Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System. Central Nervous System (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functio ...
... Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System. Central Nervous System (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functio ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System. Central Nervous System (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functio ...
... Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System. Central Nervous System (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functio ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
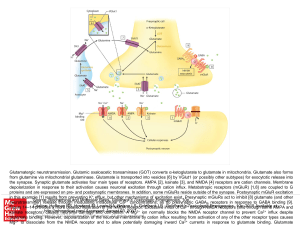
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
Chapter 13 and 16
... A. Astrocyte- function in creating bloodbrain barrier, provide structure B. Oligodendocyte- produce myelin sheath C. Microglia- immune cells of CNS, similar to macrophages D. Ependymal- found in ventricles of brain, produce cerebrospinal fluid ...
... A. Astrocyte- function in creating bloodbrain barrier, provide structure B. Oligodendocyte- produce myelin sheath C. Microglia- immune cells of CNS, similar to macrophages D. Ependymal- found in ventricles of brain, produce cerebrospinal fluid ...
Unit 4 Test Nervous System
... b. Stops transmission of signals along the axon c. Speeds up the transmission of signals along the axon d. To protect the cell body of the neuron ...
... b. Stops transmission of signals along the axon c. Speeds up the transmission of signals along the axon d. To protect the cell body of the neuron ...
Slide ()
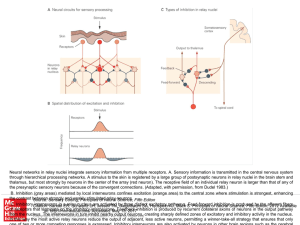
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
BOX 25.3 GIANT SYNAPTIC TERMINALS: ENDBULBS AND
... ventral cochlear nucleus (Fig. 25.18A), and (2) calyceal endings, which are found in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Calyces are so large that it is possible to use patch electrodes to record and clamp the presynaptic terminal while simultaneously doing the same with their postsynaptic tar ...
... ventral cochlear nucleus (Fig. 25.18A), and (2) calyceal endings, which are found in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Calyces are so large that it is possible to use patch electrodes to record and clamp the presynaptic terminal while simultaneously doing the same with their postsynaptic tar ...
Central nervous system
... 3 kinds of synapses with different modes of action • Excitatory cholinergic synapse • Inhibitory GABA-ergic synapse • Excitatory adrenergic synapse Synaptic delay (.5 msec) – time from arrival of nerve signal at synapse to start of AP in postsynaptic cell ...
... 3 kinds of synapses with different modes of action • Excitatory cholinergic synapse • Inhibitory GABA-ergic synapse • Excitatory adrenergic synapse Synaptic delay (.5 msec) – time from arrival of nerve signal at synapse to start of AP in postsynaptic cell ...
Organization of Nervous System
... transmit information to another neuron are called neurotransmitters. There are several kinds of neurotransmitters, which we will discuss in later lectures. ...
... transmit information to another neuron are called neurotransmitters. There are several kinds of neurotransmitters, which we will discuss in later lectures. ...
Nervous System
... – Divided into 2 parts • Sensory or Afferent division • Motor or Efferent division (divided into 2 parts) – Somatic motor nervous system – Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) ...
... – Divided into 2 parts • Sensory or Afferent division • Motor or Efferent division (divided into 2 parts) – Somatic motor nervous system – Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) ...
CDKL5 UK study
... associated with a number of RNA splicing factors that are stored within nuclear “speckles” (Ricciardi et al. 2009) where CDKL5 may be important in the phosphorylation of the RS domain ...
... associated with a number of RNA splicing factors that are stored within nuclear “speckles” (Ricciardi et al. 2009) where CDKL5 may be important in the phosphorylation of the RS domain ...
Nervous System - teacherver.com
... There are billions of nerve cells located in the brain, which do not directly touch each other. Nerve cells communicate messages by secreting neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters can excite or inhibit neurons (nerve cells) or both. Drugs that interfere with neurotransmitters are called agonist (drug ...
... There are billions of nerve cells located in the brain, which do not directly touch each other. Nerve cells communicate messages by secreting neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters can excite or inhibit neurons (nerve cells) or both. Drugs that interfere with neurotransmitters are called agonist (drug ...
Slide 1
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... The giraffe’s sensory and motor neurons! Some must bring impulses from the bottom of their legs to their spinal cord ...
... The giraffe’s sensory and motor neurons! Some must bring impulses from the bottom of their legs to their spinal cord ...
CHAPTER 2 outline
... 1. Drugs may increase or decrease the amount of neurotransmitter released by neurons. 2. Drugs may affect the length of time the neurotransmitter remains in the synaptic gap, either increasing or decreasing the amount available to the postsynaptic receptor. 3. Drugs may prolong the effects of the ne ...
... 1. Drugs may increase or decrease the amount of neurotransmitter released by neurons. 2. Drugs may affect the length of time the neurotransmitter remains in the synaptic gap, either increasing or decreasing the amount available to the postsynaptic receptor. 3. Drugs may prolong the effects of the ne ...
CH 3 Practice Test
... Johnny was awakened by a loud, crashing sound in the middle of the night. He was frightened and he jumped out of bed to investigate. Johnny realized that the loud sound was just his cat playing around in the living room. Needless to say, Johnny was extremely relieved. Which subdivision of the nervou ...
... Johnny was awakened by a loud, crashing sound in the middle of the night. He was frightened and he jumped out of bed to investigate. Johnny realized that the loud sound was just his cat playing around in the living room. Needless to say, Johnny was extremely relieved. Which subdivision of the nervou ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint Notes
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness. ...
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness. ...
CHAPTER 5: SIMPLE NERVOUS SYSTEMS AND BEHAVIOR
... and objects, and it requires the medial temporal lobe and the hippocampus. • Implicit or procedural memory: perceptual/motor skills, habits, including classical and operant conditioning, habituation, and sensitization. • Aplysia: a simple animal, simple nervous system, and simple behavior, a reduced ...
... and objects, and it requires the medial temporal lobe and the hippocampus. • Implicit or procedural memory: perceptual/motor skills, habits, including classical and operant conditioning, habituation, and sensitization. • Aplysia: a simple animal, simple nervous system, and simple behavior, a reduced ...
Learning Styles PowerPoint
... Left Brain dominant people respect rules and deadlines. Rational thinking and organization come easily A left brain thinker can be seen as very serious ...
... Left Brain dominant people respect rules and deadlines. Rational thinking and organization come easily A left brain thinker can be seen as very serious ...
Synapses
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTERS 48 and 50 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... J. Modulated signaling at synapses. Summarize the events that occur when norepinephrine binds to its metabotropic receptor. K. After reading about Neurotransmitters, make a list of the functions of each: Acetylcholine, Glutamate, GABA, Norepinephrine, Dopamine, Serotonin, Substance P, Endorphins, Ni ...
... J. Modulated signaling at synapses. Summarize the events that occur when norepinephrine binds to its metabotropic receptor. K. After reading about Neurotransmitters, make a list of the functions of each: Acetylcholine, Glutamate, GABA, Norepinephrine, Dopamine, Serotonin, Substance P, Endorphins, Ni ...
Power Point
... Fig. 3. SAPNS allows axons to regenerate through the lesion site in brain. The dark-field composite photos are parasagittal sections from animals 30 days after lesion and treatment. (a) Section from brain of 30-day-old hamster with 10 µl of saline injected in the lesion at P2. The cavity shows the ...
... Fig. 3. SAPNS allows axons to regenerate through the lesion site in brain. The dark-field composite photos are parasagittal sections from animals 30 days after lesion and treatment. (a) Section from brain of 30-day-old hamster with 10 µl of saline injected in the lesion at P2. The cavity shows the ...
Nervous System - De Anza College
... Dendrites: branched extensions of the cell body that receive signals Axon: single extension that transmits signals to other cells ...
... Dendrites: branched extensions of the cell body that receive signals Axon: single extension that transmits signals to other cells ...
Synaptic plasticity: taming the beast
... cases, synaptic plasticity depends on the relative timing of the preand postsynaptic spikes, but not on their order (Fig. 2d and e). In the cerebellum-like structure of electric fish, LTP and LTD are reversed relative to other systems (Fig. 2c), perhaps because the postsynaptic neuron is inhibitory ...
... cases, synaptic plasticity depends on the relative timing of the preand postsynaptic spikes, but not on their order (Fig. 2d and e). In the cerebellum-like structure of electric fish, LTP and LTD are reversed relative to other systems (Fig. 2c), perhaps because the postsynaptic neuron is inhibitory ...
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
... in the PNS and CNS. It promotes smooth muscle relaxation and is implicated in memory. ...
... in the PNS and CNS. It promotes smooth muscle relaxation and is implicated in memory. ...