Answer the following questions
... 4- Conjuction and transformation. 5- Septic and aseptic meningitis. Give reasons (s) for each of the following: 1- False negative results may be obtained in Brucella agglutination test. 2- Bacillus anthracis can be chosen as a weapon of bioterrorism. 3- Loss of certain antigen may be associated with ...
... 4- Conjuction and transformation. 5- Septic and aseptic meningitis. Give reasons (s) for each of the following: 1- False negative results may be obtained in Brucella agglutination test. 2- Bacillus anthracis can be chosen as a weapon of bioterrorism. 3- Loss of certain antigen may be associated with ...
... of tachykinins from sensory nerve endings. Epinastine (WAL 801CL) is an antihistaminic drug with binding affinity at certain other receptors, including α-adrenergic receptors and various serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes. It is used in asthma treatment; however, its mechanism of action remains to b ...
13. Major R&D Pipeline In-House R&D Pipeline List New Approval
... Description: Anti-obesity agent with novel mechanism of action. By selectively activating serotonin 2C receptors in the brain, it is believed to decrease food consumption and promote satiety. Approved in the United States by the U.S Food and Drug Administration in June 2012 as an adjunct to a reduce ...
... Description: Anti-obesity agent with novel mechanism of action. By selectively activating serotonin 2C receptors in the brain, it is believed to decrease food consumption and promote satiety. Approved in the United States by the U.S Food and Drug Administration in June 2012 as an adjunct to a reduce ...
Marie-Chantal Bonhomme1, Nadia Cardillo Marricco1
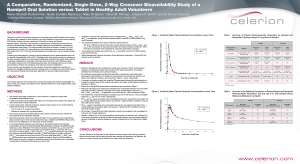
... • The washout period was 35 days between doses which covered more than 5 times the mean half-life of the metabolite ramiprilat. • Serial blood samples drawn from predose through 72 hours postdose were quantified for plasma ramipril (up to 12 hours) and ramiprilat using a validated LC-MS/MS method ...
... • The washout period was 35 days between doses which covered more than 5 times the mean half-life of the metabolite ramiprilat. • Serial blood samples drawn from predose through 72 hours postdose were quantified for plasma ramipril (up to 12 hours) and ramiprilat using a validated LC-MS/MS method ...
Medical Marijuana? - Commonwealth Prevention Alliance
... were four times as likely to have used marijuana in the past year than youth with an average grade of A. National Institute on Drug Abuse: Marijuana: Facts Parents Need To Know. , March 2014. http://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/marijuana-facts-parents-need-to-know/talking-to-your-kidscommunicating ...
... were four times as likely to have used marijuana in the past year than youth with an average grade of A. National Institute on Drug Abuse: Marijuana: Facts Parents Need To Know. , March 2014. http://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/marijuana-facts-parents-need-to-know/talking-to-your-kidscommunicating ...
Pharmacokinetics of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate
... represent the chronic form of the disease. Therefore, the prognosis is guarded. The required course of antimicrobial treatment is prolonged and expensive, and the most common treatment regimen used is associated with important adverse effects.2 Erythromycin, a macrolide antibiotic, is suitable for t ...
... represent the chronic form of the disease. Therefore, the prognosis is guarded. The required course of antimicrobial treatment is prolonged and expensive, and the most common treatment regimen used is associated with important adverse effects.2 Erythromycin, a macrolide antibiotic, is suitable for t ...
Phenytoin: A Guide to Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
... Furthermore, phenytoin demonstrates non-linear pharmacokinetics even within the therapeutic range. The enzyme system involved in phenytoin metabolism gradually becomes saturated, resulting in a decrease in the rate of elimination of phenytoin as the dose is increased4. This means that once the enzym ...
... Furthermore, phenytoin demonstrates non-linear pharmacokinetics even within the therapeutic range. The enzyme system involved in phenytoin metabolism gradually becomes saturated, resulting in a decrease in the rate of elimination of phenytoin as the dose is increased4. This means that once the enzym ...
PDF - Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America
... Antibiotic resistance is a significant and progressively worsening problem at healthcare facilities around the world. This fact, combined with the lack of new antimicrobial agents in the drug development pipeline, indicates that judicious antimicrobial management is necessary to preserve the antibio ...
... Antibiotic resistance is a significant and progressively worsening problem at healthcare facilities around the world. This fact, combined with the lack of new antimicrobial agents in the drug development pipeline, indicates that judicious antimicrobial management is necessary to preserve the antibio ...
Chemistry Report
... ventral thalamic complex, pons, inferior colliculus, and globus pallidus. This selective binding of zolpidem on the BZ1 receptor is not absolute, but it may explain the relative absence of myorelaxant and anticonvulsant effects in animal studies as well as the preservation of deep sleep (stages 3 an ...
... ventral thalamic complex, pons, inferior colliculus, and globus pallidus. This selective binding of zolpidem on the BZ1 receptor is not absolute, but it may explain the relative absence of myorelaxant and anticonvulsant effects in animal studies as well as the preservation of deep sleep (stages 3 an ...
tamoxifen - Cancer Care Ontario
... disease and in women at an increased risk of endometrial cancer. Some brands of tamoxifen contain lactose; carefully consider use in patients with hereditary galactose intolerance, severe lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption. Use with caution in patients with pre-existing myelosuppr ...
... disease and in women at an increased risk of endometrial cancer. Some brands of tamoxifen contain lactose; carefully consider use in patients with hereditary galactose intolerance, severe lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption. Use with caution in patients with pre-existing myelosuppr ...
COPPER 0.4 mg/mL
... (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section.) There are limited data in infants weighing less than 1500 grams. Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with cupric chloride. It is also not known whether cupric chloride can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant ...
... (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section.) There are limited data in infants weighing less than 1500 grams. Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with cupric chloride. It is also not known whether cupric chloride can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant ...
Substance Related Disorders
... – They argue that the temporary reduction of tension produced by a drug has a rewarding effect, thus increasing the likelihood that the user will seek this reaction again – Similarly, the rewarding effects may also lead users to try higher doses or more powerful methods of ingestion Comer, Fundament ...
... – They argue that the temporary reduction of tension produced by a drug has a rewarding effect, thus increasing the likelihood that the user will seek this reaction again – Similarly, the rewarding effects may also lead users to try higher doses or more powerful methods of ingestion Comer, Fundament ...
Subuphine sublingual tablet ENG
... Buprenorphine is an partial opioid agonist/antagonist which attaches to the - and -receptors of the brain. Its activity in opioid maintenance treatment is attributed to its slowly reversible binding to the -receptors which over a longer period reduces the adapted patients need for drugs. Buprenor ...
... Buprenorphine is an partial opioid agonist/antagonist which attaches to the - and -receptors of the brain. Its activity in opioid maintenance treatment is attributed to its slowly reversible binding to the -receptors which over a longer period reduces the adapted patients need for drugs. Buprenor ...
calibration - Beckman Coulter
... The calibration factor generated is non-functional for sample result calculation. 2. The system must have a valid calibrator cutoff value in memory before controls or patient samples can be run. The cutoff value for each DAT chemistry represents the mean reaction rate of the Low Calibrator, and is r ...
... The calibration factor generated is non-functional for sample result calculation. 2. The system must have a valid calibrator cutoff value in memory before controls or patient samples can be run. The cutoff value for each DAT chemistry represents the mean reaction rate of the Low Calibrator, and is r ...
for immediate release
... Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken. • Risk of High Sodium Load: Avoid use of Vancomycin in patients with congestive heart failure, elderly patients and patients requiring restricted sodium intake. • Reversibl ...
... Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken. • Risk of High Sodium Load: Avoid use of Vancomycin in patients with congestive heart failure, elderly patients and patients requiring restricted sodium intake. • Reversibl ...
BY SULTAN SULEMAN (B. Pharm)
... Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that affects people in every country throughout the world. Epilepsy is also one of the oldest conditions known to mankind. It is characterized by a tendency to recurrent seizures and it is defined by two or more unprovoked seizures. The belief widely held in many ...
... Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that affects people in every country throughout the world. Epilepsy is also one of the oldest conditions known to mankind. It is characterized by a tendency to recurrent seizures and it is defined by two or more unprovoked seizures. The belief widely held in many ...
Heat Loss, Sleepiness, and Impaired Performance after
... assessed by means of an actigraph (AMI Inc., Ardsley, NY) fitted to the nondominant wrist of each subject; the data were analyzed for computer-calculated sleep–wake determinations by Cole’s algorithm (Cole et al, 1992). For each subject, the sleep onset times calculated by actigraph during the prest ...
... assessed by means of an actigraph (AMI Inc., Ardsley, NY) fitted to the nondominant wrist of each subject; the data were analyzed for computer-calculated sleep–wake determinations by Cole’s algorithm (Cole et al, 1992). For each subject, the sleep onset times calculated by actigraph during the prest ...
Helicobacter pylori PYLERA® Capsules were designed to ease the burden of
... References: 1. Fennerty MB. Patient screening and selection for therapy. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;5(4)(suppl 13):4-6. http://www.clinicaladvances.com/article_pdfs/gh-article-200904-sup13.pdf#page=4. Accessed October 28, 2011. 2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Helicobacter pylori and ...
... References: 1. Fennerty MB. Patient screening and selection for therapy. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;5(4)(suppl 13):4-6. http://www.clinicaladvances.com/article_pdfs/gh-article-200904-sup13.pdf#page=4. Accessed October 28, 2011. 2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Helicobacter pylori and ...
SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF OXCARBAZEPINE IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATIONS Research Article M. A. SATHISH AND G. NAGENDRAPPA*
... The developed method is found to be rapid, simple, economical and more sensitive with low values of relative standard deviation. The method is using inexpensive instruments compared to the reported methods14‐40, further it does not require any expensive reagents and hazardous chemicals ...
... The developed method is found to be rapid, simple, economical and more sensitive with low values of relative standard deviation. The method is using inexpensive instruments compared to the reported methods14‐40, further it does not require any expensive reagents and hazardous chemicals ...
Continual Reassessment Method for Partial Ordering
... Generally, without further randomization, a difficulty can occur in which the ordering corresponding to the greatest posterior probability is chosen over orderings that may never have been tried. Information on these can only ever be obtained through experimentation. Early in the trial, within the pos ...
... Generally, without further randomization, a difficulty can occur in which the ordering corresponding to the greatest posterior probability is chosen over orderings that may never have been tried. Information on these can only ever be obtained through experimentation. Early in the trial, within the pos ...
UV SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION FOR THE
... Methods: The optimized method uses a diluent 100% potassium dihydrogen ortho phosphate buffer (pH 4.0) for the estimation of assay of Indinavir sulphate whose λmax is 259 nm. Results: The developed method resulted in Indinavir sulphate exhibiting linearity in the range 20-80 μg/ml. The precision is ...
... Methods: The optimized method uses a diluent 100% potassium dihydrogen ortho phosphate buffer (pH 4.0) for the estimation of assay of Indinavir sulphate whose λmax is 259 nm. Results: The developed method resulted in Indinavir sulphate exhibiting linearity in the range 20-80 μg/ml. The precision is ...
Cardiovascular Drug Therapy in the Elderly
... length of time in hours that it takes for the serum concentration of that drug to decrease to half of its peak level. This can be described by the kinetic equation t1/2 ⫽ 0.693 ⫻ Vd/Cl, where t1/2 is directly related to drug distribution and inversely to clearance. Therefore, as previously mentioned ...
... length of time in hours that it takes for the serum concentration of that drug to decrease to half of its peak level. This can be described by the kinetic equation t1/2 ⫽ 0.693 ⫻ Vd/Cl, where t1/2 is directly related to drug distribution and inversely to clearance. Therefore, as previously mentioned ...
under Modified BVoc Regulations 2014
... 5. Jain NK & Gupta GD. Modern Dispensing Pharmacy, II edition, 2009, Pharma Book Syndicate, Hyderabad ...
... 5. Jain NK & Gupta GD. Modern Dispensing Pharmacy, II edition, 2009, Pharma Book Syndicate, Hyderabad ...
Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults
... These slides were developed using the December 2009 guidelines. The intended audience is clinicians involved in the care of patients with HIV. Because the field of HIV care is rapidly changing, users are cautioned that the information in this presentation may become out of date quickly. It is intend ...
... These slides were developed using the December 2009 guidelines. The intended audience is clinicians involved in the care of patients with HIV. Because the field of HIV care is rapidly changing, users are cautioned that the information in this presentation may become out of date quickly. It is intend ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.