Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves
... specific space–time behavior that is simple but consistent with Maxwell’s equations. To understand the prediction of electromagnetic waves more fully, let us focus our attention on an electromagnetic wave that travels in the x direction (the direction of propagation). In this wave, the electric fiel ...
... specific space–time behavior that is simple but consistent with Maxwell’s equations. To understand the prediction of electromagnetic waves more fully, let us focus our attention on an electromagnetic wave that travels in the x direction (the direction of propagation). In this wave, the electric fiel ...
Canonical commutation relations, the Weierstrass Zeta function, and
... Recently Wiegmann and Zabrodin8 considered a quantum system of a particle on a twodimensional square lattice in a magnetic field and showed that magnetic translations on the lattice are related to finite-dimensional representations of the quantum group U q ~sl2!. Inspired by their work, we investiga ...
... Recently Wiegmann and Zabrodin8 considered a quantum system of a particle on a twodimensional square lattice in a magnetic field and showed that magnetic translations on the lattice are related to finite-dimensional representations of the quantum group U q ~sl2!. Inspired by their work, we investiga ...
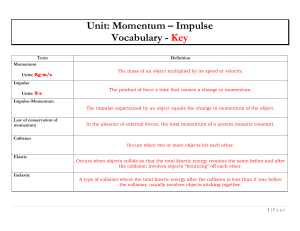
9.1 Impulse - 9.2 Momentum and the Impulse Momentum Theorem
... • Impulse has units of N ⋅ s, but N ⋅ s are equivalent to kg ⋅ m/s. • The latter are the preferred units for impulse. • The impulse is a vector quantity, pointing in the direction of the average force vector: ...
... • Impulse has units of N ⋅ s, but N ⋅ s are equivalent to kg ⋅ m/s. • The latter are the preferred units for impulse. • The impulse is a vector quantity, pointing in the direction of the average force vector: ...
Chapter 8 Accelerated Circular Motion
... Synchronous satellites are put into an orbit whose radius is 4.23×107m. If the angular separation of the two satellites is 2.00 degrees, find the arc length that separates them. Convert degree to radian measure ...
... Synchronous satellites are put into an orbit whose radius is 4.23×107m. If the angular separation of the two satellites is 2.00 degrees, find the arc length that separates them. Convert degree to radian measure ...
Conservation Laws
... In an isolated system, the sum of momentum before a collision is equal to the sum of momentum after the collision. *Isolated – nothing is coming in and nothing is leaving* Friction must be negligible. A system is a collection of two or more objects. An isolated system is a system that is free from t ...
... In an isolated system, the sum of momentum before a collision is equal to the sum of momentum after the collision. *Isolated – nothing is coming in and nothing is leaving* Friction must be negligible. A system is a collection of two or more objects. An isolated system is a system that is free from t ...
RelativityWorkbook-Teacher
... Einstein’s’ famous equation E = mc2 relates a particles mass to its energy. We can see that using the mass of an electron in kilograms we’d get its energy as: E = mc2 = (9.11 10-31kg)(3.0 108 m/s)2 = 8.2 10-14 J This is again another extremely tiny number. If however we use the mass of the elec ...
... Einstein’s’ famous equation E = mc2 relates a particles mass to its energy. We can see that using the mass of an electron in kilograms we’d get its energy as: E = mc2 = (9.11 10-31kg)(3.0 108 m/s)2 = 8.2 10-14 J This is again another extremely tiny number. If however we use the mass of the elec ...
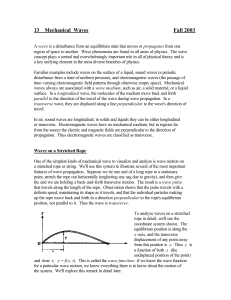
13 Mechanical Waves Fall 2003
... the displacement of every particle is proportional to sin ωt, so the particles all move in phase (or 1/2 cycle out of phase) with angular frequency ω. The amplitude of motion of each particle is (apart from sign) 2A sin k x . Thus the appearance is that of a sinusoidal shape that doesn't move along ...
... the displacement of every particle is proportional to sin ωt, so the particles all move in phase (or 1/2 cycle out of phase) with angular frequency ω. The amplitude of motion of each particle is (apart from sign) 2A sin k x . Thus the appearance is that of a sinusoidal shape that doesn't move along ...
entangled photon pairs: efficient generation and detection, and bit
... quantum communication and to study fundamental quantum mechanics. This thesis consists of two experiments: bit commitment and the generation and detection of polarization entangled photon pairs with a high heralding efficiency. Bit commitment is a two-party protocol that can be used as a cryptograph ...
... quantum communication and to study fundamental quantum mechanics. This thesis consists of two experiments: bit commitment and the generation and detection of polarization entangled photon pairs with a high heralding efficiency. Bit commitment is a two-party protocol that can be used as a cryptograph ...
Classical field theory
... function is called a “functional”, and we denote it here by S[qi (t)]. It turns out that it is possible to define a functional, called the action, such that the number assigned to the physical path between qi1 and qi2 that is prescribed by Newton’s law corresponds to a stationary value (usually a mi ...
... function is called a “functional”, and we denote it here by S[qi (t)]. It turns out that it is possible to define a functional, called the action, such that the number assigned to the physical path between qi1 and qi2 that is prescribed by Newton’s law corresponds to a stationary value (usually a mi ...
Class Notes - St. Bonaventure University
... line/arrow on top. A vector may also be represented by an ordered list of numbers, which are called the components: [t,x,y,z]. Written this way, mathematically the vector would t x be called a row matrix. A column matrix is a vertical list of components: . ...
... line/arrow on top. A vector may also be represented by an ordered list of numbers, which are called the components: [t,x,y,z]. Written this way, mathematically the vector would t x be called a row matrix. A column matrix is a vertical list of components: . ...
Momentum Impulse Notes Packet - Answer Key PDF
... 1. Follow the written and spoken instructions of the referee (teacher) at all times. Failure to do so is grounds for disqualification. 2. Each team shall have a thrower, a catcher, and a courier 3. The thrower is in charge of throwing the balloon to the catcher. The thrower must keep his/her throws ...
... 1. Follow the written and spoken instructions of the referee (teacher) at all times. Failure to do so is grounds for disqualification. 2. Each team shall have a thrower, a catcher, and a courier 3. The thrower is in charge of throwing the balloon to the catcher. The thrower must keep his/her throws ...