Foundations of Social Studies GEOGRAPHY
... forces are weathering and erosion. Weathering occurs when rock surfaces decompose and begin to break up. Erosion refers to the actual movement of the broken particles away from their source. These two processes occur at the same time and result in the changing shape of land, that is, the creation of ...
... forces are weathering and erosion. Weathering occurs when rock surfaces decompose and begin to break up. Erosion refers to the actual movement of the broken particles away from their source. These two processes occur at the same time and result in the changing shape of land, that is, the creation of ...
Characteristics of Life - Glasgow Independent Schools
... from the foods they eat or, in the case of plants and several other types of organisms, the foods that they produce. Organisms that get energy from the food they eat are called heterotrophs. Organisms that use energy from the sun to make their own food (which they then use for energy) are called aut ...
... from the foods they eat or, in the case of plants and several other types of organisms, the foods that they produce. Organisms that get energy from the food they eat are called heterotrophs. Organisms that use energy from the sun to make their own food (which they then use for energy) are called aut ...
- Catalyst - University of Washington
... within a context of plate tectonics. Plate configurations during the late Paleozoic placed the present day land masses of southern South America, Africa, India, Australia and Antarctica over the South Pole, where continental ice sheets could develop and expand. ...
... within a context of plate tectonics. Plate configurations during the late Paleozoic placed the present day land masses of southern South America, Africa, India, Australia and Antarctica over the South Pole, where continental ice sheets could develop and expand. ...
Earthquakes! Causes. Predictions.
... sets of electromagnetic signals were ignored, because they were unexpected and the scientific connection between such signals and earthquakes was unknown. The designers of this project have stated, “the links between the seismo-tectonic process and atmosphere/ionosphere earthquake precursors remain ...
... sets of electromagnetic signals were ignored, because they were unexpected and the scientific connection between such signals and earthquakes was unknown. The designers of this project have stated, “the links between the seismo-tectonic process and atmosphere/ionosphere earthquake precursors remain ...
Layers of the Earth
... The asthenosphere is the layer of Earth that lies at a depth 100–250 km beneath Earth's surface. The asthenosphere gets its name from the Greek word for weak, asthenis, because of the relatively fragile nature of the materials of which it is made. It lies in the upper portion of Earth's structure tr ...
... The asthenosphere is the layer of Earth that lies at a depth 100–250 km beneath Earth's surface. The asthenosphere gets its name from the Greek word for weak, asthenis, because of the relatively fragile nature of the materials of which it is made. It lies in the upper portion of Earth's structure tr ...
Lafayette Parish School System 2013
... Volcanoes form when molten rock arises from deep within Earth and erupts from a crack in the crust A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic solid with a crystalline form, Igneous rocks form when molten material cools and crystallizes Sedimentary rocks form from consolidated rock particles or cry ...
... Volcanoes form when molten rock arises from deep within Earth and erupts from a crack in the crust A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic solid with a crystalline form, Igneous rocks form when molten material cools and crystallizes Sedimentary rocks form from consolidated rock particles or cry ...
Chapter 22.1: Earth’s Structure
... forces affect Earth’s surface. 2. List the 3 layers of Earth. 3. Which layer has currents of moving rock? 4. Which is the most dense layer? 5. Which layer is made of light rocks like silicates? 6. Which is more dense: Continental or Oceanic Crust? 7. Which layer of the mantle is part of Earth’s ...
... forces affect Earth’s surface. 2. List the 3 layers of Earth. 3. Which layer has currents of moving rock? 4. Which is the most dense layer? 5. Which layer is made of light rocks like silicates? 6. Which is more dense: Continental or Oceanic Crust? 7. Which layer of the mantle is part of Earth’s ...
Earth`s Structure
... • Crust: a thin, nearly solid rock layer that is uppermost in Earth’s structure. (Let’s go back to the hard-boiled egg example. If the yolk represents the core, then what part of the egg would represent the crust?) ...
... • Crust: a thin, nearly solid rock layer that is uppermost in Earth’s structure. (Let’s go back to the hard-boiled egg example. If the yolk represents the core, then what part of the egg would represent the crust?) ...
Earthquakes
... Forces In Earth’s Crust • How does stress in earth’s crust change earth’s surface? ...
... Forces In Earth’s Crust • How does stress in earth’s crust change earth’s surface? ...
Earth has several layers.
... As scientists studied Earth’s surface, they discovered that the lithosphere does not form a continuous shell around Earth. Instead, they found that the lithosphere is broken into many large and small slabs of rock called tectonic plates (tehk-TAHN-ihk). Scientists do not know exactly how or when in ...
... As scientists studied Earth’s surface, they discovered that the lithosphere does not form a continuous shell around Earth. Instead, they found that the lithosphere is broken into many large and small slabs of rock called tectonic plates (tehk-TAHN-ihk). Scientists do not know exactly how or when in ...
“Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks” Newcomer Academy
... Igneous rocks can form above and below the surface of the Earth. The rocks that form below the surface are made from the magma and are called intrusive (HINT: “IN”trusive = IN the Earth). ...
... Igneous rocks can form above and below the surface of the Earth. The rocks that form below the surface are made from the magma and are called intrusive (HINT: “IN”trusive = IN the Earth). ...
Chapter 22 Planet Earth
... Key Words – define these words on your paper as you read the following chapter. Sphere Axis Rotation Revolution Ellipse Equinox Solstice ...
... Key Words – define these words on your paper as you read the following chapter. Sphere Axis Rotation Revolution Ellipse Equinox Solstice ...
_____, meaning *all land,* is the name for the great landmass that
... • Wegener’s belief was a scientific hypothesis based on observations. • Continental drift was not accepted by all scientists because there was no evidence at the time to explain how continents could move. ...
... • Wegener’s belief was a scientific hypothesis based on observations. • Continental drift was not accepted by all scientists because there was no evidence at the time to explain how continents could move. ...
Chapter 18 Section One
... As scientists studied Earth’s surface, they discovered that the lithosphere does not form a continuous shell around Earth. Instead, they found that the lithosphere is broken into many large and small slabs of rock called tectonic plates (tehk-TAHN-ihk). Scientists do not know exactly how or when in ...
... As scientists studied Earth’s surface, they discovered that the lithosphere does not form a continuous shell around Earth. Instead, they found that the lithosphere is broken into many large and small slabs of rock called tectonic plates (tehk-TAHN-ihk). Scientists do not know exactly how or when in ...
part – i (mcq) (compulsory)
... (b) the Theory of Evolution is proven by the succession of fossils observed in rocks (c) the fossil record of life proves that life has succeeded on Earth (d) it is unlikely that life could have succeeded on other planets (e) None of these ...
... (b) the Theory of Evolution is proven by the succession of fossils observed in rocks (c) the fossil record of life proves that life has succeeded on Earth (d) it is unlikely that life could have succeeded on other planets (e) None of these ...
What Is Inside Earth?
... • The lithosphere is the top part of the mantle and the crust together. It is a rigid layer. • The asthenosphere is a soft layer underneath the lithosphere. This layer is hotter and under increasing pressure but still solid. • The lower mantle is solid. This solid material extends all the way to Ear ...
... • The lithosphere is the top part of the mantle and the crust together. It is a rigid layer. • The asthenosphere is a soft layer underneath the lithosphere. This layer is hotter and under increasing pressure but still solid. • The lower mantle is solid. This solid material extends all the way to Ear ...
Layers of the Earth
... Definition: This layer of the earth lies between the mantle and the solid inner core. It is the only liquid layer, a sea of mostly iron and nickel ...
... Definition: This layer of the earth lies between the mantle and the solid inner core. It is the only liquid layer, a sea of mostly iron and nickel ...
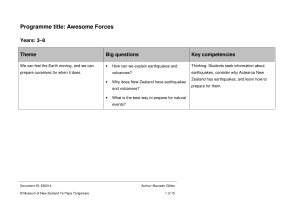
Programme title: Awesome Forces
... In this programme, students explore the inner workings of our planet. They experience what it is like at the centre of the Earth and uncover the layers of the Earth. Students piece together the puzzle of plate tectonics before investigating the causes of earthquakes and volcanoes. Finally, they disc ...
... In this programme, students explore the inner workings of our planet. They experience what it is like at the centre of the Earth and uncover the layers of the Earth. Students piece together the puzzle of plate tectonics before investigating the causes of earthquakes and volcanoes. Finally, they disc ...
Plate Tectonics
... 12. Why did most scientists reject Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift? 13. Do you think the scientists of Wegener’s time should have accepted his hypothesis? Why or why not? ...
... 12. Why did most scientists reject Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift? 13. Do you think the scientists of Wegener’s time should have accepted his hypothesis? Why or why not? ...
Continental Drift Powerpoint
... one time all of the continents had been joined together to form one huge continent His name was Alfred Wegener He called this supercontinent Pangaea (it means “all Earth”) And, over time (millions of years), the continents slowly drifted apart and ended up in the positions we see on Earth toda ...
... one time all of the continents had been joined together to form one huge continent His name was Alfred Wegener He called this supercontinent Pangaea (it means “all Earth”) And, over time (millions of years), the continents slowly drifted apart and ended up in the positions we see on Earth toda ...
6.E.2- Layers of Earth
... Identity where earthquakes and volcanoes occur Explain which geological features are associated with moving plates Summarize how the energy of an earthquake Describe how the movement of crustal plants causes geologic events and structures Analyze/describe the forces that share the lithosphere includ ...
... Identity where earthquakes and volcanoes occur Explain which geological features are associated with moving plates Summarize how the energy of an earthquake Describe how the movement of crustal plants causes geologic events and structures Analyze/describe the forces that share the lithosphere includ ...
Earth and Space Science Pacing Guide
... cross-cutting relations, and original lateral continuity) to support an opinion related to Earth’s geological history. (DOK 3) • Types of unconformity (e.g., disconformity, angular unconformity, nonconformity) Geological timetable Apply an understanding of ecological factors to explain relationships ...
... cross-cutting relations, and original lateral continuity) to support an opinion related to Earth’s geological history. (DOK 3) • Types of unconformity (e.g., disconformity, angular unconformity, nonconformity) Geological timetable Apply an understanding of ecological factors to explain relationships ...
The Earth`s Crust
... – They are formed by the pressing together of smaller particles of rock or the remains of living things. – They take a long time to form. – Beds of clay, sand, or gravel may harden to make sedimentary rock. – Types include: shale, sandstone, coal, and limestone. – Sedimentary Rocks are the most comm ...
... – They are formed by the pressing together of smaller particles of rock or the remains of living things. – They take a long time to form. – Beds of clay, sand, or gravel may harden to make sedimentary rock. – Types include: shale, sandstone, coal, and limestone. – Sedimentary Rocks are the most comm ...