Chapter 7 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... shape of the orbital • l can have integer values from 0 to (n – 1) • each value of l is called by a particular letter that designates the shape of the orbital s orbitals are spherical p orbitals are like two balloons tied at the knots d orbitals are mainly like 4 balloons tied at the knot f orbi ...
... shape of the orbital • l can have integer values from 0 to (n – 1) • each value of l is called by a particular letter that designates the shape of the orbital s orbitals are spherical p orbitals are like two balloons tied at the knots d orbitals are mainly like 4 balloons tied at the knot f orbi ...
Document
... • For a plane wave, wavevector Ghkl, the difference in phase between a point on the plane that goes through the origin, and a point in the plane shown in the diagram above is: G hkl a hA kB lC a 2 h h (The phase difference between two points separation r is k.r. Ghkl is perpendicular ...
... • For a plane wave, wavevector Ghkl, the difference in phase between a point on the plane that goes through the origin, and a point in the plane shown in the diagram above is: G hkl a hA kB lC a 2 h h (The phase difference between two points separation r is k.r. Ghkl is perpendicular ...
Chapter 7 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... shape of the orbital • l can have integer values from 0 to (n – 1) • each value of l is called by a particular letter that designates the shape of the orbital s orbitals are spherical p orbitals are like two balloons tied at the knots d orbitals are mainly like 4 balloons tied at the knot f orbi ...
... shape of the orbital • l can have integer values from 0 to (n – 1) • each value of l is called by a particular letter that designates the shape of the orbital s orbitals are spherical p orbitals are like two balloons tied at the knots d orbitals are mainly like 4 balloons tied at the knot f orbi ...
Lectures on Atomic Physics
... Comparison of the nuclear potential |V (r)| and field-shift factor F (r) calculated assuming a uniform distribution (given by solid lines) with values calculated assuming a Fermi distribution (dashed lines). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142 ...
... Comparison of the nuclear potential |V (r)| and field-shift factor F (r) calculated assuming a uniform distribution (given by solid lines) with values calculated assuming a Fermi distribution (dashed lines). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142 ...
Strong-Field Photodetachment of Negative Ions
... An atom consists of a nucleus of integer positive charge and an equal amount of negatively charged electrons. The electrons can be thought to be added one by one to the Coulomb potential of the core, in accordance with the Aufbauprinzip, with the probability cloud of each added electron screening on ...
... An atom consists of a nucleus of integer positive charge and an equal amount of negatively charged electrons. The electrons can be thought to be added one by one to the Coulomb potential of the core, in accordance with the Aufbauprinzip, with the probability cloud of each added electron screening on ...
Delft University of Technology
... the micro and nano meter range are trapped by the surrounding electromagnetic fields. The first observation of this trapping force using a single beam was in the mid 1980s [1]. The trapping of these small particles has a wide range of applications. One can think of separation of particles with diffe ...
... the micro and nano meter range are trapped by the surrounding electromagnetic fields. The first observation of this trapping force using a single beam was in the mid 1980s [1]. The trapping of these small particles has a wide range of applications. One can think of separation of particles with diffe ...
Electron and photon with solution
... Q 35: The work function of metal A and B are in the ratio 1: 2. If light of frequenciesf and 2f are incident on metal surfacesA and B respectively, the ratio of the maximum kinetic energiesof photoelectrons emitted is: (f is greater than threshold frequency of A, 2f is greater than threshold frequen ...
... Q 35: The work function of metal A and B are in the ratio 1: 2. If light of frequenciesf and 2f are incident on metal surfacesA and B respectively, the ratio of the maximum kinetic energiesof photoelectrons emitted is: (f is greater than threshold frequency of A, 2f is greater than threshold frequen ...
Unit 4: Energy and Momentum
... Machines make work easier. Remember that work is force times distance (W = F × d). The unit for work is the newton-meter, or often called the joule. Remembering that a joule is the same as a newton-meter will help you cancel units as you work through the problems in this section. We put work into a ...
... Machines make work easier. Remember that work is force times distance (W = F × d). The unit for work is the newton-meter, or often called the joule. Remembering that a joule is the same as a newton-meter will help you cancel units as you work through the problems in this section. We put work into a ...
Lecture 12: Photodiode detectors
... photodiodes, and InGaAsP photodiodes have shown high quantum efficiencies. ...
... photodiodes, and InGaAsP photodiodes have shown high quantum efficiencies. ...
Study guide
... concepts/experiments you do not understand. You can always ask questions if you want to know more. During breaks or office hours, the lecturers are available for questions and problems. We are always in for remarks/advice about our lecturing/instructions. As preparation for each lecture we minima ...
... concepts/experiments you do not understand. You can always ask questions if you want to know more. During breaks or office hours, the lecturers are available for questions and problems. We are always in for remarks/advice about our lecturing/instructions. As preparation for each lecture we minima ...
lecture1423903135
... for the understanding, analysis and design of various electrical, electromechanical and electronic systems. Electromagnetic theory can be thought of as generalization of circuit theory. Electromagnetic theory deals directly with the electric and magnetic field vectors where as circuit theory deals w ...
... for the understanding, analysis and design of various electrical, electromechanical and electronic systems. Electromagnetic theory can be thought of as generalization of circuit theory. Electromagnetic theory deals directly with the electric and magnetic field vectors where as circuit theory deals w ...
Particle self-bunching in the Schwinger effect in spacetime
... however, the various results differ substantially. As expected, the leading order derivative expansion becomes worse for small λ. Whereas a previous study of higher derivative terms signalled a potential failure at large momenta [27], we here observe a breakdown of this approximation for small momen ...
... however, the various results differ substantially. As expected, the leading order derivative expansion becomes worse for small λ. Whereas a previous study of higher derivative terms signalled a potential failure at large momenta [27], we here observe a breakdown of this approximation for small momen ...
Aging and Stiffness
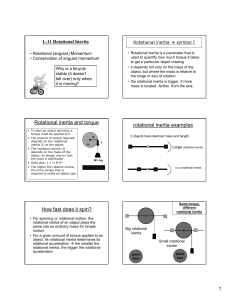
... Review Newton’s laws of motion, and extend to angular motion. Expand on the technique of the free body diagram Define torque as a rotary force Describe the forces due to body mass Explain the forces exerted by the surroundings To quantify the concept of momentum To characterize the rel ...
... Review Newton’s laws of motion, and extend to angular motion. Expand on the technique of the free body diagram Define torque as a rotary force Describe the forces due to body mass Explain the forces exerted by the surroundings To quantify the concept of momentum To characterize the rel ...