Disjoint/Addition Rule
... are basketball players. It is also noted that within the group of 100 athletes, 25% are over 6-feet tall. What is the probability that an athlete is a basketball player OR is 6 feet tall? – As with the previous example, you may be tempted to use our addition rule for disjoint events: P(Basketball Pl ...
... are basketball players. It is also noted that within the group of 100 athletes, 25% are over 6-feet tall. What is the probability that an athlete is a basketball player OR is 6 feet tall? – As with the previous example, you may be tempted to use our addition rule for disjoint events: P(Basketball Pl ...
Chapter 1: Statistics
... together, that is, they have no intersection b. Independence says each event does not affect the other event’s probability 2. P(A and B) = P(A) P(B) when A and B are independent a. Since P(A) and P(B) are not zero, P(A and B) is nonzero b. Thus, independent events have an intersection 3. Events cann ...
... together, that is, they have no intersection b. Independence says each event does not affect the other event’s probability 2. P(A and B) = P(A) P(B) when A and B are independent a. Since P(A) and P(B) are not zero, P(A and B) is nonzero b. Thus, independent events have an intersection 3. Events cann ...
Analysis of State Transitions
... income were invested by the insurer in assets that did not provide a certain interest rate, this would change the interest rate and the Actual Reserves held at future time periods. Perhaps the policy might have a condition that allows it to be closed down before the end of the term, and a lump sum c ...
... income were invested by the insurer in assets that did not provide a certain interest rate, this would change the interest rate and the Actual Reserves held at future time periods. Perhaps the policy might have a condition that allows it to be closed down before the end of the term, and a lump sum c ...
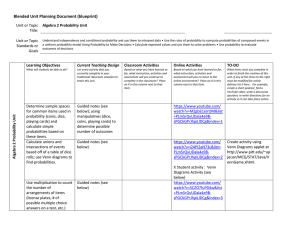
BlendedUnitPlanningDocument-Probability
... What items must you complete in order to finish the creation of this unit. If any of the items to the right must be modified for online delivery list it here. For example, create a short podcast, find a YouTube video, write a discussion question, re-write directions for an activity so it can take pl ...
... What items must you complete in order to finish the creation of this unit. If any of the items to the right must be modified for online delivery list it here. For example, create a short podcast, find a YouTube video, write a discussion question, re-write directions for an activity so it can take pl ...