ST 371 (III). Conditional Probability and Independence
... • A refers to the event that an individual having a particular disease. B refers to the event that the blood test result is positive. Then the probability of A occurs be affected by the information on whether B occurs. • An experiment consists of rolling a die once. Let E = {5, 6} and F = {6}. If th ...
... • A refers to the event that an individual having a particular disease. B refers to the event that the blood test result is positive. Then the probability of A occurs be affected by the information on whether B occurs. • An experiment consists of rolling a die once. Let E = {5, 6} and F = {6}. If th ...
8.2 The Geometric Distribution
... The Geometric Distribution •Suppose an experiment consists of a sequence of trials with the following conditions: 1. The trials are independent. 2. Each trial can result in one of two possible outcomes, success and failure. 3. The probability of success is the same for all trials. ...
... The Geometric Distribution •Suppose an experiment consists of a sequence of trials with the following conditions: 1. The trials are independent. 2. Each trial can result in one of two possible outcomes, success and failure. 3. The probability of success is the same for all trials. ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research Volume Title: Consumer Buying Intentions and Purchase Probability:
... intentions questions rest on a comparison of the respondents' purchase probability with the probability threshold implied by the question, respondents are being asked to make two difficult judgments when the first (actual probability) is the only one of any real use.9 And if respondents are capable ...
... intentions questions rest on a comparison of the respondents' purchase probability with the probability threshold implied by the question, respondents are being asked to make two difficult judgments when the first (actual probability) is the only one of any real use.9 And if respondents are capable ...
P(n,r)
... number of ways an event can occur to the number of possible outcomes. In symbols P(event) = ...
... number of ways an event can occur to the number of possible outcomes. In symbols P(event) = ...
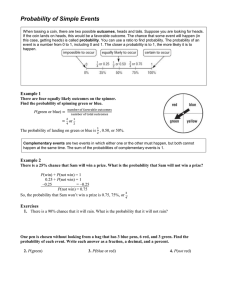
Probability of Simple Events
... Probability of Simple Events When tossing a coin, there are two possible outcomes, heads and tails. Suppose you are looking for heads. If the coin lands on heads, this would be a favorable outcome. The chance that some event will happen (in this case, getting heads) is called probability. You can us ...
... Probability of Simple Events When tossing a coin, there are two possible outcomes, heads and tails. Suppose you are looking for heads. If the coin lands on heads, this would be a favorable outcome. The chance that some event will happen (in this case, getting heads) is called probability. You can us ...