Impedance Matching Networks Applied to RF Power Transistors
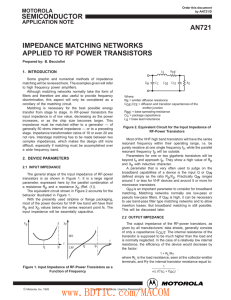
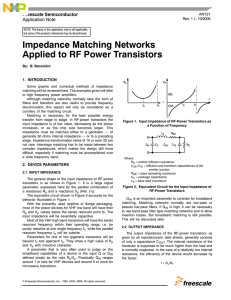
... The general shape of the input impedance of RF-power transistors is as shown in Figure 1. It is a large signal parameter, expressed here by the parallel combination of a resistance Rp and a reactance Xp (Ref. (1)). The equivalent circuit shown in Figure 2 accounts for the behavior illustrated in Fig ...
... The general shape of the input impedance of RF-power transistors is as shown in Figure 1. It is a large signal parameter, expressed here by the parallel combination of a resistance Rp and a reactance Xp (Ref. (1)). The equivalent circuit shown in Figure 2 accounts for the behavior illustrated in Fig ...
A VIEW OF ELECTROMAGNETIC LIFE ABOVE 100 MHz
... New Culprit signal is modulation envelope generally a low frequency waveform EMC analysis can be performed on rectified waveform “Audio” rectification can cause EMC problems even if culprit frequency is outside frequency range of system under analysis Culprit signal gets into and overloads the c ...
... New Culprit signal is modulation envelope generally a low frequency waveform EMC analysis can be performed on rectified waveform “Audio” rectification can cause EMC problems even if culprit frequency is outside frequency range of system under analysis Culprit signal gets into and overloads the c ...
EEE-PP-006 - 3642
... Inductors can be avoided. Passive filters without inductors cannot obtain a high Q (low damping), but with them are often large and expensive (at low frequencies), may have significant internal resistance, and may pick up surrounding electromagnetic signals. The shape of the response, the Q (Qua ...
... Inductors can be avoided. Passive filters without inductors cannot obtain a high Q (low damping), but with them are often large and expensive (at low frequencies), may have significant internal resistance, and may pick up surrounding electromagnetic signals. The shape of the response, the Q (Qua ...
Problems to resolve:
... We are going to use two inexpensive Hittite amplifiers as defined in Jeff Keefer’s email (above). The reason for two different amps is that we can not find a cheap amplifier that conforms to all of our requirements. We are going to use two transfer switches that, when selecting one amp, the other wi ...
... We are going to use two inexpensive Hittite amplifiers as defined in Jeff Keefer’s email (above). The reason for two different amps is that we can not find a cheap amplifier that conforms to all of our requirements. We are going to use two transfer switches that, when selecting one amp, the other wi ...
LCL Filter Design for Grid-connected NPC Inverters
... frequencies; for example in overhead lines. Nevertheless, in grids with noticeable underground cable share, the grid impedance under higher frequencies (over 2000 Hz) is generally smaller in such a way that high frequency components can be neglected. A requirement for such a procedure is the calcula ...
... frequencies; for example in overhead lines. Nevertheless, in grids with noticeable underground cable share, the grid impedance under higher frequencies (over 2000 Hz) is generally smaller in such a way that high frequency components can be neglected. A requirement for such a procedure is the calcula ...
AN301: LCR Meter Measurement Accuracy
... LCR meters make taking L, C and R measurements very easy. One can simply hook up the test component between the clip terminals and get the reading on the display with very little effort. However, if you want to be certain of the measurement that you have made, you must understand how an LCR meter op ...
... LCR meters make taking L, C and R measurements very easy. One can simply hook up the test component between the clip terminals and get the reading on the display with very little effort. However, if you want to be certain of the measurement that you have made, you must understand how an LCR meter op ...
1422-1 Resonance and Filters - Cleveland Institute of Electronics
... from the resonant frequency calibration point in step 4. The purpose of this procedure is to adjust the variable resistor (potentiometer) so that the voltage drop across the resistor (ER) and the voltage drop across terminals A and B are equal Record their value in the Exp. 4, data table . ...
... from the resonant frequency calibration point in step 4. The purpose of this procedure is to adjust the variable resistor (potentiometer) so that the voltage drop across the resistor (ER) and the voltage drop across terminals A and B are equal Record their value in the Exp. 4, data table . ...
DY34760764
... inverters for the purpose of eliminating the sideeffects mentioned above. Generally, the filters are classified into two categories: passive and active. So far, various types of passive filter configuration, based on inductors, capacitors and resistors or diodes, have been proposed in [6]-[11]. For ...
... inverters for the purpose of eliminating the sideeffects mentioned above. Generally, the filters are classified into two categories: passive and active. So far, various types of passive filter configuration, based on inductors, capacitors and resistors or diodes, have been proposed in [6]-[11]. For ...
Optimal Single Resistor Damping of Input Filters
... (nonminimum phase) zero pair in the vicinity of the filter resonant frequency f0. This introduces an additional 360˚ of phase lag into the converter loop gain T’(s) at frequencies greater than f0. If the feedback loop crossover frequency is greater than f0, then negative phase margin and instability ...
... (nonminimum phase) zero pair in the vicinity of the filter resonant frequency f0. This introduces an additional 360˚ of phase lag into the converter loop gain T’(s) at frequencies greater than f0. If the feedback loop crossover frequency is greater than f0, then negative phase margin and instability ...
inductors - Murata Power Solutions
... Simple filters can be easily constructed with inductor and capacitor elements. These filters have the advantage of being easy to calculate and characterise the frequency response. They exhibit few of the secondary effects and stability problems associated with their active counterparts. In power lin ...
... Simple filters can be easily constructed with inductor and capacitor elements. These filters have the advantage of being easy to calculate and characterise the frequency response. They exhibit few of the secondary effects and stability problems associated with their active counterparts. In power lin ...
IMPEDANCE MATCHING NETWORKS APPLIED TO RF POWER TRANSISTORS 1. INTRODUCTION
... Some graphic and numerical methods of impedance matching will be reviewed here. The examples given will refer to high frequency power amplifiers. Although matching networks normally take the form of filters and therefore are also useful to provide frequency discrimination, this aspect will only be c ...
... Some graphic and numerical methods of impedance matching will be reviewed here. The examples given will refer to high frequency power amplifiers. Although matching networks normally take the form of filters and therefore are also useful to provide frequency discrimination, this aspect will only be c ...
TUNING TAPS TRANSDUCERS Begin by measuring the voltage
... Add this series reactance to the transducer and measure the series impedance. (Note that the phase will not, in general, be zero.) Rs = (V/I) cos(pi*phase/180) Xs = (V/I) sin(pi*phase/180) Convert this to parallel impedance using Rp = (Rs2 + Xs2)/Rs Xp = (Rs2 + Xs2)/Xs. The parallel resistance, Rp, ...
... Add this series reactance to the transducer and measure the series impedance. (Note that the phase will not, in general, be zero.) Rs = (V/I) cos(pi*phase/180) Xs = (V/I) sin(pi*phase/180) Convert this to parallel impedance using Rp = (Rs2 + Xs2)/Rs Xp = (Rs2 + Xs2)/Xs. The parallel resistance, Rp, ...
EN (3321102)
... We can see that the Pi-pad attenuator is symmetrical looking at the attenuator from either end and this type of attenuator design can be used to impedance match either equal or unequal transmission lines. Generally, resistors R1 and R3 are of the same value but when designed to operate between circu ...
... We can see that the Pi-pad attenuator is symmetrical looking at the attenuator from either end and this type of attenuator design can be used to impedance match either equal or unequal transmission lines. Generally, resistors R1 and R3 are of the same value but when designed to operate between circu ...
SiGe BiCMOS LNA`S AND TUNABLE ACTIVE FILTER FOR
... may be used in the receiver front-ends of future wide-band multi-purpose array antennas, for example. Two low-noise amplifiers (LNA’s) and one tunable filter have been designed in a 0.35µm bipolar complementary metal oxide semiconductor (BiCMOS) technology containing high frequency silicongermanium ...
... may be used in the receiver front-ends of future wide-band multi-purpose array antennas, for example. Two low-noise amplifiers (LNA’s) and one tunable filter have been designed in a 0.35µm bipolar complementary metal oxide semiconductor (BiCMOS) technology containing high frequency silicongermanium ...
Series Active Filters
... case), the SAF based on the p-q theory inject a voltage in order to have a sinusoidal voltage wave form at the load side despite the presence of any perturbation in the source. It will also compensate all the non-active power, including the reactive an oscillating portion of active power, and the so ...
... case), the SAF based on the p-q theory inject a voltage in order to have a sinusoidal voltage wave form at the load side despite the presence of any perturbation in the source. It will also compensate all the non-active power, including the reactive an oscillating portion of active power, and the so ...
The Product Detector
... The SW+ product detector circuit uses an NE602 for the mixer just like we’ve seen before. Here, the input comes in from the output of the 4 MHz crystal filter to pin 2. R1 is used to load the output of the filter to match it to the input impedance of the mixer. Since pin 1 isn’t being used it’s tied ...
... The SW+ product detector circuit uses an NE602 for the mixer just like we’ve seen before. Here, the input comes in from the output of the 4 MHz crystal filter to pin 2. R1 is used to load the output of the filter to match it to the input impedance of the mixer. Since pin 1 isn’t being used it’s tied ...
Transmission Lines
... ground wire must go wherever any of the signal wires go. Sometimes this creates a problem because a length of wire has resistance, inductance, and capacitance and, therefore, a small potential difference may exist between any two points on the ground wire. Consequently, the ground wire is not a perf ...
... ground wire must go wherever any of the signal wires go. Sometimes this creates a problem because a length of wire has resistance, inductance, and capacitance and, therefore, a small potential difference may exist between any two points on the ground wire. Consequently, the ground wire is not a perf ...
1. Introduction - About the journal
... (or all-pass filter) topologies employing various types of active elements have been presented in the literature [1][29]. A good design of all-pass filter should possess the following features: Employing minimum number of active and passive elements, i.e., one active element, one resistor (or thre ...
... (or all-pass filter) topologies employing various types of active elements have been presented in the literature [1][29]. A good design of all-pass filter should possess the following features: Employing minimum number of active and passive elements, i.e., one active element, one resistor (or thre ...
... use of the object integral in optimization tool box. The initial elements and the frequency of switching for optimization element have a lot of influence on the final conclusion with software Matlab. The Design of CM Filter: The inverter of three phase power electronic produces 2 elements of DM and ...
System Level Review
... ports will also be equally split to the Diode 1 and Diode 2 ports, or 3dB lower (plus insertion losses) from the input signal. The split signals will also have a 180-degree phase difference between them. The 180-degree hybrid is not a readily realized structure in a surface mount component. It could ...
... ports will also be equally split to the Diode 1 and Diode 2 ports, or 3dB lower (plus insertion losses) from the input signal. The split signals will also have a 180-degree phase difference between them. The 180-degree hybrid is not a readily realized structure in a surface mount component. It could ...
E040339-00 - DCC - LIGO Document Control Center Portal
... There are two black cylindrical resistor stacks located on the main pressure manifold on the top side. These two resistors have valves located on the top their purpose is to allow trapped air to be removed from the system by migrating to this ‘high point’. The air can escape when the valve is opened ...
... There are two black cylindrical resistor stacks located on the main pressure manifold on the top side. These two resistors have valves located on the top their purpose is to allow trapped air to be removed from the system by migrating to this ‘high point’. The air can escape when the valve is opened ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSRJEEE)
... An electric filter is a frequency selective circuit that either allows a specified band of frequencies or attenuates particular signal of frequencies [1]. Filter circuit can be designed using passive elements (resistor, capacitor, inductor) called Passive filter and also the combination of active an ...
... An electric filter is a frequency selective circuit that either allows a specified band of frequencies or attenuates particular signal of frequencies [1]. Filter circuit can be designed using passive elements (resistor, capacitor, inductor) called Passive filter and also the combination of active an ...
Distributed element filter
A distributed element filter is an electronic filter in which capacitance, inductance and resistance (the elements of the circuit) are not localised in discrete capacitors, inductors and resistors as they are in conventional filters. Its purpose is to allow a range of signal frequencies to pass, but to block others. Conventional filters are constructed from inductors and capacitors, and the circuits so built are described by the lumped element model, which considers each element to be ""lumped together"" at one place. That model is conceptually simple, but it becomes increasingly unreliable as the frequency of the signal increases, or equivalently as the wavelength decreases. The distributed element model applies at all frequencies, and is used in transmission line theory; many distributed element components are made of short lengths of transmission line. In the distributed view of circuits, the elements are distributed along the length of conductors and are inextricably mixed together. The filter design is usually concerned only with inductance and capacitance, but because of this mixing of elements they cannot be treated as separate ""lumped"" capacitors and inductors. There is no precise frequency above which distributed element filters must be used but they are especially associated with the microwave band (wavelength less than one metre).Distributed element filters are used in many of the same applications as lumped element filters, such as selectivity of radio channel, bandlimiting of noise and multiplexing of many signals into one channel. Distributed element filters may be constructed to have any of the bandforms possible with lumped elements (low-pass, band-pass, etc.) with the exception of high-pass, which is usually only approximated. All filter classes used in lumped element designs (Butterworth, Chebyshev, etc.) can be implemented using a distributed element approach.There are many component forms used to construct distributed element filters, but all have the common property of causing a discontinuity on the transmission line. These discontinuities present a reactive impedance to a wavefront travelling down the line, and these reactances can be chosen by design to serve as approximations for lumped inductors, capacitors or resonators, as required by the filter.The development of distributed element filters was spurred on by the military need for radar and electronic counter measures during World War II. Lumped element analogue filters had long before been developed but these new military systems operated at microwave frequencies and new filter designs were required. When the war ended, the technology found applications in the microwave links used by telephone companies and other organisations with large fixed-communication networks, such as television broadcasters. Nowadays the technology can be found in several mass-produced consumer items, such as the converters (figure 1 shows an example) used with satellite television dishes.