Formula “Card” For Basic Biostat 9/24/2007 Draft
... Use the mean and standard deviation as the primary summary statistics for symmetrical distributions. It is often advisable to check your calculations with technology (i.e., you calculator or a computer application). ...
... Use the mean and standard deviation as the primary summary statistics for symmetrical distributions. It is often advisable to check your calculations with technology (i.e., you calculator or a computer application). ...
THE LAW OF LARGE NUMBERS and Part IV N. H. BINGHAM
... product; Pythagoras’ theorem holds; we can use projections as in Euclidean space; so we can think geometrically, and draw diagrams). The SLLN holds also in Banach space (Stefan BANACH (1892-1945), in 1932) – Robert FORTET (1912-98) in 1954. Some more detailed results hold in some but not all Banach ...
... product; Pythagoras’ theorem holds; we can use projections as in Euclidean space; so we can think geometrically, and draw diagrams). The SLLN holds also in Banach space (Stefan BANACH (1892-1945), in 1932) – Robert FORTET (1912-98) in 1954. Some more detailed results hold in some but not all Banach ...
Chapter 5: Regression
... The probability we assign to an event can change if we know that some other event has occurred. This idea is the key to many applications of probability. When we are trying to find the probability that one event will happen under the condition that some other event is already known to have occurred, ...
... The probability we assign to an event can change if we know that some other event has occurred. This idea is the key to many applications of probability. When we are trying to find the probability that one event will happen under the condition that some other event is already known to have occurred, ...
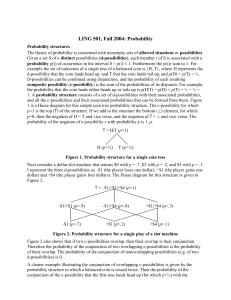
Probability structures
... is false for both the d-possibilities. The propositions it is likely that the coin will land head up and it is likely the coin will land tail up are both false. On the other hand, using Figure 2, Ls is true for the d-possibility –$1; the proposition it is likely that the player will lose $1 is true, ...
... is false for both the d-possibilities. The propositions it is likely that the coin will land head up and it is likely the coin will land tail up are both false. On the other hand, using Figure 2, Ls is true for the d-possibility –$1; the proposition it is likely that the player will lose $1 is true, ...