Physics - Oak Park Unified School District
... solve for FL: FL + FR = m1g + m2g d. planetary problems 1. rotational momentum is conserved: L = rmv 2. elliptical orbits: r1v1 = r2v2 3. rotation motion problems a. Summary of translational and rotational formulas corrects for mass distribution ( = 1 for a hoop, mass on the end of a string, or ...
... solve for FL: FL + FR = m1g + m2g d. planetary problems 1. rotational momentum is conserved: L = rmv 2. elliptical orbits: r1v1 = r2v2 3. rotation motion problems a. Summary of translational and rotational formulas corrects for mass distribution ( = 1 for a hoop, mass on the end of a string, or ...
Exercises 2013 - Oxford School on Neutron Scattering
... by measuring their time-of-flight (t.o.f.), t, from source to detector. Using the table of physical constants at the back, show that the relation between wavelength and t.o.f. is given by t (μsecs) = 252.8 × λ (Å) × L (m) where L is the total flight path between the source and detector. (b) A powder ...
... by measuring their time-of-flight (t.o.f.), t, from source to detector. Using the table of physical constants at the back, show that the relation between wavelength and t.o.f. is given by t (μsecs) = 252.8 × λ (Å) × L (m) where L is the total flight path between the source and detector. (b) A powder ...
A Novel Model of the Atom - Scientific Research Publishing
... spin direction. There is force of attraction between energy quanta which have the same frequency and opposite spin direction. The centre of the universe emits a broad spectrum of energy quanta with different frequencies and positive as well as negative spin. Furthermore, the novel model builds on th ...
... spin direction. There is force of attraction between energy quanta which have the same frequency and opposite spin direction. The centre of the universe emits a broad spectrum of energy quanta with different frequencies and positive as well as negative spin. Furthermore, the novel model builds on th ...
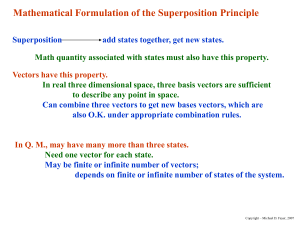
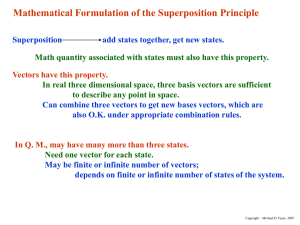
Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle
... Assume: Each state of a dynamical system at a particular time corresponds to a ket vector, the correspondence being such that if a state results from a superposition of other states, its corresponding ket vector is expressible linearly in terms of the corresponding ket vectors of the other states. ...
... Assume: Each state of a dynamical system at a particular time corresponds to a ket vector, the correspondence being such that if a state results from a superposition of other states, its corresponding ket vector is expressible linearly in terms of the corresponding ket vectors of the other states. ...
The Law of Conservation of Momentum
... The Law of Conservation of Momentum The total momentum of an isolated system (system of objects) equals the system’s initial momentum at all times. Alternately, whenever two or more particles interact, the total momentum of the two or more particle system is constant. The isolated system is one wher ...
... The Law of Conservation of Momentum The total momentum of an isolated system (system of objects) equals the system’s initial momentum at all times. Alternately, whenever two or more particles interact, the total momentum of the two or more particle system is constant. The isolated system is one wher ...
Piezoelectric Materials
... a dipole moment is formed. For a net polarization to develop, the dipole formed must not be canceled out by other dipoles in the unit cell. Therefore the piezoelectric atomic structure must be non-centrosymmetric. When a piezoelectric material is loaded electrically then the electrical dipoles appea ...
... a dipole moment is formed. For a net polarization to develop, the dipole formed must not be canceled out by other dipoles in the unit cell. Therefore the piezoelectric atomic structure must be non-centrosymmetric. When a piezoelectric material is loaded electrically then the electrical dipoles appea ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... The type of process that may be induced in an atom by the interaction with a single photon is strongly dependent on the photon energy. An overview of the energy regimes in the electromagnetic spectrum is given in Fig. 2.1. For wavelengths in the infrared (IR) and optical regime, electron-photon inte ...
... The type of process that may be induced in an atom by the interaction with a single photon is strongly dependent on the photon energy. An overview of the energy regimes in the electromagnetic spectrum is given in Fig. 2.1. For wavelengths in the infrared (IR) and optical regime, electron-photon inte ...
The spin-up of contracting red supergiants
... where M is the mass of the star. The larger χ the more efficient is the loss of angular momentum per unit mass lost. A value of χ > 1 corresponds to a decrease of the mean specific angular momentum of the envelope, χ < 1 to an increase. For the case of mass loss from the surface of a rigidly rotatin ...
... where M is the mass of the star. The larger χ the more efficient is the loss of angular momentum per unit mass lost. A value of χ > 1 corresponds to a decrease of the mean specific angular momentum of the envelope, χ < 1 to an increase. For the case of mass loss from the surface of a rigidly rotatin ...