Document
... 6. Scientists were surprised about how much the DNA molecule could do, because they thought only ____________________ molecules could give instructions and be copied during cell division. ...
... 6. Scientists were surprised about how much the DNA molecule could do, because they thought only ____________________ molecules could give instructions and be copied during cell division. ...
DNA Notes Review
... ______________24. The sides of the DNA double helix are made of the Nitrogenous bases ______________25. The enzyme that pairs up the nucleotides to their complementary pairs is the DNA Ligase ______________26. The process of DNA replication is how DNA makes copies of itself. ______________27. During ...
... ______________24. The sides of the DNA double helix are made of the Nitrogenous bases ______________25. The enzyme that pairs up the nucleotides to their complementary pairs is the DNA Ligase ______________26. The process of DNA replication is how DNA makes copies of itself. ______________27. During ...
DNA Replication
... fragment. A complex containing helicase and 2 DNA polymerases carries out the coordinated synthesis of both strands. The two polymerases are attached to each other and move with the replication fork. The fidelity of DNA polymerization is very high, one error per 109 bases (proofreading!). ...
... fragment. A complex containing helicase and 2 DNA polymerases carries out the coordinated synthesis of both strands. The two polymerases are attached to each other and move with the replication fork. The fidelity of DNA polymerization is very high, one error per 109 bases (proofreading!). ...
DNA Test Review Answer Key
... 9. Where does Translation take place in the cell? RIBOSOME 10. What nitrogenous base is not found in DNA, but found in RNA? URACIL 11. A five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base make up what monomer? NUCLEOTIDE 12. What does AGG code for? ARGININE 13. What does TAC code for? MET ...
... 9. Where does Translation take place in the cell? RIBOSOME 10. What nitrogenous base is not found in DNA, but found in RNA? URACIL 11. A five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base make up what monomer? NUCLEOTIDE 12. What does AGG code for? ARGININE 13. What does TAC code for? MET ...
DNA
... possible? (NOTE: This is a mathematical problem that you can figure out using permutations, i.e. how many different combinations are there with 4 letters if each letter can be used as many as four times per combination ex. CCCC or CCGG, etc) ...
... possible? (NOTE: This is a mathematical problem that you can figure out using permutations, i.e. how many different combinations are there with 4 letters if each letter can be used as many as four times per combination ex. CCCC or CCGG, etc) ...
DNA - TeacherWeb
... Is it DNA? In 1928, Griffith found out that the information carried in the cell could be transferred to another cell. He called this transfer “transformation”. He did not yet know about DNA and the prevailing thought of the time was that protein was the more likely culprit. ...
... Is it DNA? In 1928, Griffith found out that the information carried in the cell could be transferred to another cell. He called this transfer “transformation”. He did not yet know about DNA and the prevailing thought of the time was that protein was the more likely culprit. ...
Vocabulary Assignment Unit 06
... a. 3 nucleotide bases on a tRNA that will pair with three bases on the mRNA b. Term for two nucleotide bases joining up, A with T and C with G c. The genetic material of an organism is changed by the addition of another organism’s DNA (in this unit, used referring to the bacteria changed in Griffith ...
... a. 3 nucleotide bases on a tRNA that will pair with three bases on the mRNA b. Term for two nucleotide bases joining up, A with T and C with G c. The genetic material of an organism is changed by the addition of another organism’s DNA (in this unit, used referring to the bacteria changed in Griffith ...
DNA Prot Syn Engineer
... List and discuss differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic replication of DNA. Explain why the replication process is a source of few mutations (mismatch repair and excision repair). What are the biochemical differences between RNA and DNA? What are two steps required for the expression of a ge ...
... List and discuss differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic replication of DNA. Explain why the replication process is a source of few mutations (mismatch repair and excision repair). What are the biochemical differences between RNA and DNA? What are two steps required for the expression of a ge ...
Holiday time test notes
... fork" so the machinery of replication is operating both two forks in each of the thousands of bubbles. At each fork there is a leading strand and a lagging strand. As the "semiconservative" replication continues, the bubbles will coalesce until all of the DNA molecules are replicated (semiconservati ...
... fork" so the machinery of replication is operating both two forks in each of the thousands of bubbles. At each fork there is a leading strand and a lagging strand. As the "semiconservative" replication continues, the bubbles will coalesce until all of the DNA molecules are replicated (semiconservati ...
FREE Sample Here
... 15. The nucleotides in a single strand of DNA are held together by which of the following bonds? A) Disulfide B) Phosphodiester C) Hydrogen D) Peptide 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which o ...
... 15. The nucleotides in a single strand of DNA are held together by which of the following bonds? A) Disulfide B) Phosphodiester C) Hydrogen D) Peptide 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which o ...
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS QUESTIONS
... 2. Briefly describe how Watson and Crick came to the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA. ...
... 2. Briefly describe how Watson and Crick came to the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA. ...
DNA Structure Review Questions Name: 1. Know the following 3
... 23. What is translation? Where does translation occur? ...
... 23. What is translation? Where does translation occur? ...
Chapter 12 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... DNA unzips: nucleotide pieces bond to each exposed half of DNA molecule Enzyme Polymerase bonds to monomers to create 2 identical strands ...
... DNA unzips: nucleotide pieces bond to each exposed half of DNA molecule Enzyme Polymerase bonds to monomers to create 2 identical strands ...
Unit 5- Molecular Biology
... a. Describe the basic structure and function of DNA, mRNA, tRNA, amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins (e.g., replication, transcription, and translation) b. Describe the experiments of major scientists in determining both the structure of DNA and the central dogma c. Use mRNA codon charts to dete ...
... a. Describe the basic structure and function of DNA, mRNA, tRNA, amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins (e.g., replication, transcription, and translation) b. Describe the experiments of major scientists in determining both the structure of DNA and the central dogma c. Use mRNA codon charts to dete ...
Chapter Three The Biological Basis of Life
... DNA Structure • For a cell to work, it needs DNA to direct it. • An organism’s inheritance depends on the structure and function of DNA. • DNA is composed of two chains of nucleotides, comprising a double strand or double helix. • A nucleotide consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of four nitro ...
... DNA Structure • For a cell to work, it needs DNA to direct it. • An organism’s inheritance depends on the structure and function of DNA. • DNA is composed of two chains of nucleotides, comprising a double strand or double helix. • A nucleotide consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of four nitro ...
DNA and RNA study guide Answer Key
... 7. Before a cell divides, it must duplicate its own DNA in a process known as… DNA Replication 8. The genetic code in DNA depends upon the order or sequence of… Nitrogenous Bases 9. If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence ATCGT, the sequence of bases on the COMPLEMENTARY STRAND of DNA ...
... 7. Before a cell divides, it must duplicate its own DNA in a process known as… DNA Replication 8. The genetic code in DNA depends upon the order or sequence of… Nitrogenous Bases 9. If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence ATCGT, the sequence of bases on the COMPLEMENTARY STRAND of DNA ...
Genes and DNA
... packages the chromatin into chromatids. Two identical chromatids make up a chromosome that is ready to divide ...
... packages the chromatin into chromatids. Two identical chromatids make up a chromosome that is ready to divide ...
2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA
... • DNA differs from RNA in the number of strands present, the base composition and the type of pentose. • DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. Applications and skills: • Application: Crick and Watson’s eluci ...
... • DNA differs from RNA in the number of strands present, the base composition and the type of pentose. • DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. Applications and skills: • Application: Crick and Watson’s eluci ...
Worksheet on DNA and RNA
... 18. Which 2 scientists correctly determined the structure of DNA? a. Aristotle and Galileo b. Watson and Crick c. Avery and Franklin d. None of the above 19. What are the sides of the DNA ladder made of? a. Nitrogenous bases b. Phosphates and sugars c. Nitrogenous bases and sugars d. Phosphates and ...
... 18. Which 2 scientists correctly determined the structure of DNA? a. Aristotle and Galileo b. Watson and Crick c. Avery and Franklin d. None of the above 19. What are the sides of the DNA ladder made of? a. Nitrogenous bases b. Phosphates and sugars c. Nitrogenous bases and sugars d. Phosphates and ...
Microbial Genetics: Chapter 8 expression)
... Genotype (potential properties) and Phenotype (expressed properties-gene expressed as protein) Bacteria: single, double stranded, circular chromosome; looped, folded, and attached to plasma membrane/supercoiled by topoisomerase II or DNA gyrase (antibiotic ciprofloxacin (a fluoroquinolone) inhibits ...
... Genotype (potential properties) and Phenotype (expressed properties-gene expressed as protein) Bacteria: single, double stranded, circular chromosome; looped, folded, and attached to plasma membrane/supercoiled by topoisomerase II or DNA gyrase (antibiotic ciprofloxacin (a fluoroquinolone) inhibits ...
12-1 Practice 12-1 Write the complementary strand of DNA to the
... Remember, A pairs with T and G pairs with C. Go through the original 5′′ to 3′′ sequence pairing each A with T and each C with G. Keep in mind that the complementary strand will read from left to right in the 3′′ to 5′′ direction. Therefore, the complementary strand starts with 3’ and ends with 5’. ...
... Remember, A pairs with T and G pairs with C. Go through the original 5′′ to 3′′ sequence pairing each A with T and each C with G. Keep in mind that the complementary strand will read from left to right in the 3′′ to 5′′ direction. Therefore, the complementary strand starts with 3’ and ends with 5’. ...
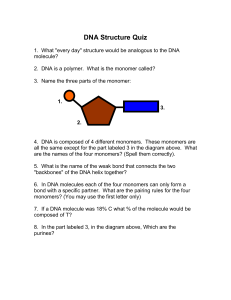
DNA Structure quick review/quiz
... all the same except for the part labeled 3 in the diagram above. What are the names of the four monomers? (Spell them correctly). 5. What is the name of the weak bond that connects the two "backbones" of the DNA helix together? 6. In DNA molecules each of the four monomers can only form a bond with ...
... all the same except for the part labeled 3 in the diagram above. What are the names of the four monomers? (Spell them correctly). 5. What is the name of the weak bond that connects the two "backbones" of the DNA helix together? 6. In DNA molecules each of the four monomers can only form a bond with ...
DNA replication
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. This biological process occurs in all living organisms and is the basis for biological inheritance. DNA is made up of two strands and each strand of the original DNA molecule serves as a template for the production of the complementary strand, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. Cellular proofreading and error-checking mechanisms ensure near perfect fidelity for DNA replication.In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations, or origins of replication, in the genome. Unwinding of DNA at the origin and synthesis of new strands results in replication forks growing bidirectional from the origin. A number of proteins are associated with the replication fork which helps in terms of the initiation and continuation of DNA synthesis. Most prominently, DNA polymerase synthesizes the new DNA by adding complementary nucleotides to the template strand.DNA replication can also be performed in vitro (artificially, outside a cell). DNA polymerases isolated from cells and artificial DNA primers can be used to initiate DNA synthesis at known sequences in a template DNA molecule. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a common laboratory technique, cyclically applies such artificial synthesis to amplify a specific target DNA fragment from a pool of DNA.