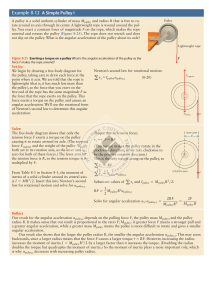
PWE 8-12: A Simple Pulley I
... Our result for the angular acceleration apulley,z depends on the pulling force F, the pulley mass Mpulley, and the pulley radius R. It makes sense that our result is proportional to the ratio F>Mpulley: A greater force F means a stronger pull and a greater angular acceleration, while a greater mass ...
... Our result for the angular acceleration apulley,z depends on the pulling force F, the pulley mass Mpulley, and the pulley radius R. It makes sense that our result is proportional to the ratio F>Mpulley: A greater force F means a stronger pull and a greater angular acceleration, while a greater mass ...
Concept Question: Rotating Rod
... b) Find the time derivative of the angular momentum about the joint (about the point P in the figure above) dL P / dt . c) What is the torque about the joint (ab out the point P in the figure above ? d) What is the value of ? ...
... b) Find the time derivative of the angular momentum about the joint (about the point P in the figure above) dL P / dt . c) What is the torque about the joint (ab out the point P in the figure above ? d) What is the value of ? ...
Deformation Rotational Motion Rotation of Rigid Objects
... rotating about a fixed axis Pr moves through arcfor length is constant in an time a rigid object. through O perpendicular to the s on a circular path of radius r. plane of the figure. The angular position of P is u. Units for θ: radians. Often written as “rad”. But notice, that a ...
... rotating about a fixed axis Pr moves through arcfor length is constant in an time a rigid object. through O perpendicular to the s on a circular path of radius r. plane of the figure. The angular position of P is u. Units for θ: radians. Often written as “rad”. But notice, that a ...
F g - mrbernabo
... An object will only change its Rotational speed if a Net Torque is applied. No net Torque = keeps rotating at the same speed ...
... An object will only change its Rotational speed if a Net Torque is applied. No net Torque = keeps rotating at the same speed ...
Circular Motion
... (a) Is the beetle's tangential velocity different or the same at different radial positions? (b)Is the beetle's angular velocity different or the same at the different radial positions? Remember; all points on a rigid rotating object will experience the same angular velocity ...
... (a) Is the beetle's tangential velocity different or the same at different radial positions? (b)Is the beetle's angular velocity different or the same at the different radial positions? Remember; all points on a rigid rotating object will experience the same angular velocity ...
Unit 2
... • Also known as the Law of Inertia • Inertia is the resistance to change in motion. • It is hard for en elephant to stop quickly because it has a lot of inertia carrying it forward. ...
... • Also known as the Law of Inertia • Inertia is the resistance to change in motion. • It is hard for en elephant to stop quickly because it has a lot of inertia carrying it forward. ...
Tuesday, June 27, 2006
... The above condition is sufficient for a point-like particle to be at its translational equilibrium. However for object with size this is not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal magnitude but in opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown in ...
... The above condition is sufficient for a point-like particle to be at its translational equilibrium. However for object with size this is not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal magnitude but in opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown in ...