Animal Notes
... 7. Nutrition – takes in soil through mouth, crop holds soil, and gizzard grinds organic matter from soil and is absorbed through intestine. Undigested through anus 8. Reproduction – most are hermaphrodites, have both male and female sex organs; exchange sperm and fertilizes within capsules; 9. Growt ...
... 7. Nutrition – takes in soil through mouth, crop holds soil, and gizzard grinds organic matter from soil and is absorbed through intestine. Undigested through anus 8. Reproduction – most are hermaphrodites, have both male and female sex organs; exchange sperm and fertilizes within capsules; 9. Growt ...
WHAT IS AN ANIMAL?
... The relationship between form and function has repeated itself throughout the year... At many levels of biological hierarchy...from molecules, to cellular structures, to tissues, to organs and systems, to body shapes... the forms taken by structures have been shaped by natural selection for their fu ...
... The relationship between form and function has repeated itself throughout the year... At many levels of biological hierarchy...from molecules, to cellular structures, to tissues, to organs and systems, to body shapes... the forms taken by structures have been shaped by natural selection for their fu ...
Cell Physiology
... well as intracellular membranous barriers that separate the different cell compartments. • Some cells contain large quantities of triglycerides (or neutral fat). These fat cells store fat as the body’s main storehouse of energy-giving nutrient. ...
... well as intracellular membranous barriers that separate the different cell compartments. • Some cells contain large quantities of triglycerides (or neutral fat). These fat cells store fat as the body’s main storehouse of energy-giving nutrient. ...
Chemistry of Life notes
... Do lipids have a true monomer? NO why? Because triglycerides no more than 3 fatty acids can be added to a glycerol. And fatty acids don’t join to each other, they join to a glycerol ...
... Do lipids have a true monomer? NO why? Because triglycerides no more than 3 fatty acids can be added to a glycerol. And fatty acids don’t join to each other, they join to a glycerol ...
1 | Page Glossary: Atom: Molecule: Compound: Atomic number
... the blood, thereby causing a fall in blood pressure, tingling of the extremities, and sometimes fainting. The sum of chemical and physical process, consisting of anabolism and catabolism, by which cells p ...
... the blood, thereby causing a fall in blood pressure, tingling of the extremities, and sometimes fainting. The sum of chemical and physical process, consisting of anabolism and catabolism, by which cells p ...
Page 1 Edexcel 2011 Biology B2 Topic 1 The building blocks of
... muscle cells may not receive sufficient oxygen for their energy requirements and so start to respire anaerobically Demonstrate an understanding of how anaerobic respiration releases energy from glucose and how this process can be modelled using the word equation for anaerobic respiration Recall that ...
... muscle cells may not receive sufficient oxygen for their energy requirements and so start to respire anaerobically Demonstrate an understanding of how anaerobic respiration releases energy from glucose and how this process can be modelled using the word equation for anaerobic respiration Recall that ...
Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Essential Concepts
... carbon. Such compounds are referred to as organic compounds because these compounds make up the "backbone" of living systems. Carbon is unique among elements in that it can bond to other carbon atoms to form long chains and rings. Millions of organic compounds exist. Among them are hydrocarbons (whi ...
... carbon. Such compounds are referred to as organic compounds because these compounds make up the "backbone" of living systems. Carbon is unique among elements in that it can bond to other carbon atoms to form long chains and rings. Millions of organic compounds exist. Among them are hydrocarbons (whi ...
“The Classification of Living Things” Video
... Some cause illness strep throat Many are helpful make cheese, yogurt, etc. o Most monerans trap the sun’s energy to make food. o Other bacteria, called Archaebacteria, use a chemical reaction to make food because they live where there is no sunlight (deep ocean floor). Kingdom Protista o M ...
... Some cause illness strep throat Many are helpful make cheese, yogurt, etc. o Most monerans trap the sun’s energy to make food. o Other bacteria, called Archaebacteria, use a chemical reaction to make food because they live where there is no sunlight (deep ocean floor). Kingdom Protista o M ...
2015 TX STAAR Biology Released Book - ESC-20
... to find genetic variations associated with common diseases such as cancer, asthma, and diabetes. These studies are possible because of computer databases that allow researchers to compare the genomes of people who do not have a particular condition with the genomes of people who have the condition. ...
... to find genetic variations associated with common diseases such as cancer, asthma, and diabetes. These studies are possible because of computer databases that allow researchers to compare the genomes of people who do not have a particular condition with the genomes of people who have the condition. ...
CHAPTER 11: Gene Expression
... Turing Operons on & off depends on presence of lactose. • Inducer- molecule that (if lactose is present) – turns on the gene with its 3 structural proteins – to start translating which makes 3 enzymes needed to break up lactose ...
... Turing Operons on & off depends on presence of lactose. • Inducer- molecule that (if lactose is present) – turns on the gene with its 3 structural proteins – to start translating which makes 3 enzymes needed to break up lactose ...
Organization of life - PBS Science Grade 7
... The digestive system which enables to breakdown food into very small particles is made up of many different organs such as: ...
... The digestive system which enables to breakdown food into very small particles is made up of many different organs such as: ...
Middle School Science glossary
... occupying a particular area compaction- sediments pressed together by gravity and their own weight compound- a substance made of a combination of two or more elements held together by chemical bonds that cannot be separated by physical means conclusion- a summation of what is learned from an experim ...
... occupying a particular area compaction- sediments pressed together by gravity and their own weight compound- a substance made of a combination of two or more elements held together by chemical bonds that cannot be separated by physical means conclusion- a summation of what is learned from an experim ...
Honors Biology Chapter 8 Mitosis Notes 3-13
... Bacteria reproduce asexually. The chromosome is duplicated (copied) Cell grows in size Copies are separated from each other and moved to opposite sides of cell. Plasma membrane and cell wall pinches inward to form two separate cells. ...
... Bacteria reproduce asexually. The chromosome is duplicated (copied) Cell grows in size Copies are separated from each other and moved to opposite sides of cell. Plasma membrane and cell wall pinches inward to form two separate cells. ...
Plant and Animal Adaptations
... surroundings. • A structure is a body part that does a certain “job”. ...
... surroundings. • A structure is a body part that does a certain “job”. ...
Biology Unit-1 AQA Core revision-Summary
... What are the advantages of asexual reproduction? 1. Large number of identical offspring 2. Guaranteed desired features 3. Quick 4. Economic ...
... What are the advantages of asexual reproduction? 1. Large number of identical offspring 2. Guaranteed desired features 3. Quick 4. Economic ...
Marine Taxonomy / Zoology Lecture
... About 1.4 million species of plants and animals have been identified. Some scientists estimate that there may be as many as 100 million species! How do we keep track of them all? More than 2,000 years ago Aristotle, a Greek philosopher, devised the first classification system with two kingdoms and s ...
... About 1.4 million species of plants and animals have been identified. Some scientists estimate that there may be as many as 100 million species! How do we keep track of them all? More than 2,000 years ago Aristotle, a Greek philosopher, devised the first classification system with two kingdoms and s ...
document
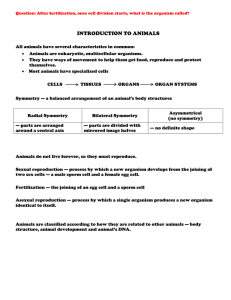
... two sex cells — a male sperm cell and a female egg cell. Fertilization — the joining of an egg cell and a sperm cell Asexual reproduction — process by which a single organism produces a new organism identical to itself. ...
... two sex cells — a male sperm cell and a female egg cell. Fertilization — the joining of an egg cell and a sperm cell Asexual reproduction — process by which a single organism produces a new organism identical to itself. ...
Review PPT – Life Science – Cells and Human
... Every living things is made up of one or more cells • Prokaryotes are unicellular. This means that all functions of life happen within that one cell • Eukaryotes are unicellular (protists) and multicellular. If the organism is multicellular, different cells have different jobs and they all work tog ...
... Every living things is made up of one or more cells • Prokaryotes are unicellular. This means that all functions of life happen within that one cell • Eukaryotes are unicellular (protists) and multicellular. If the organism is multicellular, different cells have different jobs and they all work tog ...
File - SCIENTIST CINDY
... together to form rings. Recall that C H O N = 96% of living things. But, how did these carbonbased molecules necessary for life first form? Scientists believe that the first organic molecules formed about 4 billion years ago. It is thought that lightening sparked chemical reactions in Earth’s early ...
... together to form rings. Recall that C H O N = 96% of living things. But, how did these carbonbased molecules necessary for life first form? Scientists believe that the first organic molecules formed about 4 billion years ago. It is thought that lightening sparked chemical reactions in Earth’s early ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.