KD-4 power point review
... Uniform Circular Motion-The motion of an object traveling in a circular path at a constant speed Ex) A tetherball moving in a circular path Is the tetherball accelerating? ...
... Uniform Circular Motion-The motion of an object traveling in a circular path at a constant speed Ex) A tetherball moving in a circular path Is the tetherball accelerating? ...
Unit 1
... If two skateboarders have the same mass, and one pushes on the other, they both move away from the center at the same speed If one skateboarder has more mass than the other, the same push will send the smaller person off at a higher speed, and the larger one off in the opposite direction at a smalle ...
... If two skateboarders have the same mass, and one pushes on the other, they both move away from the center at the same speed If one skateboarder has more mass than the other, the same push will send the smaller person off at a higher speed, and the larger one off in the opposite direction at a smalle ...
Answers
... Divergence occurs when the denominator of the above equation becomes zero. This allows the critical speed for divergence to be determined as ...
... Divergence occurs when the denominator of the above equation becomes zero. This allows the critical speed for divergence to be determined as ...
Chapter 2, 4 &5 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. ...
... Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. ...
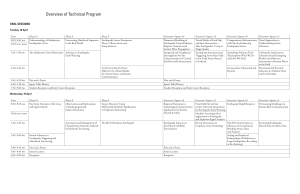
Overview of Technical Program
... Source Discovery Using Differential Methods: Applications to Explosion Monitoring Observations and Mechanisms of Anthropogenically Induced Seismicity Assessment and Management of Hazards from Seismicity Induced by Hydraulic Fracturing Recent Innovations in Geophone Array Seismology Regional Variatio ...
... Source Discovery Using Differential Methods: Applications to Explosion Monitoring Observations and Mechanisms of Anthropogenically Induced Seismicity Assessment and Management of Hazards from Seismicity Induced by Hydraulic Fracturing Recent Innovations in Geophone Array Seismology Regional Variatio ...
Exam 2 Physics 125 Fall 2008 Name:
... 13. The diagram shows three blocks on a frictionless table connected together with two identical strings, which can be subject to a maximum tension of 50.0N before breaking. The masses of the blocks are indicated, and the assembly is pulled by a horizontal force P. What is the maximum acceleration t ...
... 13. The diagram shows three blocks on a frictionless table connected together with two identical strings, which can be subject to a maximum tension of 50.0N before breaking. The masses of the blocks are indicated, and the assembly is pulled by a horizontal force P. What is the maximum acceleration t ...
Homework Week 6
... 2. A physics book with a mass of 2.8 kg is pushed along a table with a net force of 1 N. What is the book's acceleration? 3. Calculate the momentum of a 16-kg bicycle traveling north at 3 m/s. 4. Calculate the momentum of a 12-kg bicycle traveling east at 2 m/s. 5. Calculate the acceleration of a bu ...
... 2. A physics book with a mass of 2.8 kg is pushed along a table with a net force of 1 N. What is the book's acceleration? 3. Calculate the momentum of a 16-kg bicycle traveling north at 3 m/s. 4. Calculate the momentum of a 12-kg bicycle traveling east at 2 m/s. 5. Calculate the acceleration of a bu ...
Newton`s 2nd power point
... • How are weight and mass different? • Mass is the amount of matter in an object and Weight is the force of gravity acting on a Mass • Weight will vary with location, but mass will remain constant. • What does this mean? ...
... • How are weight and mass different? • Mass is the amount of matter in an object and Weight is the force of gravity acting on a Mass • Weight will vary with location, but mass will remain constant. • What does this mean? ...
Objectives 6 E Review- TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 4th Part A: Read
... a. By recording the seismic waves with a seismograph and measuring magnitude with a Richter Scale b. By recording the seismic waves with a Richter Scale and measuring magnitude with a seismograph c. By recording the Richter scale and measuring the distance between seismic waves d. By recording the s ...
... a. By recording the seismic waves with a seismograph and measuring magnitude with a Richter Scale b. By recording the seismic waves with a Richter Scale and measuring magnitude with a seismograph c. By recording the Richter scale and measuring the distance between seismic waves d. By recording the s ...
Newton`s 1st Law of Motion
... Krishna Gopal Shrivestava of India set an unofficial world record in 1999 by pulling a ship with a mass of 244,000 kg with his teeth. We can use this feat to learn about force, mass, and acceleration. ...
... Krishna Gopal Shrivestava of India set an unofficial world record in 1999 by pulling a ship with a mass of 244,000 kg with his teeth. We can use this feat to learn about force, mass, and acceleration. ...
Questions 5-6
... between the block and the wall is μ. What value of F is necessary to keep the block from slipping down the wall? (A) mg (B) μ mg (C) mg/μ (D) mg(1 - μ) (E) mg(1 + μ) 29. A mass M suspended by a spring with force constant k has a period T when set into oscillation on Earth. Its period on Mars, whose ...
... between the block and the wall is μ. What value of F is necessary to keep the block from slipping down the wall? (A) mg (B) μ mg (C) mg/μ (D) mg(1 - μ) (E) mg(1 + μ) 29. A mass M suspended by a spring with force constant k has a period T when set into oscillation on Earth. Its period on Mars, whose ...
Motion – many examples surround us an ice skater coasting
... an ice skater coasting along a car screeching to a halt a ball dropped from the hand a feather floating in the wind a shell fired from a canon ...
... an ice skater coasting along a car screeching to a halt a ball dropped from the hand a feather floating in the wind a shell fired from a canon ...