Biology 320 Invertebrate Zoology Fall 2005
... Muscles are usually arranged in antagonistic sets One muscle moves body part one way, while the other restores its original position Human example – biceps and triceps Tubular invertebrates – longitudinal and circular ...
... Muscles are usually arranged in antagonistic sets One muscle moves body part one way, while the other restores its original position Human example – biceps and triceps Tubular invertebrates – longitudinal and circular ...
Body in Action
... A person who is in training will notice that the factors above will return to normal resting values quicker than a person who is not in training. It can therefore be used as an indicator of fitness. ...
... A person who is in training will notice that the factors above will return to normal resting values quicker than a person who is not in training. It can therefore be used as an indicator of fitness. ...
Practice Exam
... per minute. Provide reasons as to why the increase in heart rate occurred. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ ...
... per minute. Provide reasons as to why the increase in heart rate occurred. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ ...
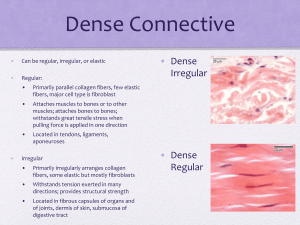
P2 The main tissue types of the body and the role these
... the heart is made of a muscle called the cardiac muscle unlike other muscles in the body the cardiac muscle never gets tiered its constantly working and never stops. It squeezes blood out of the heart and then relaxes it to fill it back with blood again in and this process continues and happens ever ...
... the heart is made of a muscle called the cardiac muscle unlike other muscles in the body the cardiac muscle never gets tiered its constantly working and never stops. It squeezes blood out of the heart and then relaxes it to fill it back with blood again in and this process continues and happens ever ...
Science Chapter 4 Body Systems Study Guide 1. What part of the
... get food to your body’s cells? The digestive system breaks food down into a form that the body’s cells can use. The circulatory system carries the food to each cell in the body. ...
... get food to your body’s cells? The digestive system breaks food down into a form that the body’s cells can use. The circulatory system carries the food to each cell in the body. ...
Microsoft PowerPoint - VZFTITININMZ.ppt [\310\243\310
... • Frogs, chicken, fish (zebrafish) – Develop in eggs outside the mother’s body • Mouse – Identifying the gene function using genetically modified mice ...
... • Frogs, chicken, fish (zebrafish) – Develop in eggs outside the mother’s body • Mouse – Identifying the gene function using genetically modified mice ...
Lec. No.10 Centrosome In cell biology, the centrosome is an
... In cells with a flagellum, e.g. sperm, the flagellum develops from a single basal body. (While sperm cells have a basal body, eggs have none. So the sperm's basal body is absolutely essential for forming a centrosome which will form a spindle enabling the first division of the zygote to take place. ...
... In cells with a flagellum, e.g. sperm, the flagellum develops from a single basal body. (While sperm cells have a basal body, eggs have none. So the sperm's basal body is absolutely essential for forming a centrosome which will form a spindle enabling the first division of the zygote to take place. ...
New B1 B2 B3 Revision
... The concentration of blood plasma varies with external temperature, exercise level, intake of fluids and salt. The concentration of urine is controlled by a hormone called ADH, which is released into the bloodstream by the ...
... The concentration of blood plasma varies with external temperature, exercise level, intake of fluids and salt. The concentration of urine is controlled by a hormone called ADH, which is released into the bloodstream by the ...
Body Systems Notes
... ___________________________ • ____________________ (mature) Lymph – fluid that ____________ ____________ of blood – between cells Lymphatic vessels – __________ • lymph and _________________ it to bloodstream Bone marrow – ______________ ___________________________ ...
... ___________________________ • ____________________ (mature) Lymph – fluid that ____________ ____________ of blood – between cells Lymphatic vessels – __________ • lymph and _________________ it to bloodstream Bone marrow – ______________ ___________________________ ...
100 Biology
... 74. White blood cells react to bacterial infection by producing antibodies which attack the disease and reduce the symptoms. 75. Wind pollinated plants produce huge amounts of tiny pollen grains. 76. Invertebrates are animals without a backbone. 77. Respiration and photosynthesis together form the c ...
... 74. White blood cells react to bacterial infection by producing antibodies which attack the disease and reduce the symptoms. 75. Wind pollinated plants produce huge amounts of tiny pollen grains. 76. Invertebrates are animals without a backbone. 77. Respiration and photosynthesis together form the c ...
Topic 1 – Measurement and graphing
... Statement: Rockets that have 4 fins will fly higher than rockets that have no fins. ANSWER: Problem: If I make a rocket with 4 fins, will it fly higher than a rocket with 0 fins? Independent variable: The number of fins Dependent variable: Flight height Control variables: The size of the bod ...
... Statement: Rockets that have 4 fins will fly higher than rockets that have no fins. ANSWER: Problem: If I make a rocket with 4 fins, will it fly higher than a rocket with 0 fins? Independent variable: The number of fins Dependent variable: Flight height Control variables: The size of the bod ...
File
... • Nervous systems are composed of nerve cells/neurons and glia (support cells). • Neurons are organized into informationprocessing neural networks • The nervous system regulates and controls body functions; they respond to stimuli and transmit electrical impulses over substantial distances within th ...
... • Nervous systems are composed of nerve cells/neurons and glia (support cells). • Neurons are organized into informationprocessing neural networks • The nervous system regulates and controls body functions; they respond to stimuli and transmit electrical impulses over substantial distances within th ...
PPT
... • One drop of blood has 250 million RBC’s • Adult human has total of 25 trillion RBC’s—1/3 of all cells in the body • Each RBC lives about 120 days and travels 700 miles. Membrane rupture or other damage is noticed by phagocytes which then engulf the cell • One percent of RBC’s are replaced each day ...
... • One drop of blood has 250 million RBC’s • Adult human has total of 25 trillion RBC’s—1/3 of all cells in the body • Each RBC lives about 120 days and travels 700 miles. Membrane rupture or other damage is noticed by phagocytes which then engulf the cell • One percent of RBC’s are replaced each day ...
UROCHORDATES
... Atrium has two parts who are continous. One part surrounds the pharynx except on the anterior and ventral side,where the pharyngeal wall is joined to the mantle.this is the PERIBRANCHIAL CAVITY.stigmata of pharynx open into this cavity. Otherpart of atrium is dorsal to the pharynx .it is wide ...
... Atrium has two parts who are continous. One part surrounds the pharynx except on the anterior and ventral side,where the pharyngeal wall is joined to the mantle.this is the PERIBRANCHIAL CAVITY.stigmata of pharynx open into this cavity. Otherpart of atrium is dorsal to the pharynx .it is wide ...
File
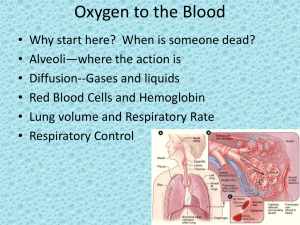
... Pulse is the number of times your heart beats in a period of time (BPM’s). When you exercise your muscles need/use more oxygen (and to remove more co2) so your heart beats faster and you breath increases to help send oxygen around your body. 17.) trade off with microscopes As you increase magnificat ...
... Pulse is the number of times your heart beats in a period of time (BPM’s). When you exercise your muscles need/use more oxygen (and to remove more co2) so your heart beats faster and you breath increases to help send oxygen around your body. 17.) trade off with microscopes As you increase magnificat ...
Cell theory - Unidad Educativa Monte Tabor
... scientific discovery and how it was made. Papers are collected together and published in 'journals'. Scientists buy journals to find out what other scientists have done. One famous journal today is called Nature. Matthias Schleiden (1804-1881), ...
... scientific discovery and how it was made. Papers are collected together and published in 'journals'. Scientists buy journals to find out what other scientists have done. One famous journal today is called Nature. Matthias Schleiden (1804-1881), ...
Human Homeostasis Study Aid Circulatory System Main Connective
... Pump the blood around the body Deoxygenated blood from the body is carried to the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava and received by the right atrium, pumped to the right ventricle, pumped through the pulmonary artery to the lungs for gas exchange, oxygenated blood returns to the hear ...
... Pump the blood around the body Deoxygenated blood from the body is carried to the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava and received by the right atrium, pumped to the right ventricle, pumped through the pulmonary artery to the lungs for gas exchange, oxygenated blood returns to the hear ...
Phylum Porifera
... Digestion: filter feeders / many pores .Choanocytes are flagellated cells that pull food in thru ostia (pores) and the amoebocyte cells circulate food around the organism ...
... Digestion: filter feeders / many pores .Choanocytes are flagellated cells that pull food in thru ostia (pores) and the amoebocyte cells circulate food around the organism ...
Chapter 1 - SharpSchool
... cells will kill bacteria that may enter your body through your cut. The blood cells use energy to do their work! ...
... cells will kill bacteria that may enter your body through your cut. The blood cells use energy to do their work! ...
Defense against disease!
... B cells mature in the bone marrow T cells mature in the thymus B cell make antibodies to get T cells work on cells that antigens which are ‘loose in the body’ have been invaded by antigen ...
... B cells mature in the bone marrow T cells mature in the thymus B cell make antibodies to get T cells work on cells that antigens which are ‘loose in the body’ have been invaded by antigen ...
Lecture PowerPoint
... Organs: Combinations of two or more tissues. The skin is an organ because it is composed of epithelium, connective tissue and small amounts of nerve and muscle. Organ Systems: Combinations of organs that together serve a general function for the body. For example, the circulatory system pumps blood ...
... Organs: Combinations of two or more tissues. The skin is an organ because it is composed of epithelium, connective tissue and small amounts of nerve and muscle. Organ Systems: Combinations of organs that together serve a general function for the body. For example, the circulatory system pumps blood ...
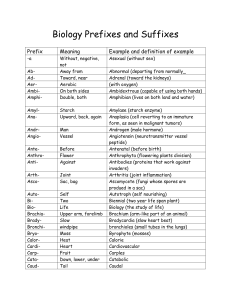
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... neuroblast (embryonic cell that develops into a nerve cell) Oculus (an eye) Odontoid (tooth-like) oligosaccharide (a carbohydrate that contains a small number of component sugars) oogenesis (formation and development of an ovum) ophthalmoscope (instrument for examining the retina of the eye orbis (r ...
... neuroblast (embryonic cell that develops into a nerve cell) Oculus (an eye) Odontoid (tooth-like) oligosaccharide (a carbohydrate that contains a small number of component sugars) oogenesis (formation and development of an ovum) ophthalmoscope (instrument for examining the retina of the eye orbis (r ...
Multiple Choice. Answer all questions. _____1. When comparing
... _____51. When an individual is first exposed to the smallpox virus, several days pass before significant numbers of specific antibody molecules and T cells are produced. However, a second exposure to the virus causes a large and rapid production of antibodies and T cells. This later response is an ...
... _____51. When an individual is first exposed to the smallpox virus, several days pass before significant numbers of specific antibody molecules and T cells are produced. However, a second exposure to the virus causes a large and rapid production of antibodies and T cells. This later response is an ...