Part 2 - Haiku
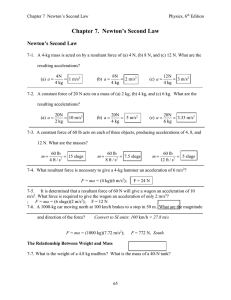
... 1. Weight or “Force due to Gravity,” Fg, equals mass x gravitational acceleration. Gravitational acceleration, g, on Earth is accepted to be 9.8 m/s2, but for ease you may use a value of g = 10 m/s2. Oftentimes, the gravitational acceleration is just called, “Gravity.” Calculate the Weight of each i ...
... 1. Weight or “Force due to Gravity,” Fg, equals mass x gravitational acceleration. Gravitational acceleration, g, on Earth is accepted to be 9.8 m/s2, but for ease you may use a value of g = 10 m/s2. Oftentimes, the gravitational acceleration is just called, “Gravity.” Calculate the Weight of each i ...
Wednesday, Apr. 3, 2002
... What is a system that has this kind of character? A system consists of a mass and a spring When a spring is stretched from its equilibrium position by a length x, the force acting on the mass is ...
... What is a system that has this kind of character? A system consists of a mass and a spring When a spring is stretched from its equilibrium position by a length x, the force acting on the mass is ...
File
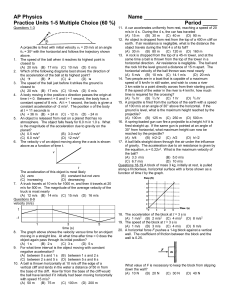
... Q 9 If the period of oscillation of mass m suspended from a spring is 2s, find the period of mass 4m? Marks (2) View Answer Q 10 A mass m is vertically suspended from a spring of negligible mass. The system oscillates with a frequency v. Find the frequency of the system if a mass 4m is suspended fr ...
... Q 9 If the period of oscillation of mass m suspended from a spring is 2s, find the period of mass 4m? Marks (2) View Answer Q 10 A mass m is vertically suspended from a spring of negligible mass. The system oscillates with a frequency v. Find the frequency of the system if a mass 4m is suspended fr ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... of your body parts, mostly at a point of contact. If your body is not stretched or compressed, you will feel like you are floating. Gravity ALONE will not stretch or compress your body. Hanging from the board, the board also pulls up on your arms. Newton’s 3rd law! Standing on the ground, the ground ...
... of your body parts, mostly at a point of contact. If your body is not stretched or compressed, you will feel like you are floating. Gravity ALONE will not stretch or compress your body. Hanging from the board, the board also pulls up on your arms. Newton’s 3rd law! Standing on the ground, the ground ...
Question Bank - India Study Channel
... 2. Consider a planet whose radius and mass were half that of earth. What will be the value of acceleration due to gravity at its surface? 3. Write the S.I. units of (i) pressure (ii) relative density 4. The earth attracts the moon. Does moon attract the earth? If so, why does earth does not move tow ...
... 2. Consider a planet whose radius and mass were half that of earth. What will be the value of acceleration due to gravity at its surface? 3. Write the S.I. units of (i) pressure (ii) relative density 4. The earth attracts the moon. Does moon attract the earth? If so, why does earth does not move tow ...
Sample Course Outline
... chapter is covered. Students are strongly advised to attempt all these selected problems and other endchapter problems from the textbook. The success in courses like this one depends on once comprehension of the subject matter and ability to solve as many problems as possible. ...
... chapter is covered. Students are strongly advised to attempt all these selected problems and other endchapter problems from the textbook. The success in courses like this one depends on once comprehension of the subject matter and ability to solve as many problems as possible. ...
CST Review - cloudfront.net
... A tuning fork is used to produce sound waves with a frequency of 440 hertz. The waves travel through the air at 344 m/s. What is the wavelength of the sound waves? A 0.15 m B 0.39 m C 0.78 m D 1.28 m ...
... A tuning fork is used to produce sound waves with a frequency of 440 hertz. The waves travel through the air at 344 m/s. What is the wavelength of the sound waves? A 0.15 m B 0.39 m C 0.78 m D 1.28 m ...
Chapter 7: Using Vectors: Motion and Force
... When we drop a ball from a height we know that its speed increases as it falls. The increase in speed is due to the acceleration gravity, g = 9.8 m/sec2. ...
... When we drop a ball from a height we know that its speed increases as it falls. The increase in speed is due to the acceleration gravity, g = 9.8 m/sec2. ...
Chapter 9 Problems - University of Colorado Colorado Springs
... In a slow-pitch softball game, a 0.200-kg softball crosses the plate at 15.0 m/s at an angle of 45.0 below the horizontal. The batter hits the ball toward center field, giving it a velocity of 40.0 m/s at 30.0 above the horizontal. (a) Determine the impulse delivered to the ball. (b) If the force ...
... In a slow-pitch softball game, a 0.200-kg softball crosses the plate at 15.0 m/s at an angle of 45.0 below the horizontal. The batter hits the ball toward center field, giving it a velocity of 40.0 m/s at 30.0 above the horizontal. (a) Determine the impulse delivered to the ball. (b) If the force ...
Document
... • The acceleration produced by a net force acting on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force and in the same direction as the net force, and the acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. • Acceleration = net force/mass • a=Fnet/m Physics 3050: Lec ...
... • The acceleration produced by a net force acting on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force and in the same direction as the net force, and the acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. • Acceleration = net force/mass • a=Fnet/m Physics 3050: Lec ...