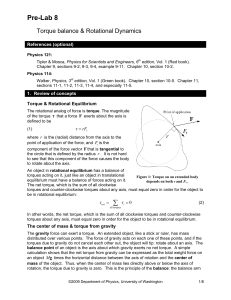
Circular Motion Notes File
... will be pulled away from its straight-line path, and will follow a circular path. As long as the string is pulled toward this central point, the ball will continue moving in a circle at a constant speed. An object moving in a circle at a constant speed is said to be in uniform circular motion (UCM). ...
... will be pulled away from its straight-line path, and will follow a circular path. As long as the string is pulled toward this central point, the ball will continue moving in a circle at a constant speed. An object moving in a circle at a constant speed is said to be in uniform circular motion (UCM). ...
Semester Exam Review
... Two forces F1 and F2 are applied to a block on a frictionless horizontal surface as shown. If the magnitude of the block’s acceleration is 2 m/s2, what is the mass of the block? ...
... Two forces F1 and F2 are applied to a block on a frictionless horizontal surface as shown. If the magnitude of the block’s acceleration is 2 m/s2, what is the mass of the block? ...
newtons laws practice
... • A sheet of paper can be withdrawn from under a milk carton without toppling it as long as the sheet is pulled quickly. This demonstrates: • A) gravity tends to hold the carton to the ground • B) the carton has inertia • C) for every action there’s an equal reaction ...
... • A sheet of paper can be withdrawn from under a milk carton without toppling it as long as the sheet is pulled quickly. This demonstrates: • A) gravity tends to hold the carton to the ground • B) the carton has inertia • C) for every action there’s an equal reaction ...
Document
... than the U.S gallon by a factor of 1.2. Applying this to the result of part (a), we find the answer for part (b) is 22.5 gallons. 59. (a) When is measured in radians, it is equal to the arc length divided by the radius. For very large radius circles and small values of , such as we deal with in t ...
... than the U.S gallon by a factor of 1.2. Applying this to the result of part (a), we find the answer for part (b) is 22.5 gallons. 59. (a) When is measured in radians, it is equal to the arc length divided by the radius. For very large radius circles and small values of , such as we deal with in t ...
T072 Q13. Assume that a disk starts from rest and rotates with an
... momentarily at rest is (Ans: 3.5 rad/s2 clockwise) Q14 A disk of rotational inertia 5.0 kg m2 starts rotating from rest and accelerates with a constant angular acceleration of 1.0 rad/s2. During the first 4.0 s, the work done on the disk is: (Ans: 40 J) Q15: The rotational inertia of a solid sphere ...
... momentarily at rest is (Ans: 3.5 rad/s2 clockwise) Q14 A disk of rotational inertia 5.0 kg m2 starts rotating from rest and accelerates with a constant angular acceleration of 1.0 rad/s2. During the first 4.0 s, the work done on the disk is: (Ans: 40 J) Q15: The rotational inertia of a solid sphere ...
Dynamics Powerpoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... with a constant speed. When the bus slows down, the package continues to move forward with the same constant speed that it had until some force stops it. ...
... with a constant speed. When the bus slows down, the package continues to move forward with the same constant speed that it had until some force stops it. ...
Ballistic Pendulum - Mississippi State Physics Labs
... You cannot, however, equate the kinetic energy of the pendulum after the collision with the kinetic energy of the ball before the swing, because the collision between ball and pendulum is inelastic, and kinetic energy is not conserved in inelastic collisions. Momentum, however, is conserved in all f ...
... You cannot, however, equate the kinetic energy of the pendulum after the collision with the kinetic energy of the ball before the swing, because the collision between ball and pendulum is inelastic, and kinetic energy is not conserved in inelastic collisions. Momentum, however, is conserved in all f ...
The Pendulum Introduction
... remain periodic but the actual period may change. In the pendulum period doubling of the base period occurs many times before aperiodic, chaotic motion is observed Evidently the motion of the damped, driven nonlinear pendulum is much more complex than even the damped pendulum. A convenient way of r ...
... remain periodic but the actual period may change. In the pendulum period doubling of the base period occurs many times before aperiodic, chaotic motion is observed Evidently the motion of the damped, driven nonlinear pendulum is much more complex than even the damped pendulum. A convenient way of r ...
Introduction to Classical Mechanics 1 HISTORY
... breaks down for extreme speeds (approaching the speed of light) and at atomic dimensions. The theory of relativity, and quantum mechanics, were developed in the early 20th century to describe these cases. But for macroscopic systems Newton’s theory is valid and extremely accurate. This early history ...
... breaks down for extreme speeds (approaching the speed of light) and at atomic dimensions. The theory of relativity, and quantum mechanics, were developed in the early 20th century to describe these cases. But for macroscopic systems Newton’s theory is valid and extremely accurate. This early history ...
forces christina danielle ali
... the bottom arrow, it does not mean it is only moving up. It could also be slowing down in the negative direction. If the arrows are equal to each other, it does not only mean it is in motion, because if an object has a constant speed of 0 m/s, it has the same free-body diagram as an object that is t ...
... the bottom arrow, it does not mean it is only moving up. It could also be slowing down in the negative direction. If the arrows are equal to each other, it does not only mean it is in motion, because if an object has a constant speed of 0 m/s, it has the same free-body diagram as an object that is t ...
實驗3:轉動-剛體的轉動運動Lab. 3 : Rotation
... of inertia (rotational inertia) ~ mass for linear motion. It appears in the relationships for the dynamics of rotational motion. The moment of inertia must be specified with respect to a chosen axis of rotation. For a point mass the moment of inertia is just the mass times the square of perpen ...
... of inertia (rotational inertia) ~ mass for linear motion. It appears in the relationships for the dynamics of rotational motion. The moment of inertia must be specified with respect to a chosen axis of rotation. For a point mass the moment of inertia is just the mass times the square of perpen ...
Forces and Motion
... constant speed. This speed is called terminal velocity. • This occurs because eventually air resistance will be evenly balanced with gravity. What will happen in the following scenarios? • A. a coin and a feather are dropped, they have the same mass. • B. two coins are dropped, one is heavier but bo ...
... constant speed. This speed is called terminal velocity. • This occurs because eventually air resistance will be evenly balanced with gravity. What will happen in the following scenarios? • A. a coin and a feather are dropped, they have the same mass. • B. two coins are dropped, one is heavier but bo ...