On the interaction of electromagnetic waves with conductors
... is the mean time between successive collisions, then the electrons are really free, only for a time t ≪ τ ; and consequently, Zener’s theory is only good as long as the period of oscillation of the radiation 1/ω is smaller than τ . That means ωτ ≫ 1. If ωτ ≪ 1, then Zener’s theory cannot be applied. ...
... is the mean time between successive collisions, then the electrons are really free, only for a time t ≪ τ ; and consequently, Zener’s theory is only good as long as the period of oscillation of the radiation 1/ω is smaller than τ . That means ωτ ≫ 1. If ωτ ≪ 1, then Zener’s theory cannot be applied. ...
Physics GRE Comprehensive Notes - Are you sure you want to look
... does it take an air pilot to travel due North? The pilot must fly at some angle toward the incoming wind direction such that the component of the speed of the pilot in the east-west direction is equal to the speed of the wind. It is then straight forward to calculate the time it take the pilot to tr ...
... does it take an air pilot to travel due North? The pilot must fly at some angle toward the incoming wind direction such that the component of the speed of the pilot in the east-west direction is equal to the speed of the wind. It is then straight forward to calculate the time it take the pilot to tr ...
Radiation reaction in ultrarelativistic laser
... related to bremsstrahlung since there is an energy loss mechanism. Lorentz considered the electron model in which the charge is distributed on a sphere to investigate this force. His model was applied only in the nonrelativistic regime, the case in which the electron has low velocity. One part of th ...
... related to bremsstrahlung since there is an energy loss mechanism. Lorentz considered the electron model in which the charge is distributed on a sphere to investigate this force. His model was applied only in the nonrelativistic regime, the case in which the electron has low velocity. One part of th ...
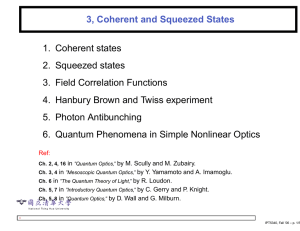
PART-B
... 2. What is cavitation? Mention its use. 3. What is piezo-electric effect? 4. What is sonogram? Mention its application. 5. Calculate the number of photons emitted per second at a wavelength 632.8nm by He-Ne laser of 3mW power. 6. What is the role of helium and nitrogen in CO2 laser? 7. What is the p ...
... 2. What is cavitation? Mention its use. 3. What is piezo-electric effect? 4. What is sonogram? Mention its application. 5. Calculate the number of photons emitted per second at a wavelength 632.8nm by He-Ne laser of 3mW power. 6. What is the role of helium and nitrogen in CO2 laser? 7. What is the p ...
SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND RAOTATIONAL DYNAMICS Various
... Statement − The moment of inertia of a body about any axis is equal to the sum of the moments of inertia of the body about a parallel axis passing through its centre of mass and the product of its mass and the square of distance between the two parallel axes. Proof − Consider a particle of mass m at ...
... Statement − The moment of inertia of a body about any axis is equal to the sum of the moments of inertia of the body about a parallel axis passing through its centre of mass and the product of its mass and the square of distance between the two parallel axes. Proof − Consider a particle of mass m at ...
Lecture 13. Polarization of Light
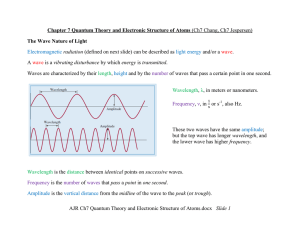
... Light is a very complex phenomenon, but in many situations its behavior can be understood with a simple model based on rays and wave fronts. A ray is a thin beam of light that travels in a straight line. A wave front is the line (not necessarily straight) or surface connecting all the light that lef ...
... Light is a very complex phenomenon, but in many situations its behavior can be understood with a simple model based on rays and wave fronts. A ray is a thin beam of light that travels in a straight line. A wave front is the line (not necessarily straight) or surface connecting all the light that lef ...
Circular Motion
... which is the average angular acceleration. a) Whereas the instantaneous acceleration is ∆ω α ≡ lim ∆t→0 ∆t b) ...
... which is the average angular acceleration. a) Whereas the instantaneous acceleration is ∆ω α ≡ lim ∆t→0 ∆t b) ...
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics
... Principle of linear impulse and momentum (continued) (Section 15.1) The next method we will consider for solving particle kinetics problems is obtained by integrating the equation of motion with respect to time. The result is referred to as the principle of impulse and momentum. It can be applied t ...
... Principle of linear impulse and momentum (continued) (Section 15.1) The next method we will consider for solving particle kinetics problems is obtained by integrating the equation of motion with respect to time. The result is referred to as the principle of impulse and momentum. It can be applied t ...