Chap004
... calculate P(X = 2) + P(X = 3) + P(X = 4) + P(X = 5). Or, one may use the BINOMDIST function to get the cumulative probability P(X 1), and then calculate the answer as its complement, namely, 1P(X 1). An easier way is to use the template shown in Figure 4.2.1. After making sure that n is filled ...
... calculate P(X = 2) + P(X = 3) + P(X = 4) + P(X = 5). Or, one may use the BINOMDIST function to get the cumulative probability P(X 1), and then calculate the answer as its complement, namely, 1P(X 1). An easier way is to use the template shown in Figure 4.2.1. After making sure that n is filled ...
5.2 full notes
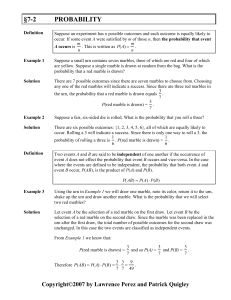
... • License plates in the State of Altered require 2 letters followed by 4 digits. No two letters can be the same, but it is ok to repeat digits. How many different license plates can me made? ...
... • License plates in the State of Altered require 2 letters followed by 4 digits. No two letters can be the same, but it is ok to repeat digits. How many different license plates can me made? ...
Handout1B - Harvard Math Department
... P(B|A). Now, P(A|B) = 12 since if we know heads happens on the first flip, then we can get two heads only with {HHT} and {HTH}. These events are independent and their probabilities sum to 14 . Meanwhile, P(B) = 12 so P(A|B) = 14 / 12 = 12 . On the other hand, P(A) = 38 since A = {HHT, HTH, THH}. Thu ...
... P(B|A). Now, P(A|B) = 12 since if we know heads happens on the first flip, then we can get two heads only with {HHT} and {HTH}. These events are independent and their probabilities sum to 14 . Meanwhile, P(B) = 12 so P(A|B) = 14 / 12 = 12 . On the other hand, P(A) = 38 since A = {HHT, HTH, THH}. Thu ...
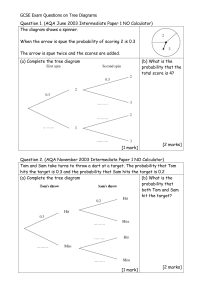
GCSE Exam Questions on Tree Diagrams
... Tom and Sam take turns to throw a dart at a target. The probability that Tom hits the target is 0.3 and the probability that Sam hits the target is 0.2 (a) Complete the tree diagram (b) What is the probability that both Tom and Sam hit the target? ...
... Tom and Sam take turns to throw a dart at a target. The probability that Tom hits the target is 0.3 and the probability that Sam hits the target is 0.2 (a) Complete the tree diagram (b) What is the probability that both Tom and Sam hit the target? ...
Recommendation of a Strategy
... Since it would nearly impossible to predict the precise value of a CRV, you must include it within a range. ...
... Since it would nearly impossible to predict the precise value of a CRV, you must include it within a range. ...