vert strand 3 - csi-parent-student
... Describe the structure of cell parts (e.g., cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondrion, ribosomes, vacuole) found in different types of cells (e.g., bacterial, plant, skin, nerve, blood, muscle) and the functions they perform (e.g., structural support, transport of mate ...
... Describe the structure of cell parts (e.g., cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondrion, ribosomes, vacuole) found in different types of cells (e.g., bacterial, plant, skin, nerve, blood, muscle) and the functions they perform (e.g., structural support, transport of mate ...
01st lecture
... principles in order to the technological use of microorganisms animal and plant cells/tissues or parts of these (e.g. enzymes) to produce something. ...
... principles in order to the technological use of microorganisms animal and plant cells/tissues or parts of these (e.g. enzymes) to produce something. ...
Syllabus - PBworks
... Students know and understand the characteristics and structure of living things, the processes of life, and how living things interact with each other and their environment. 3. Cellular metabolic activities are carried out by biomolecules produced by organisms e. Analyze and interpret data on the bo ...
... Students know and understand the characteristics and structure of living things, the processes of life, and how living things interact with each other and their environment. 3. Cellular metabolic activities are carried out by biomolecules produced by organisms e. Analyze and interpret data on the bo ...
Cell Structure & Function
... grow and divide and to make needed materials. B. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions. C. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems, and systems into organisms. D. Explain that tis ...
... grow and divide and to make needed materials. B. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions. C. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems, and systems into organisms. D. Explain that tis ...
Types of Tissues A tissue is composed of similarly specialized cells
... cell. This epithelium is found lining the digestive tract. Ciliated columnar epithelium is found lining the oviducts, where it propels the egg toward the uterus. An epithelium can be simple or stratified. Simple means the tissue has a single layer of cells, and stratified means the tissue has layers ...
... cell. This epithelium is found lining the digestive tract. Ciliated columnar epithelium is found lining the oviducts, where it propels the egg toward the uterus. An epithelium can be simple or stratified. Simple means the tissue has a single layer of cells, and stratified means the tissue has layers ...
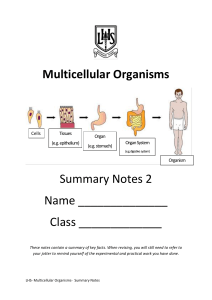
Multicellular Organisms summary notes
... Blood enters and leaves the heart via major blood vessels. Veins transport blood into the heart under low pressure and arteries take blood away from the heart under high pressure. The RIGHT side of the heart contains DEOXYGENATED blood. The LEFT side of the heart contains OXYGENATED blood. ...
... Blood enters and leaves the heart via major blood vessels. Veins transport blood into the heart under low pressure and arteries take blood away from the heart under high pressure. The RIGHT side of the heart contains DEOXYGENATED blood. The LEFT side of the heart contains OXYGENATED blood. ...
Homeostasis
... environmental conditions – generally moving away from heat and light, and towards food. • Multicellular organisms such as sponges rely on the cellular membrane to regulate concentration of cytoplasmic contents while being bathed directly in the fluids of the external environment. • Homeostatic mecha ...
... environmental conditions – generally moving away from heat and light, and towards food. • Multicellular organisms such as sponges rely on the cellular membrane to regulate concentration of cytoplasmic contents while being bathed directly in the fluids of the external environment. • Homeostatic mecha ...
New AHSGE Science Study Guide
... "twisted ladder" structure. The sugar-phosphate backbone is on the outside of the double helix, and the bases are on the inside, so that a base on one strand points directly toward a base on the second strand. When using the twisted ladder analogy, think of the sugar-phosphate backbones as the two s ...
... "twisted ladder" structure. The sugar-phosphate backbone is on the outside of the double helix, and the bases are on the inside, so that a base on one strand points directly toward a base on the second strand. When using the twisted ladder analogy, think of the sugar-phosphate backbones as the two s ...
TISSUES AND OTHER LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
... (iii) are not supplied with blood vessels. Function : Epithelian tissues line the surfaces, help in absorption, secretion, and also bear protoplasmic projections such as the cilia. (See Table 5.4 and Fig. 5.7) Table 5.4 : Types of epithelial tissue ...
... (iii) are not supplied with blood vessels. Function : Epithelian tissues line the surfaces, help in absorption, secretion, and also bear protoplasmic projections such as the cilia. (See Table 5.4 and Fig. 5.7) Table 5.4 : Types of epithelial tissue ...
No Slide Title
... synthesis of hormone begins 5 weeks into pregnancy, by full term it is 20x normal level steroid hormones from placenta oppose it until birth ...
... synthesis of hormone begins 5 weeks into pregnancy, by full term it is 20x normal level steroid hormones from placenta oppose it until birth ...
Catalyst: Describe the shape of one of the following cells: nerve
... 15.) Which of these is the smallest unit of living things that carries out basic processes of life? A. B. C. D. ...
... 15.) Which of these is the smallest unit of living things that carries out basic processes of life? A. B. C. D. ...
Chapter 20 Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function
... cells scattered through an extracellular matrix – The matrix consists of a web of protein fibers embedded in a uniform foundation ...
... cells scattered through an extracellular matrix – The matrix consists of a web of protein fibers embedded in a uniform foundation ...
Resource Pack 3.L.1 Human body - NC Science Wiki
... common to all cells, most cells in multicelled organisms perform some special functions that others do not. For example, gland cells secrete hormones, muscle cells contract, and nerve cells conduct electrical signals. BASIC FUNCTIONS in Humans The human body is a complex system of cells, most of whi ...
... common to all cells, most cells in multicelled organisms perform some special functions that others do not. For example, gland cells secrete hormones, muscle cells contract, and nerve cells conduct electrical signals. BASIC FUNCTIONS in Humans The human body is a complex system of cells, most of whi ...
Sponges and Cnidarians
... an amoeba-like cell of sponges whose functions include distribution of nutrients to other cells in the sponge ...
... an amoeba-like cell of sponges whose functions include distribution of nutrients to other cells in the sponge ...
Human Body Systems
... Levels of Organization of the Body • Specialized Cells have a particular function. • Tissues are a group of specialized cells that perform a single function. • Organs are a group of tissues that work together to perform a complex function. • Organ Systems are a group of organs that work together t ...
... Levels of Organization of the Body • Specialized Cells have a particular function. • Tissues are a group of specialized cells that perform a single function. • Organs are a group of tissues that work together to perform a complex function. • Organ Systems are a group of organs that work together t ...
Human Body Systems PPT
... and over 40 to frown. The longest muscle in the body is the sartorius, from the outside of the hip, down and across to the inside of the knee. It rotates the thigh outwards and bends the knee. The smallest muscle in the body is the stapedius, deep in the ear. It is only 5mm long and thinner than ...
... and over 40 to frown. The longest muscle in the body is the sartorius, from the outside of the hip, down and across to the inside of the knee. It rotates the thigh outwards and bends the knee. The smallest muscle in the body is the stapedius, deep in the ear. It is only 5mm long and thinner than ...
Chapter 5 notes a1 ct review
... weakened. Structures affected most seriously are the covering layer of bones (periosteum), the ligament that suspends the lens of the eye, and the walls of the large arteries. People with Marfan syndrome tend to be tall and have disproportionately long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. A common symptom ...
... weakened. Structures affected most seriously are the covering layer of bones (periosteum), the ligament that suspends the lens of the eye, and the walls of the large arteries. People with Marfan syndrome tend to be tall and have disproportionately long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. A common symptom ...
animal organization - Sakshieducation.com
... The type of coelom present in hemichordates is same as that of echinoderms. ...
... The type of coelom present in hemichordates is same as that of echinoderms. ...
www.ourpgs.com
... 21 Which of these four mechanisms that lower the body temperature is the slowest to occur? A ...
... 21 Which of these four mechanisms that lower the body temperature is the slowest to occur? A ...
Exercise 6 Classification of Tissues
... Description: Thick membrane composed of several cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal or columnar and metabolically active; surface cells are flattened (squamous); in the keratinized type, the surface cells are full of keratin and dead; basal cells are active in mitosis and produce the cells of the ...
... Description: Thick membrane composed of several cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal or columnar and metabolically active; surface cells are flattened (squamous); in the keratinized type, the surface cells are full of keratin and dead; basal cells are active in mitosis and produce the cells of the ...
Chapter 12 The Invertibrates
... organization Cnidarians have true tissues (with a middle layer of jelly-like matter called mesoglea) and are radially symmetric. Most of their 10,000 species live in the oceans (marine) while only about 50 species are freshwater dwellers. They have a primitive nerve net but no true ...
... organization Cnidarians have true tissues (with a middle layer of jelly-like matter called mesoglea) and are radially symmetric. Most of their 10,000 species live in the oceans (marine) while only about 50 species are freshwater dwellers. They have a primitive nerve net but no true ...
with High Frequency Energy
... Increasing the frequency will also decrease the opposition offer by a capacitor This occurs because the number of electrons which the capacitor is capable of handling at a given voltage will change plates more often. As result, more electrons will pass a given point in a given time ...
... Increasing the frequency will also decrease the opposition offer by a capacitor This occurs because the number of electrons which the capacitor is capable of handling at a given voltage will change plates more often. As result, more electrons will pass a given point in a given time ...
Part 2-PP File - shscience.net
... FYI – External Fertilization • Gametes join outside of the female’s body in an water environment so sperm can swim to eggs • Large number of gametes (eggs) released to be sure some will survive (No parental care after birth) ...
... FYI – External Fertilization • Gametes join outside of the female’s body in an water environment so sperm can swim to eggs • Large number of gametes (eggs) released to be sure some will survive (No parental care after birth) ...
6.6 Hormones & Reproduction
... • Must be maintained within a narrow range • Regulated by the hypothalamus ...
... • Must be maintained within a narrow range • Regulated by the hypothalamus ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.