Honors Biology
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
Worksheet 6 - Iowa State University
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
unit 5 test review dna structure dna replication
... 3) Correctly pair the nucleotide bases: 4) Look at the warm-ups on the structure of DNA 5) What holds the bases together and how many do you have between each pair? 6) The backbones of DNA are said to be antiparallel because: 7) Which of the base pairs would be more difficult to separate during repl ...
... 3) Correctly pair the nucleotide bases: 4) Look at the warm-ups on the structure of DNA 5) What holds the bases together and how many do you have between each pair? 6) The backbones of DNA are said to be antiparallel because: 7) Which of the base pairs would be more difficult to separate during repl ...
GEN2MHG – MOLECULAR AND HUMAN GENETICS DNA is made
... ▪ DNA synthesis requires single stranded DNA template ▪ a protein complex origins of replication are rich in A/T (only two hydrogen bonds, therefore easier to separate than G/C rich areas) ▪ multiple replication origins Replication occurs in two directions but is semi-discontinuous due to both stran ...
... ▪ DNA synthesis requires single stranded DNA template ▪ a protein complex origins of replication are rich in A/T (only two hydrogen bonds, therefore easier to separate than G/C rich areas) ▪ multiple replication origins Replication occurs in two directions but is semi-discontinuous due to both stran ...
DNA, Protein Synthesis, and Gene Expression Review Historical
... 3. What are the three parts of a DNA nucleotide (be specific)? 4. Which bases are purine, and which are pyrimidine? What is the basic structure of each (single ring or double ring)? 5. Why is DNA called a double helix? 6. What is in the DNA backbone, and why are they considered antiparallel? 7. What ...
... 3. What are the three parts of a DNA nucleotide (be specific)? 4. Which bases are purine, and which are pyrimidine? What is the basic structure of each (single ring or double ring)? 5. Why is DNA called a double helix? 6. What is in the DNA backbone, and why are they considered antiparallel? 7. What ...
DNA Modeling Lab Report - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
... 11. Carefully pick up the single strand of DNA. Starting from top left to bottom right, how many nucleotides (bases) are present in the model? How many are purines and how many are pyrimidines are present in the model? ...
... 11. Carefully pick up the single strand of DNA. Starting from top left to bottom right, how many nucleotides (bases) are present in the model? How many are purines and how many are pyrimidines are present in the model? ...
DNA RNA Test Review Guide
... Name the process during which copies of DNA are made. Name the process during which a complementary RNA strand is made from DNA. Name the process during which amino acids are assembled into polypeptides according to DNA instructions. Give another name for a large polypeptide Name the monomer and mon ...
... Name the process during which copies of DNA are made. Name the process during which a complementary RNA strand is made from DNA. Name the process during which amino acids are assembled into polypeptides according to DNA instructions. Give another name for a large polypeptide Name the monomer and mon ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
... The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
Cartoon Guide to Genetics DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis 1. What did
... 14. What shape is the DNA molecule? 15. State the Principle of Complementarity. 16. What is replication? 17. Where does replication start on the DNA strand? 18. How do the free nucleotides know where to attach? 19. What are the functions of the two enzymes used to replicate DNA? 20. What is the seco ...
... 14. What shape is the DNA molecule? 15. State the Principle of Complementarity. 16. What is replication? 17. Where does replication start on the DNA strand? 18. How do the free nucleotides know where to attach? 19. What are the functions of the two enzymes used to replicate DNA? 20. What is the seco ...
Intro to DNA Worksheet
... 4. Adenine will only bond to ____________________ and cytosine will only bond to _________________. This is called __________________________________. 5. How is DNA Fingerprinting possible? ...
... 4. Adenine will only bond to ____________________ and cytosine will only bond to _________________. This is called __________________________________. 5. How is DNA Fingerprinting possible? ...
Deoxyribonucleic Acids DNA
... Chromosomes- A threadlike linear strand of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that carries the genes and functions in the transmission of hereditary information. In prokaryotes (bacteria) it is a circular strand of DNA in that contains the hereditary information necessary ...
... Chromosomes- A threadlike linear strand of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that carries the genes and functions in the transmission of hereditary information. In prokaryotes (bacteria) it is a circular strand of DNA in that contains the hereditary information necessary ...
DNA - Harrison High School
... Ex- A mouse and a rosebush have the same nucleotides. However, they are different because their nucleotides are in different orders. *This sequence of nucleotides forms the genetic information(code) of an organism. ...
... Ex- A mouse and a rosebush have the same nucleotides. However, they are different because their nucleotides are in different orders. *This sequence of nucleotides forms the genetic information(code) of an organism. ...
DNA Model Lab
... Lab # ______ - DNA Model Lab DNA is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parent(s). This molecular reproduction is the basis for the continuity of life. A DNA molecule is very long and consists of hundreds of thousands of genes. A gene’s meaning to the cell is encoded in its specif ...
... Lab # ______ - DNA Model Lab DNA is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parent(s). This molecular reproduction is the basis for the continuity of life. A DNA molecule is very long and consists of hundreds of thousands of genes. A gene’s meaning to the cell is encoded in its specif ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
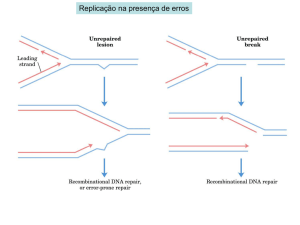
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
DNA structure and replication Three key features needed for any
... Primase - RNA polymerase - synthesizes a primer Helicase - unwinding enzyme - acts upstream of the replication fork Okazaki fragments - DNA fragment synthesized on lagging strand SS binding proteins - bind single stranded DNA around the replication fork DNA ligase - links the okazaki fragments by ma ...
... Primase - RNA polymerase - synthesizes a primer Helicase - unwinding enzyme - acts upstream of the replication fork Okazaki fragments - DNA fragment synthesized on lagging strand SS binding proteins - bind single stranded DNA around the replication fork DNA ligase - links the okazaki fragments by ma ...
DNA Polymerase: “ase”
... DNA duplication takes place in the “S” phase of the cell cycle DNA is found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell; linear DNA DNA is found in the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell; single, circular DNA ...
... DNA duplication takes place in the “S” phase of the cell cycle DNA is found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell; linear DNA DNA is found in the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell; single, circular DNA ...
Questions - Humble ISD
... 5. A single-ringed N-base is called _____ & includes ________ & _______ 6. A double-ringed N-base is called ______ & includes _______ & _______ 7. a. Name the bond that holds the nucleotide together __________________ b. Name the bond between the nitrogen bases __________________ 8. What is DNA repl ...
... 5. A single-ringed N-base is called _____ & includes ________ & _______ 6. A double-ringed N-base is called ______ & includes _______ & _______ 7. a. Name the bond that holds the nucleotide together __________________ b. Name the bond between the nitrogen bases __________________ 8. What is DNA repl ...
Biology Molecular Genetic Review
... 13. Draw a piece of mRNA 5 codons long. Draw the pieces of tRNA that would match up. ...
... 13. Draw a piece of mRNA 5 codons long. Draw the pieces of tRNA that would match up. ...
DNA polymerase

The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. This opens up or “unzips” the double-stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.