JKeehnLtalk
... Bern when all of a sudden a thought occurred to me: if a person falls freely he will not feel his own weight. This simple thought made a deep impression on me. It impelled me toward a theory of ...
... Bern when all of a sudden a thought occurred to me: if a person falls freely he will not feel his own weight. This simple thought made a deep impression on me. It impelled me toward a theory of ...
Powerpoint Slides - Faculty Web Sites
... 1. Newton’s 1st Law: An object at rest, remains at rest, OR if in motion, travels in a straight line at constant velocity, UNLESS acted on by a net force. ...
... 1. Newton’s 1st Law: An object at rest, remains at rest, OR if in motion, travels in a straight line at constant velocity, UNLESS acted on by a net force. ...
15.02.09PhysicsWeek23
... a. Do you think a larger mass will make the gravitational force weaker or stronger? b. Do you think a greater distance between the objects will make the gravitational force weaker or stronger? Ultimately predict which single factor has a greater impact on the gravitational force, the mass of an obje ...
... a. Do you think a larger mass will make the gravitational force weaker or stronger? b. Do you think a greater distance between the objects will make the gravitational force weaker or stronger? Ultimately predict which single factor has a greater impact on the gravitational force, the mass of an obje ...
PowerPoint: Physics Word Problem Review Part 2
... force) between two objects when the distance between them increases? decreases? Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation tells us the relationship of distance and mass on the gravitational force ...
... force) between two objects when the distance between them increases? decreases? Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation tells us the relationship of distance and mass on the gravitational force ...
HP Unit 3 - student handout
... A person stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator at rest on the ground floor of a building. The scale reads 836N. As the elevator begins to move upward, the scale reading briefly increases to 935N but then returns to 836N after reaching a ...
... A person stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator at rest on the ground floor of a building. The scale reads 836N. As the elevator begins to move upward, the scale reading briefly increases to 935N but then returns to 836N after reaching a ...
From last time… - University of Wisconsin–Madison
... When the vectron hovers near the ceiling, the propeller force compared to hovering near the floor is A. Greater. B. Less. C. The same. Gravity exerts a force downward. When the vectron hovers, its velocity is constant, so the acceleration is zero. This means the net force is zero. The propeller Phys ...
... When the vectron hovers near the ceiling, the propeller force compared to hovering near the floor is A. Greater. B. Less. C. The same. Gravity exerts a force downward. When the vectron hovers, its velocity is constant, so the acceleration is zero. This means the net force is zero. The propeller Phys ...
Weight as a force - Science
... starts or stops? Your acceleration (from the lift) is added vectorially to the acceleration due to gravity. • When you accelerate up, gravity must be overcome so your apparent weight is • Fw = m (g + a) you feel heavier • When you accelerate down, it is helping gravity, so your apparent weight is Fw ...
... starts or stops? Your acceleration (from the lift) is added vectorially to the acceleration due to gravity. • When you accelerate up, gravity must be overcome so your apparent weight is • Fw = m (g + a) you feel heavier • When you accelerate down, it is helping gravity, so your apparent weight is Fw ...
class-ix-science-sa-i-2015-16
... (b) A solution contains 40g of common salt in 460g of water. Calculate the concentration of the solution in mass %. 23. (a)Write Newton’s second law of motion . (b) Derive the mathematical relation of Newton’s second law of motion. 24. Ram and Shyam are students of the same school that is 18 km away ...
... (b) A solution contains 40g of common salt in 460g of water. Calculate the concentration of the solution in mass %. 23. (a)Write Newton’s second law of motion . (b) Derive the mathematical relation of Newton’s second law of motion. 24. Ram and Shyam are students of the same school that is 18 km away ...
Gravitational Mass Defect - Science and Education Publishing
... With the supernova explosions stars their luster increases by tens of stellar magnitude in the course several days. In the maximum of luster the supernova is compared in the brightness with the entire galaxy, in which it exploded even to exceed it. So the luminosity supernova SN1972E almost 13 times ...
... With the supernova explosions stars their luster increases by tens of stellar magnitude in the course several days. In the maximum of luster the supernova is compared in the brightness with the entire galaxy, in which it exploded even to exceed it. So the luminosity supernova SN1972E almost 13 times ...
AP Physics C Laws of Motion MC Sample Test
... The space shuttle increases its acceleration every second during take off, even though its engines generate the same amount of force. Which off these contributes the most significantly to this effect? (A) Gravity g is decreasing. (B) It is losing mass as it burns fuel. (C) The air gets thinner at hi ...
... The space shuttle increases its acceleration every second during take off, even though its engines generate the same amount of force. Which off these contributes the most significantly to this effect? (A) Gravity g is decreasing. (B) It is losing mass as it burns fuel. (C) The air gets thinner at hi ...
AST301.Ch22.NeutGammBH - University of Texas Astronomy
... an invisible companion of mass greater than about 3Mo. Best candidate: Cygnus X-1. Three main lines of evidence; 1. Visible companion has mass around 25Mo. Using the known period and the primary star’s orbital speed from the radial velocity, get sum of masses, and hence mass of invisible companion: ...
... an invisible companion of mass greater than about 3Mo. Best candidate: Cygnus X-1. Three main lines of evidence; 1. Visible companion has mass around 25Mo. Using the known period and the primary star’s orbital speed from the radial velocity, get sum of masses, and hence mass of invisible companion: ...
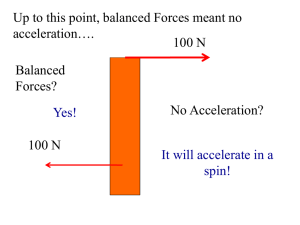
NewtonS-LawS
... • If you push the same chair with two different forces (one small & one large), describe its motion? • What can you conclude about your choice? • If you push a chair and a table with the same force, which one accelerates faster? • What can account for your choice? ...
... • If you push the same chair with two different forces (one small & one large), describe its motion? • What can you conclude about your choice? • If you push a chair and a table with the same force, which one accelerates faster? • What can account for your choice? ...
Motion in Two Dimensions
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...
Kinematics - Plain Local Schools
... • Using these equations, we can re-draw the free body diagram, replacing mg with its components. Now all the forces line up with the axes, making it straightforward to write Newton's 2nd Law Equations (FNETx and FNETy) and continue with our standard problem-solving strategy. • In the example shown w ...
... • Using these equations, we can re-draw the free body diagram, replacing mg with its components. Now all the forces line up with the axes, making it straightforward to write Newton's 2nd Law Equations (FNETx and FNETy) and continue with our standard problem-solving strategy. • In the example shown w ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.