Probability and Statistics Random Chance A tossed penny can land
... X2 is usually calculaed in table form. Once the X2 value for an experiment has been calculated, it must be evaluated by comparison with a table of X2 values. In order to use the X2 test properly, one must understand exactly what is being evaluated. The X2 test is always phrased in terms of the “Null ...
... X2 is usually calculaed in table form. Once the X2 value for an experiment has been calculated, it must be evaluated by comparison with a table of X2 values. In order to use the X2 test properly, one must understand exactly what is being evaluated. The X2 test is always phrased in terms of the “Null ...
1_ClassNotes
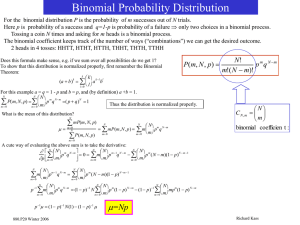
... The mean (μ), or expected value, is π and the variance can be calculated as π (π-1), which in this case, will be 0.3(0.7) or 0.21. You can see that in this type of distribution the variance and the mean cannot be independent—that is, the variance is tied to the mean. This is one key difference betwe ...
... The mean (μ), or expected value, is π and the variance can be calculated as π (π-1), which in this case, will be 0.3(0.7) or 0.21. You can see that in this type of distribution the variance and the mean cannot be independent—that is, the variance is tied to the mean. This is one key difference betwe ...
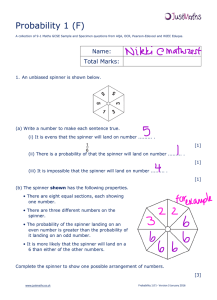
Probability 1 (F)
... (ii) What is the probability that Ann and Carol sit next to each other? (ii) ............................................ [1] (iii) What is the probability that Bob sits in seat 1 with Ann next to him? (iii) ........................................... [1] ...
... (ii) What is the probability that Ann and Carol sit next to each other? (ii) ............................................ [1] (iii) What is the probability that Bob sits in seat 1 with Ann next to him? (iii) ........................................... [1] ...
Stat 110 Strategic Practice 1, Fall 2011 1 Naive Definition of
... Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Department of Statistics, Harvard University) 1. A certain family has 6 children, consisting of 3 boys and 3 girls. Assuming that all birth orders are equally likely, what is the probability that the 3 eldest children are the 3 girls? Label the girls as 1, 2, 3 and the boys as ...
... Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Department of Statistics, Harvard University) 1. A certain family has 6 children, consisting of 3 boys and 3 girls. Assuming that all birth orders are equally likely, what is the probability that the 3 eldest children are the 3 girls? Label the girls as 1, 2, 3 and the boys as ...
Part I
... • Example: In throwing a pair of dice, we can give a statistical description by considering that a very large number N of similar pairs of dice are thrown under similar circumstances. Alternatively, we could imagine the same pair of dice thrown N times under similar circumstances. The probability of ...
... • Example: In throwing a pair of dice, we can give a statistical description by considering that a very large number N of similar pairs of dice are thrown under similar circumstances. Alternatively, we could imagine the same pair of dice thrown N times under similar circumstances. The probability of ...
Slide 1
... I do: (ex) There are 12 boys and 14 girls in Mrs. Brown’s math class. Find the number of ways Mrs. Brown can select a team of 3 students from the class to work on a group project. The team is to consist of 1 girl and 2 boys. It is a combination question because order, or position, is not ...
... I do: (ex) There are 12 boys and 14 girls in Mrs. Brown’s math class. Find the number of ways Mrs. Brown can select a team of 3 students from the class to work on a group project. The team is to consist of 1 girl and 2 boys. It is a combination question because order, or position, is not ...