Jack Bowers` Chapter 2 Biology Notes
... Diffusion, a type of passive transport, is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from higher to lower concentration regions (down the concentration gradient) Diffusion through ion channels is passive transport Facilitated diffusion, a type of diffusion, is diffusion made easier by the use ...
... Diffusion, a type of passive transport, is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from higher to lower concentration regions (down the concentration gradient) Diffusion through ion channels is passive transport Facilitated diffusion, a type of diffusion, is diffusion made easier by the use ...
Chapter 25
... Animals: multicelled heterotrophs that ingest other organisms or some portion of them Tissues are arranged into organs and organ systems Most motile at some stage of their life cycle They reproduce sexually, and in some cases asexually, or both Embryos develop through a series of stages ...
... Animals: multicelled heterotrophs that ingest other organisms or some portion of them Tissues are arranged into organs and organ systems Most motile at some stage of their life cycle They reproduce sexually, and in some cases asexually, or both Embryos develop through a series of stages ...
Human Body Systems
... and nervous systems Pituitary The main gland of the endocrine system. It is stimulated by the hypothalamus when changes in homeostasis are detected and produces chemicals and stimulates other glands. ...
... and nervous systems Pituitary The main gland of the endocrine system. It is stimulated by the hypothalamus when changes in homeostasis are detected and produces chemicals and stimulates other glands. ...
to file
... Q: Brain circle in nematodes around: A: Pharynx Nematodes don’t have circulatory system – false Free-living and parasitic nematodes – true Nematodes are dioecious – true Nematodes undergo metamorphosis – false Some nematodes turn into cysts – true ...
... Q: Brain circle in nematodes around: A: Pharynx Nematodes don’t have circulatory system – false Free-living and parasitic nematodes – true Nematodes are dioecious – true Nematodes undergo metamorphosis – false Some nematodes turn into cysts – true ...
G7SC_TEST4 rev.docx.docx
... nervous system to reduce the presence of white blood cells. C. The immune system has responded to the existence of infection caused by the bacteria, and alerted the nervous system to increase the production of white blood cells. D. The nervous system has responded to the existence of an infection ca ...
... nervous system to reduce the presence of white blood cells. C. The immune system has responded to the existence of infection caused by the bacteria, and alerted the nervous system to increase the production of white blood cells. D. The nervous system has responded to the existence of an infection ca ...
The Respiratory System - Science
... Breathing is the process in which air moves into and out of lungs. Respiration is the process in which oxygen is used to release energy from the glucose in cells. ...
... Breathing is the process in which air moves into and out of lungs. Respiration is the process in which oxygen is used to release energy from the glucose in cells. ...
NGSS Levels of Organization
... 1. Describe and sequence the 5 levels of biological organization. ! 2. What must happen in the body to maintain homeostasis? Given an example of this.! 3. Describe the outcome of the two types of feedback, and give an example for each.! ...
... 1. Describe and sequence the 5 levels of biological organization. ! 2. What must happen in the body to maintain homeostasis? Given an example of this.! 3. Describe the outcome of the two types of feedback, and give an example for each.! ...
Nervous System – General - Austin Community College
... occur esp between 20-40 yrs of age nerve fibers are severed & myelin sheaths in CNS are gradually destroyed ! short circuits; loss of impulse conduction ...
... occur esp between 20-40 yrs of age nerve fibers are severed & myelin sheaths in CNS are gradually destroyed ! short circuits; loss of impulse conduction ...
The Body Systems
... human body and other vertebrates help to maintain balance and perform a variety of functions. The Body Worlds exhibit of preserved human bodies and allows visitors to view the amazing human body in never before seen ways. This unit will introduce the major parts, functions, and interactions of each ...
... human body and other vertebrates help to maintain balance and perform a variety of functions. The Body Worlds exhibit of preserved human bodies and allows visitors to view the amazing human body in never before seen ways. This unit will introduce the major parts, functions, and interactions of each ...
Fluids and Electrolytes
... Across Cell Membrane The Na+ – K+ pump keeps Na+ concentration higher and K+ concentration lower outside the cell than inside it This is an energy consuming process Energy is derived from adenosine triphospahte (ATP) The transporter acts as an enzyme that extracts energy from ATP and converts it to ...
... Across Cell Membrane The Na+ – K+ pump keeps Na+ concentration higher and K+ concentration lower outside the cell than inside it This is an energy consuming process Energy is derived from adenosine triphospahte (ATP) The transporter acts as an enzyme that extracts energy from ATP and converts it to ...
Callyspongia plicifera
... male/female and sperm/egg – Gametes come from choanocytes and amoebocytes. Zygote develops in mesohyl – Zygote becomes larvae – Cross Fertilization – Asexual reproduction via Gemmules ...
... male/female and sperm/egg – Gametes come from choanocytes and amoebocytes. Zygote develops in mesohyl – Zygote becomes larvae – Cross Fertilization – Asexual reproduction via Gemmules ...
The Insect Gas Exchange System
... • O2 to dissolve into the watery substance for diffusion into the haemolymph. • CO2 to dissolve into the water substance for diffusion out of the haemolymph into the tracheoles ...
... • O2 to dissolve into the watery substance for diffusion into the haemolymph. • CO2 to dissolve into the water substance for diffusion out of the haemolymph into the tracheoles ...
The Insect Gas Exchange System
... • O2 to dissolve into the watery substance for diffusion into the haemolymph. • CO2 to dissolve into the water substance for diffusion out of the haemolymph into the tracheoles ...
... • O2 to dissolve into the watery substance for diffusion into the haemolymph. • CO2 to dissolve into the water substance for diffusion out of the haemolymph into the tracheoles ...
The Insect Gas Exchange System
... • O2 to dissolve into the watery substance for diffusion into the haemolymph. • CO2 to dissolve into the water substance for diffusion out of the haemolymph into the tracheoles ...
... • O2 to dissolve into the watery substance for diffusion into the haemolymph. • CO2 to dissolve into the water substance for diffusion out of the haemolymph into the tracheoles ...
NOTES Organization and Body SystemsKD11
... that perform a particular function ►Example: digestive system: supply body with the nutrients needed for growth and repair ...
... that perform a particular function ►Example: digestive system: supply body with the nutrients needed for growth and repair ...
Bio2Unit1-7.14.15 - Grainger County Schools
... CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through communication and transport. 3216.1.2Conduct an experiment or simulation to demonstrate the movement of molecules through diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. CLE 3216.1.4 Describe the en ...
... CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through communication and transport. 3216.1.2Conduct an experiment or simulation to demonstrate the movement of molecules through diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. CLE 3216.1.4 Describe the en ...
Alveolar Sac and Alveoli
... absorption of surfactant and removal of particulate contaminants from the surface. – Form part of the blood-air barrier. (b) Type II pneumocytes/great alveolar cells/septal cells – Roughly cuboidal in shape, found in groups of 2 or 3 cells between type I pneumocytes. – Cover 3% of alveolar sur ...
... absorption of surfactant and removal of particulate contaminants from the surface. – Form part of the blood-air barrier. (b) Type II pneumocytes/great alveolar cells/septal cells – Roughly cuboidal in shape, found in groups of 2 or 3 cells between type I pneumocytes. – Cover 3% of alveolar sur ...
Organisms have energy roles that they serve in their environments
... A cell is the smallest unit of life that conducts all life functions. Each cell has major structures within it that perform these life functions. Structures that are common to plant and animal cells are the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria and vacuoles. Structures that are specific to plants are ...
... A cell is the smallest unit of life that conducts all life functions. Each cell has major structures within it that perform these life functions. Structures that are common to plant and animal cells are the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria and vacuoles. Structures that are specific to plants are ...
Human Body Systems
... The endocrine system works closely with the reproductive system and the digestive system. Several hormones originate in the brain, part of the nervous system. ...
... The endocrine system works closely with the reproductive system and the digestive system. Several hormones originate in the brain, part of the nervous system. ...
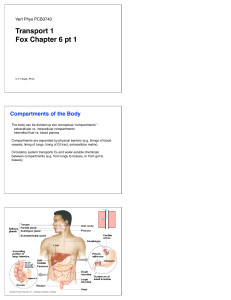
Transport 1 Fox Chapter 6 pt 1
... on the surface of muscle, liver, and fat cells; causing these cells to take up more ...
... on the surface of muscle, liver, and fat cells; causing these cells to take up more ...
The CNRS FRE 2846 (Plant Cellular and Molecular Physiology
... The main topics developed in the Unit are: - Perception and signaling of cold stress and its consequences on metabolism of membrane lipids (formation of second messengers, lipid unsaturations) and related proteins (phospholipases, synthases). - Transduction of the signal generated by abscisic acid ( ...
... The main topics developed in the Unit are: - Perception and signaling of cold stress and its consequences on metabolism of membrane lipids (formation of second messengers, lipid unsaturations) and related proteins (phospholipases, synthases). - Transduction of the signal generated by abscisic acid ( ...
SCIENCE BOOKLET GRADE 7
... One eukaryotic cell could have cytoplasm while another does not. One eukaryotic cell could have a cell membrane while another does not. Two eukaryotic cells could differ in the number and types of organelles they contain. Two eukaryotic cells could differ in the number and types of prokaryotes they ...
... One eukaryotic cell could have cytoplasm while another does not. One eukaryotic cell could have a cell membrane while another does not. Two eukaryotic cells could differ in the number and types of organelles they contain. Two eukaryotic cells could differ in the number and types of prokaryotes they ...
01 Anatomy and medicine Anatomic terminoogy
... Ipsilateral and Contralateral refer to the same or opposite sides of the body, respectively. Ipsilateral refers to the same side of the body, e.g., the right arm and right leg are ipsilateral structures. Contralateral refers to opposite sides of the body; e.g., the right arm and the left arm are co ...
... Ipsilateral and Contralateral refer to the same or opposite sides of the body, respectively. Ipsilateral refers to the same side of the body, e.g., the right arm and right leg are ipsilateral structures. Contralateral refers to opposite sides of the body; e.g., the right arm and the left arm are co ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... from smaller ones. The body stores water, food and oxygen for a time when the substances will be needed. • Catabolism - is the phase of metabolism that involves the breaking down of the stored larger substances into smaller one thus releasing the cells stored energy. Note: Anabolism and catabolism a ...
... from smaller ones. The body stores water, food and oxygen for a time when the substances will be needed. • Catabolism - is the phase of metabolism that involves the breaking down of the stored larger substances into smaller one thus releasing the cells stored energy. Note: Anabolism and catabolism a ...
Unit 7 Day 7 Anatomy
... Unit 7 Day 7 Anatomy Life is the first gift, Love is the second, Understanding the third. Marge Pierce ...
... Unit 7 Day 7 Anatomy Life is the first gift, Love is the second, Understanding the third. Marge Pierce ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.