2003 - Thephysicsteacher
... What is an electric current? An electric current is a flow of charge. Give the standard colour of the insulation on the wires connected to each of the terminals L, N and E on the plug in the diagram. L (live) is brown, N (neutral) is blue, E (earth) is green-yellow What is the purpose of the wire co ...
... What is an electric current? An electric current is a flow of charge. Give the standard colour of the insulation on the wires connected to each of the terminals L, N and E on the plug in the diagram. L (live) is brown, N (neutral) is blue, E (earth) is green-yellow What is the purpose of the wire co ...
force - the SASPhysics.com
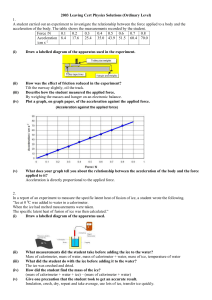
... on it so resultant force is just its weight. Remember F = ma? Acceleration of 10m/s2 is constant for all objects. ...
... on it so resultant force is just its weight. Remember F = ma? Acceleration of 10m/s2 is constant for all objects. ...
Physics 101 Fall 02 - Youngstown State University
... For Geosynchronous satellites, V = 2r/T, where T = 24 hours ...
... For Geosynchronous satellites, V = 2r/T, where T = 24 hours ...
Ch33 - Wells College
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. ...
Physics Fun - New Haven Science
... then 1 g. When you feel lighter than normal you are experiences a force less than 1 g. You are weightless when you feel no forces (free fall). On the roller coaster, when you go down a steep hill, you will get that “light stomach feeling” and will notice yourself lifting off the seat. You have just ...
... then 1 g. When you feel lighter than normal you are experiences a force less than 1 g. You are weightless when you feel no forces (free fall). On the roller coaster, when you go down a steep hill, you will get that “light stomach feeling” and will notice yourself lifting off the seat. You have just ...
3.1 TQ Centrifugal Force Apparatus
... A centripetal force acts towards the centre of a circular path and keeps the body moving in this path; otherwise the body would observe a straight line motion. In line with Newton's second law of motion, the centripetal force also produces an acceleration having the same direction it has. By definit ...
... A centripetal force acts towards the centre of a circular path and keeps the body moving in this path; otherwise the body would observe a straight line motion. In line with Newton's second law of motion, the centripetal force also produces an acceleration having the same direction it has. By definit ...
14 Mass on a spring and other systems described by linear ODE
... where m is the mass of the object, a is the acceleration, P which, as we know from Calculus, is the second derivative of the displacement x(t), a = ẍ, and Fi is the net force applied. What we know about the net force? This has to include the gravity, of course: F1 = mg, where g is the acceleration ...
... where m is the mass of the object, a is the acceleration, P which, as we know from Calculus, is the second derivative of the displacement x(t), a = ẍ, and Fi is the net force applied. What we know about the net force? This has to include the gravity, of course: F1 = mg, where g is the acceleration ...
document
... Static Friction: Push with a force F and block does not move because fs = F. The force of friction varies from 0 up to some maximum. The maximum value equals fs = msN, where N is the normal force. Above we would have fs = msmg. The coefficient of static friction ranges from 0 to 1.2 Kinetic Friction ...
... Static Friction: Push with a force F and block does not move because fs = F. The force of friction varies from 0 up to some maximum. The maximum value equals fs = msN, where N is the normal force. Above we would have fs = msmg. The coefficient of static friction ranges from 0 to 1.2 Kinetic Friction ...
Ch. 12 Review Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Physical Science Date
... 21. What really dictates who will win a game of tug-of-war (don’t say whoever pulls harder)? Since both people pull on the rope with the same force (Newton’s 3rd Law), it’s not who pulls harder. It’s how hard the team can push off the ground and thus have the ground push back on them, in essence, i ...
... 21. What really dictates who will win a game of tug-of-war (don’t say whoever pulls harder)? Since both people pull on the rope with the same force (Newton’s 3rd Law), it’s not who pulls harder. It’s how hard the team can push off the ground and thus have the ground push back on them, in essence, i ...
File
... internal forces the centre of mass of 4 fragment should continue moving along the same parabolic path. The centre of mass of 4 fragments will move on initial parabolic path PBC, which is the continuation of the initial parabolic path AP of the cracker. ...
... internal forces the centre of mass of 4 fragment should continue moving along the same parabolic path. The centre of mass of 4 fragments will move on initial parabolic path PBC, which is the continuation of the initial parabolic path AP of the cracker. ...
Background note on induced seismicity in the
... compared with earthquakes occurring elsewhere and are almost always generated in the middle crust (Basement rocks) at depths of around 15 km or so, where the crust is much stronger than the sedimentary cover which is the target for hydrocarbon activity. Earthquakes follow a well established frequenc ...
... compared with earthquakes occurring elsewhere and are almost always generated in the middle crust (Basement rocks) at depths of around 15 km or so, where the crust is much stronger than the sedimentary cover which is the target for hydrocarbon activity. Earthquakes follow a well established frequenc ...