Respiration
... • Biochemical definition aka cellular respiration: The release of energy from glucose or other organic substances inside living cells. ...
... • Biochemical definition aka cellular respiration: The release of energy from glucose or other organic substances inside living cells. ...
final exam review f12 answers
... A protein that speeds up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy 32. The cell membrane is sometimes described as a fluid mosaic because of the large molecules that move around on its surfaces. These molecules can be used as pumps, channels, or attachment points. What type of molecules are t ...
... A protein that speeds up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy 32. The cell membrane is sometimes described as a fluid mosaic because of the large molecules that move around on its surfaces. These molecules can be used as pumps, channels, or attachment points. What type of molecules are t ...
1 - Cloudfront.net
... hydrolases). They break up food so it is easier to digest. They are found in animal cells, while in yeast and plants the same roles are performed by lytic vacuoles. • The size of lysosomes varies from 0.1–1.2 μm.[2] At pH 4.8, the interior of the lysosomes is acidic compared to the slightly alkaline ...
... hydrolases). They break up food so it is easier to digest. They are found in animal cells, while in yeast and plants the same roles are performed by lytic vacuoles. • The size of lysosomes varies from 0.1–1.2 μm.[2] At pH 4.8, the interior of the lysosomes is acidic compared to the slightly alkaline ...
What you absolutely must know to pass the regent`s test
... as it provides for more genetic variation among species. A great diversity of species increases the chance that at least some living things will survive when the environment changes. ...
... as it provides for more genetic variation among species. A great diversity of species increases the chance that at least some living things will survive when the environment changes. ...
study guide - cvadultcma
... STUDY GUIDE Chapter 18: Hematology Mrs. Dasalla 1. Which of the following tests is not included in a CBC? a Differential white blood cell count b Hemoglobin c Hematocrit d Prothrombin time e Red and white blood cell counts 2. The plasma functions in a Transporting electrolytes needed by the cells b ...
... STUDY GUIDE Chapter 18: Hematology Mrs. Dasalla 1. Which of the following tests is not included in a CBC? a Differential white blood cell count b Hemoglobin c Hematocrit d Prothrombin time e Red and white blood cell counts 2. The plasma functions in a Transporting electrolytes needed by the cells b ...
Chapter 1 Biology Exam Study Guide
... All organisms are made of cells. All existing cells are produced by other living cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
... All organisms are made of cells. All existing cells are produced by other living cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
Chapter 1 Biology Exam Study Guide
... All organisms are made of cells. All existing cells are produced by other living cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
... All organisms are made of cells. All existing cells are produced by other living cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
curriculum vitae
... UCEEB, ČVUT Prague: Functionalized nanofibers for medical purposes made by forcespinning and electrospinning. Tissue engineering, IEM ASCR: Plasma modification of functionalized PVA nanofibers for the enhancement of mesenchymal stem cell adhesion, viability and proliferation, supervisor Prof. RNDr. ...
... UCEEB, ČVUT Prague: Functionalized nanofibers for medical purposes made by forcespinning and electrospinning. Tissue engineering, IEM ASCR: Plasma modification of functionalized PVA nanofibers for the enhancement of mesenchymal stem cell adhesion, viability and proliferation, supervisor Prof. RNDr. ...
review for the biology regents exam
... TISSUES – groups of cells that are specialized to do certain jobs (including muscle and nerve tissue) • Specialization or differentiation is the process that changes a stem cell into a specialized cell • Stem cells are cells that have not yet been specialized • Almost all cells have a complete set o ...
... TISSUES – groups of cells that are specialized to do certain jobs (including muscle and nerve tissue) • Specialization or differentiation is the process that changes a stem cell into a specialized cell • Stem cells are cells that have not yet been specialized • Almost all cells have a complete set o ...
Chapt04 Lecture 13ed Pt 3
... It _____ body cavities, _______ body surfaces, and is found in glands. Cells are anchored by a ____________________ on one side and free on the other side. It is named after the appearance of cell layers and the shape of the cells. There is transitional epithelium that changes in appearance in respo ...
... It _____ body cavities, _______ body surfaces, and is found in glands. Cells are anchored by a ____________________ on one side and free on the other side. It is named after the appearance of cell layers and the shape of the cells. There is transitional epithelium that changes in appearance in respo ...
Anatomy and Physiology Defined
... They are indicated in your text by a RULER BALANCED ON A PYRAMID Find 2 in your book now, give page number and explanation ...
... They are indicated in your text by a RULER BALANCED ON A PYRAMID Find 2 in your book now, give page number and explanation ...
A Journey Through the Cell: Part Two— Cells Functions: A Closer
... protein molecules. The code used is virtually the same for all life forms. Before a cell divides, the instructions are duplicated so that each of the two new cells gets all the necessary information for carrying on. ● Understands that complex interactions among the different kinds of molecules in th ...
... protein molecules. The code used is virtually the same for all life forms. Before a cell divides, the instructions are duplicated so that each of the two new cells gets all the necessary information for carrying on. ● Understands that complex interactions among the different kinds of molecules in th ...
lecture_ch03_for website_updated 11_12_14
... transport of particles. Many molecules are just too big to get into a cell by passive or active transport. ...
... transport of particles. Many molecules are just too big to get into a cell by passive or active transport. ...
Benchmark SC.F.1.2.4: The student knows that similar cells
... • All living organisms are made up of cells • “building blocks of life” • Mold on bread, your dog, pine trees, etc. are all made up of cells • Cells are so small, they need to be magnified to be seen • Microscopes are used to magnify cells ...
... • All living organisms are made up of cells • “building blocks of life” • Mold on bread, your dog, pine trees, etc. are all made up of cells • Cells are so small, they need to be magnified to be seen • Microscopes are used to magnify cells ...
Vertebrate Tissues
... ● Nonkeratinized – layers of living cells found in areas where friction occurs such as in the mouth and throat where food is chewed and swallowed. ...
... ● Nonkeratinized – layers of living cells found in areas where friction occurs such as in the mouth and throat where food is chewed and swallowed. ...
Work Booklet Workstations Answers
... 3. List the features that all animals have in common. Multicellular, eukaryotic cells Only a cell membrane, not a cell wall All heterotrophic (cannot make own food, unlike plants) 4. Explain the difference between a sessile organism and a motile organism. How would being a hermaphrodite be an ...
... 3. List the features that all animals have in common. Multicellular, eukaryotic cells Only a cell membrane, not a cell wall All heterotrophic (cannot make own food, unlike plants) 4. Explain the difference between a sessile organism and a motile organism. How would being a hermaphrodite be an ...
Chapter 19 – Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life
... that do not communicate with each other. Aggregation There are also groups which communicate with each other. These are also unicellular. They live a normal life and when in need of food, they join together. Aggregation is a temporary collection of cells that come together for a period of time and t ...
... that do not communicate with each other. Aggregation There are also groups which communicate with each other. These are also unicellular. They live a normal life and when in need of food, they join together. Aggregation is a temporary collection of cells that come together for a period of time and t ...
Levels of Organization Notes
... 6 The food that you eat travels from your mouth, down your esophagus, into your stomach, and through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the followin ...
... 6 The food that you eat travels from your mouth, down your esophagus, into your stomach, and through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the followin ...
cells - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... The organelle that regulates calcium in muscle cells, makes lipids for membranes, and breaks down toxins in liver cells is the ____________________ ...
... The organelle that regulates calcium in muscle cells, makes lipids for membranes, and breaks down toxins in liver cells is the ____________________ ...
Membrane Potential
... The stimulation of photosensitive rod cells is made possible by a light-absorbing pigment: rhodopsin (ALWAYS present in rod cells). In the dark, rhodopsin is inactive, Na+ channels are open, and a neurotransmitter is released inhibiting the postsynaptic neuron. With light, rhodopsin is activated, ...
... The stimulation of photosensitive rod cells is made possible by a light-absorbing pigment: rhodopsin (ALWAYS present in rod cells). In the dark, rhodopsin is inactive, Na+ channels are open, and a neurotransmitter is released inhibiting the postsynaptic neuron. With light, rhodopsin is activated, ...
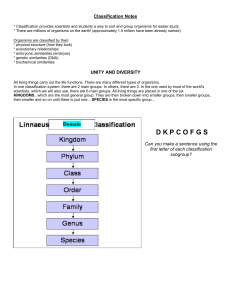
2013 Taxonomy Notes ppt
... In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed in one of the six KINGDOMS...which are the most general group. They are then broken down int ...
... In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed in one of the six KINGDOMS...which are the most general group. They are then broken down int ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.