Critical Branching Neural Computation, Neural Avalanches, and 1/f Scaling
... systems near their critical points universally exhibit scaling laws in their intrinsic dynamics (Sornette, 2004). 1/f scaling with α ~ 1 has been shown to hold for a wide range of model systems poised near transitions between ordered versus disordered states, whereas neural avalanches with β ~ 3/2 ...
... systems near their critical points universally exhibit scaling laws in their intrinsic dynamics (Sornette, 2004). 1/f scaling with α ~ 1 has been shown to hold for a wide range of model systems poised near transitions between ordered versus disordered states, whereas neural avalanches with β ~ 3/2 ...
Here - Statistical Analysis of Neuronal Data
... field. To combat this, we have used a maximum likelihood estimation approach as a less biased and more sensitive way to examine rhythmicity. In this approach, each lag within the autocorrelogram is treated as an observation. This allows statistical testing of changes in individual rhythmicity featur ...
... field. To combat this, we have used a maximum likelihood estimation approach as a less biased and more sensitive way to examine rhythmicity. In this approach, each lag within the autocorrelogram is treated as an observation. This allows statistical testing of changes in individual rhythmicity featur ...
Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse
... Extension questions Each neuron can receive chemical signals in the form of neurotransmitters from a large number of other neurons. These neurotransmitters may either stimulate or depress the activity of the post synaptic neuron. For example when dopamine acts on its receptor it stimulates the gene ...
... Extension questions Each neuron can receive chemical signals in the form of neurotransmitters from a large number of other neurons. These neurotransmitters may either stimulate or depress the activity of the post synaptic neuron. For example when dopamine acts on its receptor it stimulates the gene ...
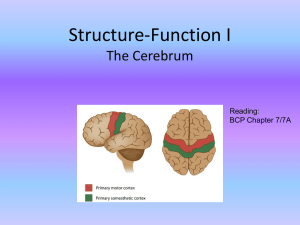
Structure-Function I
... pyramidal cells (output neurons; excitatory) vs stellate cells (local circuit; both excitatory and inhibitory) vertical axons and dendrites give rise to columnar organization layer thickness differs from brain area to area ...
... pyramidal cells (output neurons; excitatory) vs stellate cells (local circuit; both excitatory and inhibitory) vertical axons and dendrites give rise to columnar organization layer thickness differs from brain area to area ...
Slide 1
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
Determining Shape and Fringe Count in a Holographic
... the complex light wavefront reflected by objects is recorded. Obtaining image views of the object is then possible by reconstructing the recorded wavefront. Holography is a method evolved by Gabor in 1947, in which one not only records the amplitude but also the phase of the light wave. It is simply ...
... the complex light wavefront reflected by objects is recorded. Obtaining image views of the object is then possible by reconstructing the recorded wavefront. Holography is a method evolved by Gabor in 1947, in which one not only records the amplitude but also the phase of the light wave. It is simply ...
Off-axis compressed holographic microscopy in low
... can be achieved with few simple setup conditions [1]. Holographic measurements are made in dual domains, where each pixel exhibits spatially dispersed (i.e. multiplexed) information from the object. The measurement domain and the image domain are “incoherent”, which is a requirement for using compre ...
... can be achieved with few simple setup conditions [1]. Holographic measurements are made in dual domains, where each pixel exhibits spatially dispersed (i.e. multiplexed) information from the object. The measurement domain and the image domain are “incoherent”, which is a requirement for using compre ...
generalpsy2Remembering and Judging
... differences between computers and the human mind are vast, cognitive psychologists have used the computer as a model for understanding the workings of the mind. ...
... differences between computers and the human mind are vast, cognitive psychologists have used the computer as a model for understanding the workings of the mind. ...
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 5
... Having compared a variety of checker moves the next step is to make the decision to move. This is a second important function of the prefrontal association area. After lesions of this area little frustration is displayed when the patient makes mistakes in every day decisions. One might expect that a ...
... Having compared a variety of checker moves the next step is to make the decision to move. This is a second important function of the prefrontal association area. After lesions of this area little frustration is displayed when the patient makes mistakes in every day decisions. One might expect that a ...
Neural Ensemble www.AssignmentPoint.com A neural ensemble is
... principle of Wikipedia operation - multiple edits by many participants. Neuroscientists have discovered that individual neurons are very noisy. For example, by examining the activity of only a single neuron in the visual cortex, it is very difficult to reconstruct the visual scene that the owner of ...
... principle of Wikipedia operation - multiple edits by many participants. Neuroscientists have discovered that individual neurons are very noisy. For example, by examining the activity of only a single neuron in the visual cortex, it is very difficult to reconstruct the visual scene that the owner of ...
The Nervous System
... – The actual mass of the human brain is about 1400 grams; however the net weight of the brain suspended in the CSF is equivalent to a mass of 25 grams. The brain therefore exists in neutral buoyancy, which allows the brain to maintain its density without being impaired by its own weight, which would ...
... – The actual mass of the human brain is about 1400 grams; however the net weight of the brain suspended in the CSF is equivalent to a mass of 25 grams. The brain therefore exists in neutral buoyancy, which allows the brain to maintain its density without being impaired by its own weight, which would ...
Exam 1 2011 SECTION A – Multiple-choice questions Question 2
... B. the reticular activating system shows a high level of activity on a brain scan. C. the neurons in the reticular activating system are less active than when the person is awake. D. the content of a person’s consciousness is more limited and restricted than when they are in normal waking consciousn ...
... B. the reticular activating system shows a high level of activity on a brain scan. C. the neurons in the reticular activating system are less active than when the person is awake. D. the content of a person’s consciousness is more limited and restricted than when they are in normal waking consciousn ...
The generation of nondiffracting beams using
... two coherent fields: a reference wavefield and a signal wavefield of the same wavelength that contains information on the object of interest.4 For this reason, a hologram is sometimes referred to as an interferogram. A setup for making holograms usually involves the splitting of a laser beam to obta ...
... two coherent fields: a reference wavefield and a signal wavefield of the same wavelength that contains information on the object of interest.4 For this reason, a hologram is sometimes referred to as an interferogram. A setup for making holograms usually involves the splitting of a laser beam to obta ...
NOT FOR SALE - Cengage Learning
... leads to a child’s ability to crawl and walk during the first year. Infants are not physiologically “ready” to engage in visual–motor coordination and other activities until the coating process reaches certain levels. In people with the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin is replaced with a hard fibr ...
... leads to a child’s ability to crawl and walk during the first year. Infants are not physiologically “ready” to engage in visual–motor coordination and other activities until the coating process reaches certain levels. In people with the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin is replaced with a hard fibr ...
Neurons` Short-Term Plasticity Amplifies Signals
... excitatory and inhibitory neurons at once, and then the inhibitory neuron activates its synapses with a delay of a few milliseconds. From the output neuron’s point of view, the incoming excitatory signals are closely followed by the inhibitory ones. Several previous studies that tried to sort out ho ...
... excitatory and inhibitory neurons at once, and then the inhibitory neuron activates its synapses with a delay of a few milliseconds. From the output neuron’s point of view, the incoming excitatory signals are closely followed by the inhibitory ones. Several previous studies that tried to sort out ho ...
Report Decoding Individual Episodic Memory Traces in the Human
... data, permitting prediction of mental states from local patterns of blood oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal across voxels [1, 2]. We previously demonstrated that it is possible to predict the position of individuals in a virtualreality environment from the pattern of activity across voxels in the ...
... data, permitting prediction of mental states from local patterns of blood oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal across voxels [1, 2]. We previously demonstrated that it is possible to predict the position of individuals in a virtualreality environment from the pattern of activity across voxels in the ...
Intro to Nervous System
... The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological limits. In addition, our body constantly reacts to a multitude of signals, be it external or internal signals. Two body systems are responsible for dealing with these signals a ...
... The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological limits. In addition, our body constantly reacts to a multitude of signals, be it external or internal signals. Two body systems are responsible for dealing with these signals a ...
8.1 How Memory Functions SW
... Short-term memory (STM), also called working memory, is a temporary storage system that processes incoming sensory memory; sometimes it is called working memory. Short-term memory takes information from sensory memory and sometimes connects that memory to something already in long-term memory. Short ...
... Short-term memory (STM), also called working memory, is a temporary storage system that processes incoming sensory memory; sometimes it is called working memory. Short-term memory takes information from sensory memory and sometimes connects that memory to something already in long-term memory. Short ...
Chapter 3 The Nervous System and the Brain
... The spinal nerves and the peripheral nervous system can be divided into four categories. The Somatic afferent, the Somatic efferent, the Visceral afferent, and the Visceral efferent. Somatic afferent neurons are sensory indicators that conduct impulses and send information to and from receptors in ...
... The spinal nerves and the peripheral nervous system can be divided into four categories. The Somatic afferent, the Somatic efferent, the Visceral afferent, and the Visceral efferent. Somatic afferent neurons are sensory indicators that conduct impulses and send information to and from receptors in ...
Cognitive Disorders
... •Clear organic causes, where primary symptom is a significant deficit in cognitive ability •changes in the person’s personality and behavior (due to the brain disorder) ...
... •Clear organic causes, where primary symptom is a significant deficit in cognitive ability •changes in the person’s personality and behavior (due to the brain disorder) ...
Cognitive Training Enhances Intrinsic Brain Connectivity in Childhood
... linking frontoparietal activity to working memory performance is that activity in these domain-general networks codes information about fluctuating task goals. During control-demanding tasks, long-range functional connections between frontoparietal networks and other cortical areas integrate this hi ...
... linking frontoparietal activity to working memory performance is that activity in these domain-general networks codes information about fluctuating task goals. During control-demanding tasks, long-range functional connections between frontoparietal networks and other cortical areas integrate this hi ...
aqa.cognitive.booklet
... committee?) They found that witnesses were very accurate despite the extreme levels of stress. This has been supported by a study by Christianson & Hubinette (1993) where victims of a bank robbery who had been subjected to the most stress, were actually the most accurate witnesses. Perhaps because t ...
... committee?) They found that witnesses were very accurate despite the extreme levels of stress. This has been supported by a study by Christianson & Hubinette (1993) where victims of a bank robbery who had been subjected to the most stress, were actually the most accurate witnesses. Perhaps because t ...