Welcome to Mrs. Sharp`s Classroom
... Imagine a car pulling away from a stop sign-the car’s change in velocity (velocityf – velocityi) and its acceleration both have positive values. When an object moves in one dimension (along a straight line) in the positive direction, and its velocity increases over time (it speeds up), its acceler ...
... Imagine a car pulling away from a stop sign-the car’s change in velocity (velocityf – velocityi) and its acceleration both have positive values. When an object moves in one dimension (along a straight line) in the positive direction, and its velocity increases over time (it speeds up), its acceler ...
Slide 1
... 6.1 Force Causes Acceleration Acceleration depends on the net force. To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. An object’s acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on it: acceleration ~ net force (The symbol ~ stands for “is directl ...
... 6.1 Force Causes Acceleration Acceleration depends on the net force. To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. An object’s acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on it: acceleration ~ net force (The symbol ~ stands for “is directl ...
Student Text, pp. 88-96
... Applying Newton’s Laws of Motion When riders in a roller coaster are pulled toward the top of the first and highest hill, they are putting faith in the calculations used to determine the strength of the cable pulling on the coaster. The design engineers must analyze the relationship between the tens ...
... Applying Newton’s Laws of Motion When riders in a roller coaster are pulled toward the top of the first and highest hill, they are putting faith in the calculations used to determine the strength of the cable pulling on the coaster. The design engineers must analyze the relationship between the tens ...
matter, mass and electromagnetic mass
... physicists and mathematicians around the turn of the 20th century. The reason why we need to discuss and understand this concept a century later, is two-fold: 1) Einstein based ...
... physicists and mathematicians around the turn of the 20th century. The reason why we need to discuss and understand this concept a century later, is two-fold: 1) Einstein based ...
1. Newton`s Laws of Motion and their Applications
... you hold onto the lighter bucket to keep it from moving. What is the tension in the rope? (b) You release the lighter bucket and the heavier one descends. What is the tension in the rope now? (c) Eventually the heavier bucket lands and the two buckets come to rest. What is the tension in the rope no ...
... you hold onto the lighter bucket to keep it from moving. What is the tension in the rope? (b) You release the lighter bucket and the heavier one descends. What is the tension in the rope now? (c) Eventually the heavier bucket lands and the two buckets come to rest. What is the tension in the rope no ...
F - AdvancedPlacementPhysicsC
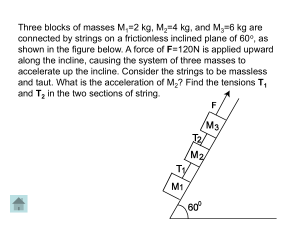
... This equation is correct according to Newton’s Second Law. The applied force on the system of blocks is in the opposite direction to the x-component of the weight of the blocks. We know from the original ...
... This equation is correct according to Newton’s Second Law. The applied force on the system of blocks is in the opposite direction to the x-component of the weight of the blocks. We know from the original ...
AP-1 Cutnell 06-10 1st Sem Rev Key Points
... the total kinetic energy of the system is not the same before and after the collision; if the objects stick together after colliding, the collision is said to be completely inelastic. Kinetic energy is not conserved. The coupling boxcars is an example of an inelastic collision. ...
... the total kinetic energy of the system is not the same before and after the collision; if the objects stick together after colliding, the collision is said to be completely inelastic. Kinetic energy is not conserved. The coupling boxcars is an example of an inelastic collision. ...
11. Rotation Translational Motion
... line that runs through the force vector. Unit: Nm--This is the same unit as energy but never quote torque in Joules! The further away from the axis of rotation a force is applied, the larger the torque. A force that tends to make an object rotate counter clockwise is defined as a positive torque, an ...
... line that runs through the force vector. Unit: Nm--This is the same unit as energy but never quote torque in Joules! The further away from the axis of rotation a force is applied, the larger the torque. A force that tends to make an object rotate counter clockwise is defined as a positive torque, an ...
From our equations of motion for constant acceleration we have
... or an air track. It travels even further. We now imagine that by using even smoother surfaces the book will travel further and further. In the limit if we have an extremely smooth (frictionless) surface the book will continue moving without slowing down. We now conclude that you do not need a force ...
... or an air track. It travels even further. We now imagine that by using even smoother surfaces the book will travel further and further. In the limit if we have an extremely smooth (frictionless) surface the book will continue moving without slowing down. We now conclude that you do not need a force ...
Forces and Motion - Catawba County Schools
... object moving at a constant speed. * Galileo – concluded that moving objects not subjected to friction or any other force would continue to move indefinitely. * Newton – Defined mass and force and laid out his laws of motion. Newton’s First Law of Motion The state of motion of an object does not cha ...
... object moving at a constant speed. * Galileo – concluded that moving objects not subjected to friction or any other force would continue to move indefinitely. * Newton – Defined mass and force and laid out his laws of motion. Newton’s First Law of Motion The state of motion of an object does not cha ...
Dynamics and Space
... 55. Using your knowledge of physics comment on the use of satellites in society. 56. An astronomer is observing one particular star in the night sky, and states that the star is moving away from the Earth. Last updated by AD May 2014 ...
... 55. Using your knowledge of physics comment on the use of satellites in society. 56. An astronomer is observing one particular star in the night sky, and states that the star is moving away from the Earth. Last updated by AD May 2014 ...
Lecture-15-10
... and mass 0.742 kg. If the bucket is allowed to fall, (a) what is its linear acceleration? (b) What is the angular acceleration of the pulley? (c) How far does the bucket drop in 1.50 s? ...
... and mass 0.742 kg. If the bucket is allowed to fall, (a) what is its linear acceleration? (b) What is the angular acceleration of the pulley? (c) How far does the bucket drop in 1.50 s? ...
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
... Time of collision is short enough that external forces may be ignored Inelastic collision: momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not Completely inelastic collision: objects stick ...
... Time of collision is short enough that external forces may be ignored Inelastic collision: momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not Completely inelastic collision: objects stick ...
Motion in Two Dimensions
... This also means that if the distance between the centers of the objects changes, the gravity will change. Therefore, if you move closer to the center of the earth, you will experience a greater gravity and you will weigh more! Conversely, if you move out into space, you will weigh less! ...
... This also means that if the distance between the centers of the objects changes, the gravity will change. Therefore, if you move closer to the center of the earth, you will experience a greater gravity and you will weigh more! Conversely, if you move out into space, you will weigh less! ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.