Document
... Problem solving is an important part of studying physics. It impels students to work constructively and independently, teaches them to analyze phenomena, define principal factors, and neglect unimportant details thus brining them to scientific research. The goal of this manual is to help students ma ...
... Problem solving is an important part of studying physics. It impels students to work constructively and independently, teaches them to analyze phenomena, define principal factors, and neglect unimportant details thus brining them to scientific research. The goal of this manual is to help students ma ...
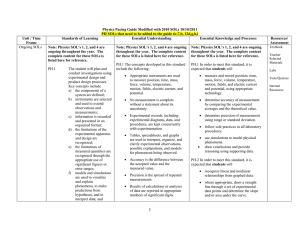
2010 Pacing Pacing Guide - High School Science Help
... Work is the mechanical transfer of energy to or from a system and is the product of a force at the point of application and the parallel component of the object’s displacement. The net work on a system equals its PH.6a The concepts developed in this standard include the following: Kinetic energy ...
... Work is the mechanical transfer of energy to or from a system and is the product of a force at the point of application and the parallel component of the object’s displacement. The net work on a system equals its PH.6a The concepts developed in this standard include the following: Kinetic energy ...
I will read the background information about Newton`s Second Law
... a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A force sensor and an accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with the cart’s acceleration. The total mass of the cart is easy to vary by adding masses. Using these tools, you can determine how the net fo ...
... a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A force sensor and an accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with the cart’s acceleration. The total mass of the cart is easy to vary by adding masses. Using these tools, you can determine how the net fo ...
Learning material
... difference is zero. However, the acceleration isn’t zero, because the direction of motion is changing. In order to remain in a circle the body trajectory is curved towards the centre. We can find the magnitude of the acceleration by comparing the two neighbouring velocities. In the diagram, the velo ...
... difference is zero. However, the acceleration isn’t zero, because the direction of motion is changing. In order to remain in a circle the body trajectory is curved towards the centre. We can find the magnitude of the acceleration by comparing the two neighbouring velocities. In the diagram, the velo ...
Differential Equations
... First suppose that the string is disturbed from its equilibrium position and then released at time t = 0 with zero velocity to vibrate freely. Then the vertical displacement u(x, t) must satisfy the wave equation a2uxx = utt, 0 < x < L, t > 0; (1) the boundary conditions u(0, t) = 0, u(L, t) = 0, t ...
... First suppose that the string is disturbed from its equilibrium position and then released at time t = 0 with zero velocity to vibrate freely. Then the vertical displacement u(x, t) must satisfy the wave equation a2uxx = utt, 0 < x < L, t > 0; (1) the boundary conditions u(0, t) = 0, u(L, t) = 0, t ...
Collisions
... a) How much thermal energy is lost due to friction ? ( The work done by friction ). b) If the hill has an angle of 20° above the horizontal what was the frictional force? ...
... a) How much thermal energy is lost due to friction ? ( The work done by friction ). b) If the hill has an angle of 20° above the horizontal what was the frictional force? ...
ω = ag/
... 14. A simple classical model of the C O2 molecule would be a linear structure of three masses with the electrical forces between the ions represented by two identical springs of equilibrium length l and force constant k , as shown in Fig. 1.90. Assume that only motion along the original equilibrium ...
... 14. A simple classical model of the C O2 molecule would be a linear structure of three masses with the electrical forces between the ions represented by two identical springs of equilibrium length l and force constant k , as shown in Fig. 1.90. Assume that only motion along the original equilibrium ...
AP physics final AP test review Mechanics
... constant, and work is zero. Friction, tension, normal force, gravity and the magnetic force are common forces that can act centripetally to cause uniform circular motion. 26. Centripetal Force (A-184 #46) A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a ...
... constant, and work is zero. Friction, tension, normal force, gravity and the magnetic force are common forces that can act centripetally to cause uniform circular motion. 26. Centripetal Force (A-184 #46) A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a ...
Unit 3 - HKU Physics
... The net force F on a body is equal to the product of the body’s mass m and the acceleration of the body a. The direction of acceleration is along the direction of net force. It is important to know that force is a vector and has a SI unit Newton (N). A well- known formula to express the idea is ∑ F ...
... The net force F on a body is equal to the product of the body’s mass m and the acceleration of the body a. The direction of acceleration is along the direction of net force. It is important to know that force is a vector and has a SI unit Newton (N). A well- known formula to express the idea is ∑ F ...