Electromagnetic waves have unique traits.
... (RAY-dee-AY-shuhn). Radiation is different from the transfer of energy through a medium by a mechanical wave. A mechanical wave must vibrate the medium as it moves, and this uses some of the wave’s energy. Eventually, every mechanical wave will give up all of its energy to the medium and disappear. ...
... (RAY-dee-AY-shuhn). Radiation is different from the transfer of energy through a medium by a mechanical wave. A mechanical wave must vibrate the medium as it moves, and this uses some of the wave’s energy. Eventually, every mechanical wave will give up all of its energy to the medium and disappear. ...
Chapter 8- Rotational Motion
... It is clear that to make an object start rotating, a force is needed; Unlike in linear motion, the position and direction of the applied force matter as well. In the figure, the applied force will be more effective in opening the door than force assuming they both have the same magnitude. The angula ...
... It is clear that to make an object start rotating, a force is needed; Unlike in linear motion, the position and direction of the applied force matter as well. In the figure, the applied force will be more effective in opening the door than force assuming they both have the same magnitude. The angula ...
Document
... direction (the angle at which it acts upon an object). Velocity is expressed with magnitude (speed) and direction (angle or compass direction). Displacement is expressed with magnitude (distance) and direction (angle or compass direction). ...
... direction (the angle at which it acts upon an object). Velocity is expressed with magnitude (speed) and direction (angle or compass direction). Displacement is expressed with magnitude (distance) and direction (angle or compass direction). ...
Wormholes and nontrivial topology.
... • If you think of these as classical solutions of Einstein plus Maxwell, we now know all such solutions to be unstable. (Sphaleron) • Quantum Wheeler wormholes ⇒ “spacetime foam”. ...
... • If you think of these as classical solutions of Einstein plus Maxwell, we now know all such solutions to be unstable. (Sphaleron) • Quantum Wheeler wormholes ⇒ “spacetime foam”. ...
Modeling Collision force for carts Experiment 7
... a) (2 points) Imagine that one drilled a hole with smooth sides straight through the center of the earth, of radius Re = 6.4 ×106 m . If the air is removed from this tube (and the tube doesn’t fill up with water, liquid rock or iron from the core), an object dropped into one end will have enough ene ...
... a) (2 points) Imagine that one drilled a hole with smooth sides straight through the center of the earth, of radius Re = 6.4 ×106 m . If the air is removed from this tube (and the tube doesn’t fill up with water, liquid rock or iron from the core), an object dropped into one end will have enough ene ...
PH212Chapter10_12
... and rotation quantity, then L(qt1,qt2,…) is a translational dynamics formula or law, if and only if L(qr1,qr2,…) is a rotational dynamics formula or law. (To the extent this is not true, the analogy is said to be limited. Most analogies are limited.) ...
... and rotation quantity, then L(qt1,qt2,…) is a translational dynamics formula or law, if and only if L(qr1,qr2,…) is a rotational dynamics formula or law. (To the extent this is not true, the analogy is said to be limited. Most analogies are limited.) ...
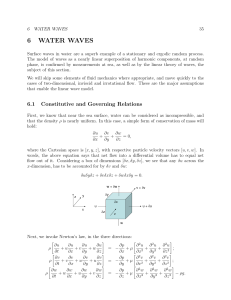
6 WATER WAVES - MIT OpenCourseWare
... Surface waves in water are a superb example of a stationary and ergodic random process. The model of waves as a nearly linear superposition of harmonic components, at random phase, is confirmed by measurements at sea, as well as by the linear theory of waves, the subject of this section. We will skip ...
... Surface waves in water are a superb example of a stationary and ergodic random process. The model of waves as a nearly linear superposition of harmonic components, at random phase, is confirmed by measurements at sea, as well as by the linear theory of waves, the subject of this section. We will skip ...
PDF only
... configuration-interaction approach, which is based on a nonlinearly optimized anisotropic Gaussian basis set of one-particle functions, W. Becken and P. Schmelcher [20] calculated the total energies of the ground state and the first four excitations in each subspace as well as their one-electron ion ...
... configuration-interaction approach, which is based on a nonlinearly optimized anisotropic Gaussian basis set of one-particle functions, W. Becken and P. Schmelcher [20] calculated the total energies of the ground state and the first four excitations in each subspace as well as their one-electron ion ...
Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
... A monoenergetic electron beam with electron speed of 5.20 × 106 m s−1 is subject to a magnetic field of 1.30 × 10−4 T normal to the beam velocity. What is the radius of the circle traced by the beam, given e/m for electron equals 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1. Is the formula you employ in (a) valid for calcula ...
... A monoenergetic electron beam with electron speed of 5.20 × 106 m s−1 is subject to a magnetic field of 1.30 × 10−4 T normal to the beam velocity. What is the radius of the circle traced by the beam, given e/m for electron equals 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1. Is the formula you employ in (a) valid for calcula ...
Chapter 9: Electromagnetic Waves
... (y-polarized in the figure), and transverse magnetic waves (TM waves) have the orthogonal linear polarization so that the magnetic field is purely transverse (again if y-polarized). TE and TM waves are typically transmitted and reflected with different amplitudes. Consider first a TE wave incident u ...
... (y-polarized in the figure), and transverse magnetic waves (TM waves) have the orthogonal linear polarization so that the magnetic field is purely transverse (again if y-polarized). TE and TM waves are typically transmitted and reflected with different amplitudes. Consider first a TE wave incident u ...