Lesson 1 - Tarleton State University
... wave but interacts as a particle as claimed by Einstein then particles must also have wave properties! Furthermore, the basic equations must be analogous since all particles are waves and vice-versa. ...
... wave but interacts as a particle as claimed by Einstein then particles must also have wave properties! Furthermore, the basic equations must be analogous since all particles are waves and vice-versa. ...
hrs_chemvocab_sa - parklandhonorsbiology
... ab. atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons changing the atomic mass ...
... ab. atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons changing the atomic mass ...
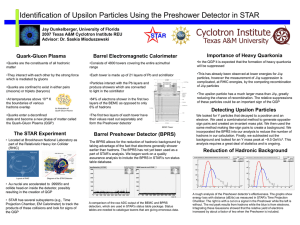
Dr. Saskia Mioduszewski Quark-Gluon Plasma
... • Au nuclei are accelerated to .99995c and collide head-on inside the detector, possibly resulting in the creation of QGP • STAR has several subsystems (e.g., Time Projection Chamber, EM Calorimeter) to track the products of these collisions and look for signs of the QGP ...
... • Au nuclei are accelerated to .99995c and collide head-on inside the detector, possibly resulting in the creation of QGP • STAR has several subsystems (e.g., Time Projection Chamber, EM Calorimeter) to track the products of these collisions and look for signs of the QGP ...
Radioactivity - Revision World
... Proton Number Z - This is the number of protons in the nucleus, and also the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Once called the atomic number. Isotopes - These are atoms with the same proton number, but different nucleon numbers. They have the same electron arrangement and, therefore, the same c ...
... Proton Number Z - This is the number of protons in the nucleus, and also the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Once called the atomic number. Isotopes - These are atoms with the same proton number, but different nucleon numbers. They have the same electron arrangement and, therefore, the same c ...
The ATLAS Detector - University of Birmingham
... layers are then ionised by the liquid argon. The excess electrons produced during this ionisation are attracted to the copper electrodes where the charge is measured. The amount of charge deposited at the electrodes can be used to deduce the energy of the original particle. A particle showering each ...
... layers are then ionised by the liquid argon. The excess electrons produced during this ionisation are attracted to the copper electrodes where the charge is measured. The amount of charge deposited at the electrodes can be used to deduce the energy of the original particle. A particle showering each ...