Unit 7 Forces and Motion Study Guide Answer Section
... 33. Freely falling objects accelerate at 9.8 m/s2 because the force of ____________________ acts on them. 34. The velocity of an object moving in a straight line changes at a constant rate when the object is experiencing constant ____________________. 35. The acceleration of a moving object is calcu ...
... 33. Freely falling objects accelerate at 9.8 m/s2 because the force of ____________________ acts on them. 34. The velocity of an object moving in a straight line changes at a constant rate when the object is experiencing constant ____________________. 35. The acceleration of a moving object is calcu ...
Chapter 10
... There is an analogy between the kinetic energies associated with linear motion (K = 1/2 mv 2) and the kinetic energy associated with rotational motion (KR= 1/2 I2) Rotational kinetic energy is not a new type of energy, the form is different because it is applied to a rotating object The units of ro ...
... There is an analogy between the kinetic energies associated with linear motion (K = 1/2 mv 2) and the kinetic energy associated with rotational motion (KR= 1/2 I2) Rotational kinetic energy is not a new type of energy, the form is different because it is applied to a rotating object The units of ro ...
Chapter 4 FORCES AND NEWTON'S LAWS
... Consider the case of your physics book resting on your study desk. The physics book acts on the table with a downward force and the study desk acts on the book with a force in the upward direction. We then have a pair of forces that are equal in magnitude and oppositely directed. One is the book act ...
... Consider the case of your physics book resting on your study desk. The physics book acts on the table with a downward force and the study desk acts on the book with a force in the upward direction. We then have a pair of forces that are equal in magnitude and oppositely directed. One is the book act ...
The chemical enrichment of the ICM from hydrodynamical simulations
... formation, they generally identify a galaxy with a suitably chosen DM particle in the collisionless simulation which is used to reconstruct the merger tree. While this DM particle defines the position of a galaxy, the corresponding stellar content is described as a superposition of SSPs, each genera ...
... formation, they generally identify a galaxy with a suitably chosen DM particle in the collisionless simulation which is used to reconstruct the merger tree. While this DM particle defines the position of a galaxy, the corresponding stellar content is described as a superposition of SSPs, each genera ...
*************a***q+***********+
... Kepler’s first law states that the paths of the planets are ellipses, with Sun at one focus. Kepler’s second law states that an imaginary line from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. Kepler’s third law states that the square of the ratio of the periods of any two pla ...
... Kepler’s first law states that the paths of the planets are ellipses, with Sun at one focus. Kepler’s second law states that an imaginary line from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. Kepler’s third law states that the square of the ratio of the periods of any two pla ...
Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium
... Conservation of angular momentum means that the total angular momentum around any axis must be constant. This is why gyroscopes are so stable. ...
... Conservation of angular momentum means that the total angular momentum around any axis must be constant. This is why gyroscopes are so stable. ...
introduction and basic concepts
... It is not proper to say that one lbm is equal to one lbf since the two units have different dimensions. ...
... It is not proper to say that one lbm is equal to one lbf since the two units have different dimensions. ...
Coriolis Force - Andrija Radovic
... rotation while on south hemisphere it rotates in opposite direction then on the north one. However, the Coriolis force in the sink is really negligible and it certainly cannot cause so vigorous rotation of the vortex! Only hope is that additional term with acceleration can handle this rotation, but ...
... rotation while on south hemisphere it rotates in opposite direction then on the north one. However, the Coriolis force in the sink is really negligible and it certainly cannot cause so vigorous rotation of the vortex! Only hope is that additional term with acceleration can handle this rotation, but ...
FREE Sample Here
... 23. An object moves at a constant 5.0 m/s. One could correctly conclude that A. no forces are acting on the object. B. a constant force is applied to the object. C. it was on a frictionless surface. D. none of the above. ...
... 23. An object moves at a constant 5.0 m/s. One could correctly conclude that A. no forces are acting on the object. B. a constant force is applied to the object. C. it was on a frictionless surface. D. none of the above. ...
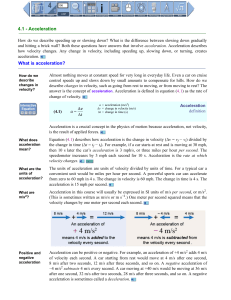
4.1 - Acceleration What is acceleration?
... Situations in which an object reverses direction always involve an acceleration that has the opposite sign from that of the velocity. For example, an acceleration of −1 m/s2 adds −1 m/s to the velocity every second, so an initial positive velocity of +3 m/s becomes +2 m/s after one second, and then ...
... Situations in which an object reverses direction always involve an acceleration that has the opposite sign from that of the velocity. For example, an acceleration of −1 m/s2 adds −1 m/s to the velocity every second, so an initial positive velocity of +3 m/s becomes +2 m/s after one second, and then ...
Rotary Homework #1
... kg, and the magnitude of the force acting on it as it settles out of the plasma is 4.0 × 10–11 N. At how many revolutions per second should the centrifuge be operated? 11. A certain light truck can go around a flat curve having a radius of 150 m with a maximum speed of 32.0 m/s. With what maximum sp ...
... kg, and the magnitude of the force acting on it as it settles out of the plasma is 4.0 × 10–11 N. At how many revolutions per second should the centrifuge be operated? 11. A certain light truck can go around a flat curve having a radius of 150 m with a maximum speed of 32.0 m/s. With what maximum sp ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... that such material be reproduced only for classroom use; be provided to students, teachers, and families without charge; and be used solely in conjunction with the Newton’s Laws of Motion program. Any other reproduction, for use or sale, is prohibited without prior written permission of the publishe ...
... that such material be reproduced only for classroom use; be provided to students, teachers, and families without charge; and be used solely in conjunction with the Newton’s Laws of Motion program. Any other reproduction, for use or sale, is prohibited without prior written permission of the publishe ...
Lecture 6
... in astrophysics as they efficiently transform gravitational potential energy into radiation. Accretion disks are seen around stars, but the most extreme disks are seen at the centre of quasars. These orbit black holes with masses of ~106-9 M¯, and radiate up to 1014 L¯, outshining all of the stars i ...
... in astrophysics as they efficiently transform gravitational potential energy into radiation. Accretion disks are seen around stars, but the most extreme disks are seen at the centre of quasars. These orbit black holes with masses of ~106-9 M¯, and radiate up to 1014 L¯, outshining all of the stars i ...
POWERPOINT JEOPARDY
... Answer 4 – 30 • What is the force that can give a 1 kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s2? ...
... Answer 4 – 30 • What is the force that can give a 1 kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s2? ...
Quiz3 Solutions
... So we can write total = vertical rod horizontal rod lamp . Each individual torque is = R F sin , where R is the distance from the part's center of gravity to the pivot point (here, the streetlight base) and F is the gravity force on that part, and θ is the angle between the two. For the ...
... So we can write total = vertical rod horizontal rod lamp . Each individual torque is = R F sin , where R is the distance from the part's center of gravity to the pivot point (here, the streetlight base) and F is the gravity force on that part, and θ is the angle between the two. For the ...
Review Exam 1-New
... A) is always greater than zero. B) is always less than zero. C) is zero. D) can be greater than or less than but not equal to zero. E) can have any value. Ans: C ...
... A) is always greater than zero. B) is always less than zero. C) is zero. D) can be greater than or less than but not equal to zero. E) can have any value. Ans: C ...
The formation of the galaxy is believed to be similar
... a) circular speed of stars around the galaxy. b) random motion of stars in the plane of the ...
... a) circular speed of stars around the galaxy. b) random motion of stars in the plane of the ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.