DNA Pre-Test
... specifies its traits, that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes located in the chromosomes of each cell, and that heredity is the passage of these instructions from one generation to another. 1. Chromosomes are located in the _________ of the cell. A. Cell wall B. Cytoplasm C. Mitoch ...
... specifies its traits, that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes located in the chromosomes of each cell, and that heredity is the passage of these instructions from one generation to another. 1. Chromosomes are located in the _________ of the cell. A. Cell wall B. Cytoplasm C. Mitoch ...
Pre/Post Test
... B. Bacterial cells contain the same organelles as human cells. C. The basic components of DNA are the same in humans and bacteria. D. Bacterial cells and human cells contain the same kind of chromosomes ...
... B. Bacterial cells contain the same organelles as human cells. C. The basic components of DNA are the same in humans and bacteria. D. Bacterial cells and human cells contain the same kind of chromosomes ...
Final Test
... 3. Polypeptides are made of 20 units called ____. List five of these. a. ______ b. ______ c. ______ d. ______ e. ______ 4. List the three types of RNA and their function. RNA type ...
... 3. Polypeptides are made of 20 units called ____. List five of these. a. ______ b. ______ c. ______ d. ______ e. ______ 4. List the three types of RNA and their function. RNA type ...
No Slide Title
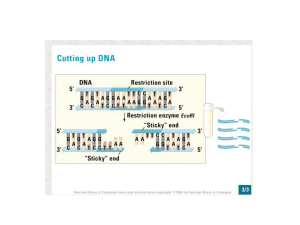
... Restriction Enzymes • Restriction enzymes cut DNA from any source into fragments • Sticky ends can pair up with complementary DNA with the help of ligase producing recombinant DNA • Example: EcoRI, HindII ...
... Restriction Enzymes • Restriction enzymes cut DNA from any source into fragments • Sticky ends can pair up with complementary DNA with the help of ligase producing recombinant DNA • Example: EcoRI, HindII ...
Title - Iowa State University
... Antiparallel-Two strands that are parallel but going in different directions. Semi-conservative- The mechanism which DNA replicate, where the parent strands separate and serve as a template for the daughter strands, etc. Complementary- Opposites that combine to form the whole. Replication fork- Wher ...
... Antiparallel-Two strands that are parallel but going in different directions. Semi-conservative- The mechanism which DNA replicate, where the parent strands separate and serve as a template for the daughter strands, etc. Complementary- Opposites that combine to form the whole. Replication fork- Wher ...
unit 5 test review dna structure dna replication
... 1) The structure of DNA is often called a: 2) The backbones of DNA are composed of: 3) Correctly pair the nucleotide bases: 4) Look at the warm-ups on the structure of DNA 5) What holds the bases together and how many do you have between each pair? 6) The backbones of DNA are said to be antiparallel ...
... 1) The structure of DNA is often called a: 2) The backbones of DNA are composed of: 3) Correctly pair the nucleotide bases: 4) Look at the warm-ups on the structure of DNA 5) What holds the bases together and how many do you have between each pair? 6) The backbones of DNA are said to be antiparallel ...
11.1 Replication of DNA
... DNA helicase ……………………………….. Double helix unwinds and the two strands ………… Each exposed ……………… acts as a ……………. to which …………………. nucleotides are attracted Energy required to …………… nucleotides Activated nucleotides are joined by the enzyme DNA ...
... DNA helicase ……………………………….. Double helix unwinds and the two strands ………… Each exposed ……………… acts as a ……………. to which …………………. nucleotides are attracted Energy required to …………… nucleotides Activated nucleotides are joined by the enzyme DNA ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
... OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
Exam 1 Study Guide – General Concepts
... Polymerases (DNA Pol I and III) Helicase (and counteracting gyrase) Single stranded binding proteins DNA Primase Ligase Okazaki fragments Exonuclease activity (5’-3’ activity vs 3’-5’ proofreading) Eukaryotic DNA Replication Multiple origins of replication Telomeres Telomerase Transcription Prokaryo ...
... Polymerases (DNA Pol I and III) Helicase (and counteracting gyrase) Single stranded binding proteins DNA Primase Ligase Okazaki fragments Exonuclease activity (5’-3’ activity vs 3’-5’ proofreading) Eukaryotic DNA Replication Multiple origins of replication Telomeres Telomerase Transcription Prokaryo ...
Notes_DNA Replication_teacher
... attaches to one strand. It reads the DNA code, and attaches complementary nucleotides to the original exposed strand. After it attaches each complementary nucleotide, it proofreads for mistakes. ...
... attaches to one strand. It reads the DNA code, and attaches complementary nucleotides to the original exposed strand. After it attaches each complementary nucleotide, it proofreads for mistakes. ...
Answer Key
... 2. transcription (nucleus) 3. translation (cytoplasm) 4. Contains the sugar ribose 5. Has the bases A, C, G, and ...
... 2. transcription (nucleus) 3. translation (cytoplasm) 4. Contains the sugar ribose 5. Has the bases A, C, G, and ...
Sect 12.2
... • DNA replicates by making a strand that is complementary to each original strand. Semiconservative Replication • In the Watson-Crick model ◦ a replication method was suggested ◦ called semiconservative replication ...
... • DNA replicates by making a strand that is complementary to each original strand. Semiconservative Replication • In the Watson-Crick model ◦ a replication method was suggested ◦ called semiconservative replication ...
Exam Review 2B -- Rodermel
... (Be sure to include leading and lagging strand, origin of replication, directionality of the strands) ...
... (Be sure to include leading and lagging strand, origin of replication, directionality of the strands) ...
Ch - TeacherWeb
... 9. Draw and label the structure of a DNA strand. Be sure to use the following: nucleotide, deoxyribose, phosphate group, nitrogenous base, hydrogen bond, base pair. SEE DIAGRAM ON YOUR WORKSHEET ...
... 9. Draw and label the structure of a DNA strand. Be sure to use the following: nucleotide, deoxyribose, phosphate group, nitrogenous base, hydrogen bond, base pair. SEE DIAGRAM ON YOUR WORKSHEET ...
phosphorus - Sacred Heart Academy
... complementary bases • Replication occurs in the 5‘ to 3‘ direction (lead strand and lag strand); bases can only be added to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule • Other enzymes correct errors, remove primers, seal “nicks” in the backbone ...
... complementary bases • Replication occurs in the 5‘ to 3‘ direction (lead strand and lag strand); bases can only be added to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule • Other enzymes correct errors, remove primers, seal “nicks” in the backbone ...
made of three parts sugar, phosphate, and base Scientist that
... prepared from killed or weakened diseasecausing agents ...
... prepared from killed or weakened diseasecausing agents ...
DNA-RNA-Protein Practice Hwk
... How do the data in the table at the right demonstrate Chargaff's rules? ...
... How do the data in the table at the right demonstrate Chargaff's rules? ...
2. DNA Replication and Repair
... an enzyme (DNA helicase) is responsible for breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs causing the helix to unwind single stranded binding proteins binds to the exposed bases and prevent hydrogen bonding from occurring during bacterial replication an enzyme called DNA gyras ...
... an enzyme (DNA helicase) is responsible for breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs causing the helix to unwind single stranded binding proteins binds to the exposed bases and prevent hydrogen bonding from occurring during bacterial replication an enzyme called DNA gyras ...
Sample Final Exam Questions
... i) On which template strand (A or B) would there be continuous replication by DNA polymerase? What is this newly synthesized daughter strand called during DNA replication? ii) On which template strand (A or B) would there be discontinous replication by DNA polymerase? What is this newly synthesized ...
... i) On which template strand (A or B) would there be continuous replication by DNA polymerase? What is this newly synthesized daughter strand called during DNA replication? ii) On which template strand (A or B) would there be discontinous replication by DNA polymerase? What is this newly synthesized ...
DNA Worksheet 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. What does DNA do
... 4. Draw a diagram to show all the parts of DNA: sugars, phosphates, nucleotides(A,T,C,G), and hydrogen bonds ...
... 4. Draw a diagram to show all the parts of DNA: sugars, phosphates, nucleotides(A,T,C,G), and hydrogen bonds ...
STUDY GUIDE for MICROBIAL GENETICS 1. Define the following
... Describe the structure of DNA. a. What are the two main functions of DNA? b. What is a nucleotide? c. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? d. What are the four nucleotides in RNA? e. How are nucleotides connected into a DNA strand? f. How are the two strands of a DNA molecule connected to one anoth ...
... Describe the structure of DNA. a. What are the two main functions of DNA? b. What is a nucleotide? c. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? d. What are the four nucleotides in RNA? e. How are nucleotides connected into a DNA strand? f. How are the two strands of a DNA molecule connected to one anoth ...
Some Replication Questions
... DnaA, DnaB, DnaC, SSBPs, DNA gyrase, Primase (DnaG), Sliding clamp, DNA pol I, DNA pol III, Clamp loader, RNAse H, DNA ligase. 12. What does bidirectional DNA replication accomplish for the cell? 13. How many replication origins can be found in E. coli? How many can be found in a typical eukaryotic ...
... DnaA, DnaB, DnaC, SSBPs, DNA gyrase, Primase (DnaG), Sliding clamp, DNA pol I, DNA pol III, Clamp loader, RNAse H, DNA ligase. 12. What does bidirectional DNA replication accomplish for the cell? 13. How many replication origins can be found in E. coli? How many can be found in a typical eukaryotic ...
DNA replication
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. This biological process occurs in all living organisms and is the basis for biological inheritance. DNA is made up of two strands and each strand of the original DNA molecule serves as a template for the production of the complementary strand, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. Cellular proofreading and error-checking mechanisms ensure near perfect fidelity for DNA replication.In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations, or origins of replication, in the genome. Unwinding of DNA at the origin and synthesis of new strands results in replication forks growing bidirectional from the origin. A number of proteins are associated with the replication fork which helps in terms of the initiation and continuation of DNA synthesis. Most prominently, DNA polymerase synthesizes the new DNA by adding complementary nucleotides to the template strand.DNA replication can also be performed in vitro (artificially, outside a cell). DNA polymerases isolated from cells and artificial DNA primers can be used to initiate DNA synthesis at known sequences in a template DNA molecule. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a common laboratory technique, cyclically applies such artificial synthesis to amplify a specific target DNA fragment from a pool of DNA.