organisms catalyze all significant redox reaction in natural waters. As illustrated in the table, with the exception of photosynthesis and hydrogen generation, all of the reactions in the table are thermodynamically favorable as written. That is, the reactions as written have a negative free energy. ...
... Organisms catalyze all significant redox reaction in natural waters. As illustrated in the table, with the exception of photosynthesis and hydrogen generation, all of the reactions in the table are thermodynamically favorable as written. That is, the reactions as written have a negative free energy. ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.