4 OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
... second when we are resting and maybe two or three times this rate as we exert ourselves. Stroboscopes can be used to freeze the motion in engines and motors where periodic motion is essential, but too strong vibrations can be potentially very destructive. The practical techniques that have been deve ...
... second when we are resting and maybe two or three times this rate as we exert ourselves. Stroboscopes can be used to freeze the motion in engines and motors where periodic motion is essential, but too strong vibrations can be potentially very destructive. The practical techniques that have been deve ...
Inequalities for Schrödinger Operators and
... 1.1. Introduction. One of the most important differences between quantum and classical mechanics is the uncertainty principle. Among many other things, it implies that position and momentum of a particle can not simultaneously take on definite values. To make this more quantitative, recall that the ...
... 1.1. Introduction. One of the most important differences between quantum and classical mechanics is the uncertainty principle. Among many other things, it implies that position and momentum of a particle can not simultaneously take on definite values. To make this more quantitative, recall that the ...
Polarimetry in Astrophysics and Cosmology
... 2.6 A M17 model from [6]. The system can be described as a central cluster of stars surrounded by successive layers of H+ , H0 , and H2 gas, that expanding with different velocities to the outer side of the cloud. . . . 2.7 M17 polarization fraction vectors are plotted over the 450 um uncalibrated f ...
... 2.6 A M17 model from [6]. The system can be described as a central cluster of stars surrounded by successive layers of H+ , H0 , and H2 gas, that expanding with different velocities to the outer side of the cloud. . . . 2.7 M17 polarization fraction vectors are plotted over the 450 um uncalibrated f ...
Quantum networking with single ions and single photons interfaced in free space
... Feynman’s idea of a quantum simulator, allows one to harness all power of quantum computation in that any quantum algorithm can be implemented through quantum logic gates [1]. Similar to classical computation, a quantum gate performs quantum operations on one or several qubits. A universal set of qu ...
... Feynman’s idea of a quantum simulator, allows one to harness all power of quantum computation in that any quantum algorithm can be implemented through quantum logic gates [1]. Similar to classical computation, a quantum gate performs quantum operations on one or several qubits. A universal set of qu ...
Quantum, Atomic and Nuclear Physics
... In an ordinary colour television set, electrons are accelerated through a potential difference of 25 kV. b. How much energy does the electron gain as it is accelerated? c. What is the de Broglie wavelength of such electrons? 2. In 1923 Compton measured the scattering of X-rays by electrons. Classica ...
... In an ordinary colour television set, electrons are accelerated through a potential difference of 25 kV. b. How much energy does the electron gain as it is accelerated? c. What is the de Broglie wavelength of such electrons? 2. In 1923 Compton measured the scattering of X-rays by electrons. Classica ...
Common Exam - 2005 Department of Physics University of Utah August 27, 2005
... [6 pts.] If the particle is in the ground state, calculate the probability for finding the particle in the region a/2 < x < a, OR !a/2 < x < 0. ...
... [6 pts.] If the particle is in the ground state, calculate the probability for finding the particle in the region a/2 < x < a, OR !a/2 < x < 0. ...
Dynamical Tides in Rotating Binary Stars
... where σα is the mode angular frequency in the inertial frame, and α = {njm} specifies the mode index: n gives the number of nodes in the radial eigenfunction (the order of the mode), j specifies the number of nodes in the θ-eigenfunction (j reduces to l in the nonrotating limit), and m is the azimut ...
... where σα is the mode angular frequency in the inertial frame, and α = {njm} specifies the mode index: n gives the number of nodes in the radial eigenfunction (the order of the mode), j specifies the number of nodes in the θ-eigenfunction (j reduces to l in the nonrotating limit), and m is the azimut ...
Designing a toroidal top-hat energy analyzer for low-energy electron measurement Y. Kazama
... imuth direction and large sensitivity, relative to a spherical top-hat analyzer. In the case of spherical top-hat analyzers, azimuth-direction focusing occur inside the shell electrodes due to its short focal length, and particles have started defocusing at the analyzer exit. Relatively large sensit ...
... imuth direction and large sensitivity, relative to a spherical top-hat analyzer. In the case of spherical top-hat analyzers, azimuth-direction focusing occur inside the shell electrodes due to its short focal length, and particles have started defocusing at the analyzer exit. Relatively large sensit ...
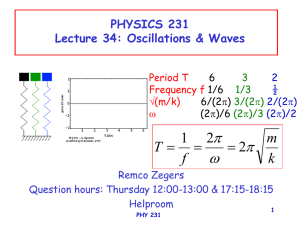
No Slide Title
... sea waves An anchored fishing boat is going up and down with the waves. It reaches a maximum height every 5 seconds and a person on the boat sees that while reaching a maximum, the previous waves has moves about 40 m away from the boat. What is the speed of the traveling waves? ...
... sea waves An anchored fishing boat is going up and down with the waves. It reaches a maximum height every 5 seconds and a person on the boat sees that while reaching a maximum, the previous waves has moves about 40 m away from the boat. What is the speed of the traveling waves? ...
paramagnetic resonance of divalent europium in lead chloride
... more reliably than the magnitude of each of theme). The presence of two parameters then permits one to check whether the splittings are linear in the crystal field strengths or not. (See appendix B.) Secondly, the two stable isotopes 151Eu and i5aEu have relatively large nuclear quadrupole moments. ...
... more reliably than the magnitude of each of theme). The presence of two parameters then permits one to check whether the splittings are linear in the crystal field strengths or not. (See appendix B.) Secondly, the two stable isotopes 151Eu and i5aEu have relatively large nuclear quadrupole moments. ...