Section 3 - WordPress.com
... • Please ensure that you have the correct examination in front of you. • Please do not open the examination booklet until directed to do so. • Students are to write in blue or black pen. • Write your name clearly in the space above when directed to do so. • Attempt all questions. For Multiple choice ...
... • Please ensure that you have the correct examination in front of you. • Please do not open the examination booklet until directed to do so. • Students are to write in blue or black pen. • Write your name clearly in the space above when directed to do so. • Attempt all questions. For Multiple choice ...
Review Questions - mom, UG, 3rd Law, centri
... 4. An 8-kg bowling ball rolling at 2 m/s bumps into a padded guardrail and stops. A) What is the momentum of the ball just before hitting the guardrail? B) How much impulse acts on the ball? C) If the time of impact is 0.5 seconds, what force did the ball exert on the guardrail? D) What force did th ...
... 4. An 8-kg bowling ball rolling at 2 m/s bumps into a padded guardrail and stops. A) What is the momentum of the ball just before hitting the guardrail? B) How much impulse acts on the ball? C) If the time of impact is 0.5 seconds, what force did the ball exert on the guardrail? D) What force did th ...
EXPERIMENT M2
... the earth: otherwise it would be no more dangerous to jump off the top of the Empire State Building than to jump off a chair! So when you drop an object its velocity increases continually (i.e. it accelerates). Sir Isaac Newton observed this, as had others before him, but his achievement was to real ...
... the earth: otherwise it would be no more dangerous to jump off the top of the Empire State Building than to jump off a chair! So when you drop an object its velocity increases continually (i.e. it accelerates). Sir Isaac Newton observed this, as had others before him, but his achievement was to real ...
Physics Final Exam Review Sheet
... Chapter 4: Forces and Laws of Motion Key formulas F = ma W = mg Fnet = Fgo - Fstop ...
... Chapter 4: Forces and Laws of Motion Key formulas F = ma W = mg Fnet = Fgo - Fstop ...
Studio Physics I
... 3. Solving for the velocity of the cart after the block hits the floor: Combine the expression for acceleration that you derived above and the expression for the velocity of the cart that you derived as part of your homework. The result should be an expression for velocity of the cart after the han ...
... 3. Solving for the velocity of the cart after the block hits the floor: Combine the expression for acceleration that you derived above and the expression for the velocity of the cart that you derived as part of your homework. The result should be an expression for velocity of the cart after the han ...
8. Newton`s Law Gravitation Rev.nb
... says the acceleration is zero a=0 so Newton's 2nd law indicates the net force in the y-direction is zero. The observer x, y knows two forces act on mass M, the upward normal force and the downward force of gravity -W. So when observer x, y applies Newton's 2nd law what follows is NW=0 and thus N=W. ...
... says the acceleration is zero a=0 so Newton's 2nd law indicates the net force in the y-direction is zero. The observer x, y knows two forces act on mass M, the upward normal force and the downward force of gravity -W. So when observer x, y applies Newton's 2nd law what follows is NW=0 and thus N=W. ...
Roller Coasters
... or 56 mph. As the cart moves through the loop, it is moving in a circle and therefore it is accelerating. An observer on the ground concludes that the forces on the cart are the force of gravity and the support from the track. The support from the track has to cancel the component of the weight perp ...
... or 56 mph. As the cart moves through the loop, it is moving in a circle and therefore it is accelerating. An observer on the ground concludes that the forces on the cart are the force of gravity and the support from the track. The support from the track has to cancel the component of the weight perp ...
StudyGuideForcesAP2016
... d. A person standing in an elevator that is moving downward and slowing down. e. A box sliding down an incline plane of θ and speeding up. 2. Write the net force equation in both the x and y directions for the FBDs in #1 3. What is the normal force and how can it change in different situations (disc ...
... d. A person standing in an elevator that is moving downward and slowing down. e. A box sliding down an incline plane of θ and speeding up. 2. Write the net force equation in both the x and y directions for the FBDs in #1 3. What is the normal force and how can it change in different situations (disc ...
f F = mg X
... forces are all manifestations of the electromagnetic force ❑ They all are the result of attractive (and repulsive) forces of atoms and molecules within an object (normal and tension) or at the interface of two objects Applications of Newton’s 2nd Law ❑ Equilibrium – an object which has zero accelera ...
... forces are all manifestations of the electromagnetic force ❑ They all are the result of attractive (and repulsive) forces of atoms and molecules within an object (normal and tension) or at the interface of two objects Applications of Newton’s 2nd Law ❑ Equilibrium – an object which has zero accelera ...
Lesson 8
... Example: A car is slowing down at a rate of 6.00 m/s2 while traveling counter clockwise on a circular track of radius 100.0 m. What is the total acceleration on the car when it has slowed to 20.0 m/s as shown below: ...
... Example: A car is slowing down at a rate of 6.00 m/s2 while traveling counter clockwise on a circular track of radius 100.0 m. What is the total acceleration on the car when it has slowed to 20.0 m/s as shown below: ...
4 Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... • We must not only consider the force (net force) applied but also the mass involved. ...
... • We must not only consider the force (net force) applied but also the mass involved. ...
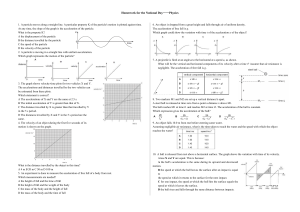
Homework for the National Day——Physics 1. A particle moves
... 18. A student investigates the speed of a trolley as it rolls down a slope, as illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The speed v of the trolley is measured using a speed sensor for different values of the time t that the trolley has moved from rest down the slope. Fig. 2.2 shows the variation with t of v. ...
... 18. A student investigates the speed of a trolley as it rolls down a slope, as illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The speed v of the trolley is measured using a speed sensor for different values of the time t that the trolley has moved from rest down the slope. Fig. 2.2 shows the variation with t of v. ...
The Galaxy Presentation 2011
... •Tried to estimate Rayleigh scattering due to ISM gas but determined it to be insignificant (because most obscuration is due to ISM dust absorption which has a smaller dependence) •Shapley (1919) noted that globular clusters are distributed asymmetrically in the sky and that if one assumes they ar ...
... •Tried to estimate Rayleigh scattering due to ISM gas but determined it to be insignificant (because most obscuration is due to ISM dust absorption which has a smaller dependence) •Shapley (1919) noted that globular clusters are distributed asymmetrically in the sky and that if one assumes they ar ...
Skill Sheet 1 Speed Problems
... 2. What does it mean when we say that weight is a force? In everyday language, we think of weight as a measure of “how heavy” something is. A 25-pound toddler, for example, is a lot heavier to carry around than an 8-pound newborn. Force, on the other hand, is defined as a push, pull, or any action ...
... 2. What does it mean when we say that weight is a force? In everyday language, we think of weight as a measure of “how heavy” something is. A 25-pound toddler, for example, is a lot heavier to carry around than an 8-pound newborn. Force, on the other hand, is defined as a push, pull, or any action ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.