ET3034TUx -‐ 2.2.1 – Band Gap I: Electrons in Atoms
... Before we will discuss the silicon atom, I am starting with the most simple atom in our universe, the hydrogen atom. The hydrogen atom has a nucleus consisting of one proton. The ...
... Before we will discuss the silicon atom, I am starting with the most simple atom in our universe, the hydrogen atom. The hydrogen atom has a nucleus consisting of one proton. The ...
Homework 8
... c) The wave function in part (a) is ⟨x|E, α⟩ (i.e., the projection on to the x-basis of the energy and momentum eigenket |E, α⟩). Derive the normalisation N such that the eigenkets {|E, α⟩} are orthonormal (i.e., ⟨E, α|E ′ , α′ ⟩ = δ(E − E ′ ) δα,α′ ). d) A particle is in the state ψ(x) = N + eipx/h ...
... c) The wave function in part (a) is ⟨x|E, α⟩ (i.e., the projection on to the x-basis of the energy and momentum eigenket |E, α⟩). Derive the normalisation N such that the eigenkets {|E, α⟩} are orthonormal (i.e., ⟨E, α|E ′ , α′ ⟩ = δ(E − E ′ ) δα,α′ ). d) A particle is in the state ψ(x) = N + eipx/h ...
Chapter 6 | Thermochemistry
... The principal quantum number gives us the shell of the orbitals. This then gives the allowed values of (n – 1) which in turn describe the type of orbital (s, p, d, or f ). The m quantum number gives us the orientation of the orbital and its allowed values (– , – , + 1, . . . , – 1, ), which gives us ...
... The principal quantum number gives us the shell of the orbitals. This then gives the allowed values of (n – 1) which in turn describe the type of orbital (s, p, d, or f ). The m quantum number gives us the orientation of the orbital and its allowed values (– , – , + 1, . . . , – 1, ), which gives us ...
Cesium D Line Data
... Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 23 January 1998 (revision 1.6, 14 October 2003) ...
... Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 23 January 1998 (revision 1.6, 14 October 2003) ...
Examination and optimization of high resolution PET detector modules
... that produce UV/visible photons after absorbing the γ-photons. These photons are then typically detected by photomultiplier tubes (PMT-s) that are coupled to the scintillator matrix via a light guide layer. Spatial resolution and image quality is basically defined by the accuracy of determining the ...
... that produce UV/visible photons after absorbing the γ-photons. These photons are then typically detected by photomultiplier tubes (PMT-s) that are coupled to the scintillator matrix via a light guide layer. Spatial resolution and image quality is basically defined by the accuracy of determining the ...
ELECTRON TRANSPORT AT THE NANOSCALE Lecture Notes, preliminary version Geert Brocks December 2005
... The device shown in Fig. 1.2 is called a tunnel junction. The left and right regions consist of metals and the middle region consists of an insulator material, usually a metal-oxide.8 Such devices can be made in a very controlled way with the middle region having a thickness of a few nm. One is inte ...
... The device shown in Fig. 1.2 is called a tunnel junction. The left and right regions consist of metals and the middle region consists of an insulator material, usually a metal-oxide.8 Such devices can be made in a very controlled way with the middle region having a thickness of a few nm. One is inte ...
Dynamics of Classical Wave Scattering by Small Obstacles
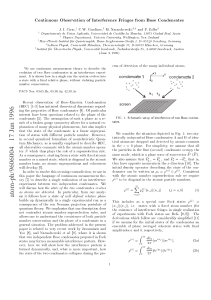
... Wave propagation in complex media is a large and interdisciplinary field of research with many unsolved problems that are scientifically challenging and technologically important [1]. Electromagnetic and acoustic waves are massless and described by a “classical” wave equation which is second order i ...
... Wave propagation in complex media is a large and interdisciplinary field of research with many unsolved problems that are scientifically challenging and technologically important [1]. Electromagnetic and acoustic waves are massless and described by a “classical” wave equation which is second order i ...
Atomic spectra
... and reach the collecting electrode. The collecting electrode is connected to a sensitive galvanometer and hence one can measure the current due to electrons reaching the collecting electrode. These electrons in travelling from the heater filament collide with the mercury atoms. By applying a small r ...
... and reach the collecting electrode. The collecting electrode is connected to a sensitive galvanometer and hence one can measure the current due to electrons reaching the collecting electrode. These electrons in travelling from the heater filament collide with the mercury atoms. By applying a small r ...
Atomic Spectroscopy
... d → p are allowed, while s → s or s → d are forbidden. The strongest allowed optical transitions are shown in Fig. 3. Note that each level for given n and l is split into two because of the fine structure splitting. This splitting is due to the effect of electron spin and its coupling with the angul ...
... d → p are allowed, while s → s or s → d are forbidden. The strongest allowed optical transitions are shown in Fig. 3. Note that each level for given n and l is split into two because of the fine structure splitting. This splitting is due to the effect of electron spin and its coupling with the angul ...
EOC_chapter28
... Assume that significant diffraction occurs when the width of the diffraction aperture is less than 10.0 times the wavelength of the wave being diffracted. (a) Determine the maximum speed at which the student can pass through the doorway so as to be significantly diffracted. (b) With that speed, how ...
... Assume that significant diffraction occurs when the width of the diffraction aperture is less than 10.0 times the wavelength of the wave being diffracted. (a) Determine the maximum speed at which the student can pass through the doorway so as to be significantly diffracted. (b) With that speed, how ...
CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I
... Finally, suppose we start with a state Ψ(x, 0) = (1/ 2)[ψ1 (x) + ψ2 (x)], and we let this state evolve in time. At any point in time, the state Ψ(x, t) will be some mixture of ψ1 (x) and ψ2 (x), and this mixture changes with time. Now, at some specific instance in time t, we measure the energy and o ...
... Finally, suppose we start with a state Ψ(x, 0) = (1/ 2)[ψ1 (x) + ψ2 (x)], and we let this state evolve in time. At any point in time, the state Ψ(x, t) will be some mixture of ψ1 (x) and ψ2 (x), and this mixture changes with time. Now, at some specific instance in time t, we measure the energy and o ...