Take a `Chance` on the volcano erupting
... is imminent: • The ratios of the gases emitted from the volcano. An increase in the sulphur dioxide/carbon dioxide ratio is particularly significant; • Increases in the emission of steam and other gases at fumaroles (minor vents on the volcano’s surface); • Shallow seismic swarms (groups of small ea ...
... is imminent: • The ratios of the gases emitted from the volcano. An increase in the sulphur dioxide/carbon dioxide ratio is particularly significant; • Increases in the emission of steam and other gases at fumaroles (minor vents on the volcano’s surface); • Shallow seismic swarms (groups of small ea ...
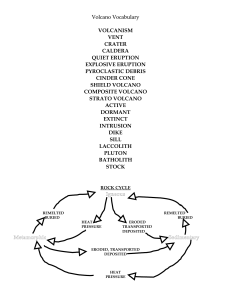
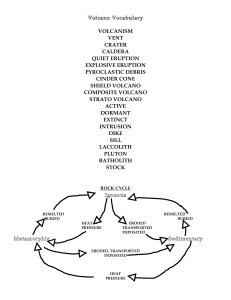
Volcano Vocabulary - watertown.k12.wi.us
... Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is ...
... Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is ...
Action at the Edge
... If you wanted to see a lot of volcanoes, where would you look? Volcanoes form where there are cracks and weak spots in Earth's crust. You'll find those mostly along the boundaries of tectonic plates that are moving apart. Volcanoes are also common where two plates are slowly colliding and one plate ...
... If you wanted to see a lot of volcanoes, where would you look? Volcanoes form where there are cracks and weak spots in Earth's crust. You'll find those mostly along the boundaries of tectonic plates that are moving apart. Volcanoes are also common where two plates are slowly colliding and one plate ...
Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
... with water to form fast-moving mudflows called lahars. • The weight of falling ash can collapse structures, bury crops, and damage engines. ...
... with water to form fast-moving mudflows called lahars. • The weight of falling ash can collapse structures, bury crops, and damage engines. ...
volcanism vent crater caldera quiet eruption explosive
... Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is ...
... Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is ...
Slide 1
... magma, comes from inside the earth and erupts onto the surface. The period of time a volcano is known to be active is unknown, because some seem to erupt forever. The volcano might be explosive and produce ashes and lava. The explosions are usually first because there are lots of gases inside the ma ...
... magma, comes from inside the earth and erupts onto the surface. The period of time a volcano is known to be active is unknown, because some seem to erupt forever. The volcano might be explosive and produce ashes and lava. The explosions are usually first because there are lots of gases inside the ma ...
Volcanoes
... and fragments of previously solidified rock), and gas erupt. - Eruption may build a mountain around the vent. (Mountain is also called a volcano). - Anatomy of a volcano: - magma chamber at depth - a vent to the surface ...
... and fragments of previously solidified rock), and gas erupt. - Eruption may build a mountain around the vent. (Mountain is also called a volcano). - Anatomy of a volcano: - magma chamber at depth - a vent to the surface ...
volcanoes
... Here are 4 of the volcanoes that make up the big island of Hawai'i. They are Mauna Kea (MK), Mauna Loa (ML), Hualalai (H), and Kohala (K). The photo was taken from near the summit of East Maui volcano (EM). These are the largest volcanoes on Earth ...
... Here are 4 of the volcanoes that make up the big island of Hawai'i. They are Mauna Kea (MK), Mauna Loa (ML), Hualalai (H), and Kohala (K). The photo was taken from near the summit of East Maui volcano (EM). These are the largest volcanoes on Earth ...
Question Report
... less dense than the surrounding solid material more dense than the surrounding solid material highly fluid ...
... less dense than the surrounding solid material more dense than the surrounding solid material highly fluid ...
The Ring of Fire
... • The Ring of Fire is 40,000 km long and is shape as a horse shoe. The Ring of Fire has 452 volcanoes and is home to 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes. • It is sometimes called the circum-Pacific belt or the circum-Pacific seismic belt. 90% of the world's earthquakes and 80% of the wor ...
... • The Ring of Fire is 40,000 km long and is shape as a horse shoe. The Ring of Fire has 452 volcanoes and is home to 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes. • It is sometimes called the circum-Pacific belt or the circum-Pacific seismic belt. 90% of the world's earthquakes and 80% of the wor ...
Volcanoes I
... Slide 6: Where Volcanoes Occur Other volcanoes can form at hotspots, places in the mantle where high temperatures melt rock. This creates a plume of magma which rises to the Earth’s surface. Slide 7:Hot Spots ...
... Slide 6: Where Volcanoes Occur Other volcanoes can form at hotspots, places in the mantle where high temperatures melt rock. This creates a plume of magma which rises to the Earth’s surface. Slide 7:Hot Spots ...
3- How do volcanoes form at convergent boundaries?
... 4- How do hot spot volcanoes form? Plumes of magma rise from deep in the mantle and melts through the crust creating volcanoes in the middle of plates. ...
... 4- How do hot spot volcanoes form? Plumes of magma rise from deep in the mantle and melts through the crust creating volcanoes in the middle of plates. ...
Volcano – An internet based Scavenger hunt
... Earth’s Moon: Mars: Venus: Io: 3. Name 3 tools that volcanologists use to study volcanoes and briefly describe each one. A. B. C. 4. Define Pahoehoe. 5. What is the name of the volcano in Oregon? ...
... Earth’s Moon: Mars: Venus: Io: 3. Name 3 tools that volcanologists use to study volcanoes and briefly describe each one. A. B. C. 4. Define Pahoehoe. 5. What is the name of the volcano in Oregon? ...
(volcanic) Landforms - Scoil Mhuire Geography
... • Subduction occurs where the heavier plate is pulled down under the lighter plate due to gravity and is melted deep in the mantle • This produces an explosive viscous (thick) lava; eruptions are violent due to intense build up of pressure • Dome volcanoes are steeply sloping cones with convex sides ...
... • Subduction occurs where the heavier plate is pulled down under the lighter plate due to gravity and is melted deep in the mantle • This produces an explosive viscous (thick) lava; eruptions are violent due to intense build up of pressure • Dome volcanoes are steeply sloping cones with convex sides ...
ErikaandCandiceVolPr..
... • Before the 1980 eruption Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1857. On May 18 1980, Mount St. Helens erupted so violently that the top of the mountain was blown off and a cloud of gases and ash was sent to an altitude of 19 km. The eruption was triggered by an earthquake measuring 5.1 on the R ...
... • Before the 1980 eruption Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1857. On May 18 1980, Mount St. Helens erupted so violently that the top of the mountain was blown off and a cloud of gases and ash was sent to an altitude of 19 km. The eruption was triggered by an earthquake measuring 5.1 on the R ...
Volcanoes
... tsunami • Destroyed 160 villages • Fine ashes from the eruption were carried by upper level winds as far away as New York City • Volcanic dust lowered global temperatures for five years, this caused ...
... tsunami • Destroyed 160 villages • Fine ashes from the eruption were carried by upper level winds as far away as New York City • Volcanic dust lowered global temperatures for five years, this caused ...
IGCSE Physical Geography
... Constructive (plates move apart – oceanic ridges) Gentle Volcanoes & weak EQ’s Conservative (plates move past each other) Frequent, sometimes violent EQ’s ...
... Constructive (plates move apart – oceanic ridges) Gentle Volcanoes & weak EQ’s Conservative (plates move past each other) Frequent, sometimes violent EQ’s ...
Volcanic ash - Cloudfront.net
... and other volcanic rocks travelling very quickly down the slopes of volcanoes. They are one of the most dangerous hazards posed by volcanoes. Pyroclastic flows are so hot and choking that if one is caught in one the ...
... and other volcanic rocks travelling very quickly down the slopes of volcanoes. They are one of the most dangerous hazards posed by volcanoes. Pyroclastic flows are so hot and choking that if one is caught in one the ...
6.1_Notes_powerpoint
... crust where molten material, or magma comes to the surface. • Volcanic Activity is a constructive force that adds new rock to existing land or forms new islands. ...
... crust where molten material, or magma comes to the surface. • Volcanic Activity is a constructive force that adds new rock to existing land or forms new islands. ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.