M.Sc._Physics_Sem_III.pdf
... Relativistic Quantum Mechanics: Klein-Gordon equations, charge & current densities, physical interpretations and short comings of K-G equation, Dirac equation and its derivation, Dirac matrices and their properties, constant of motion for Dirac equation (spin of Dirac particle), electron in electrom ...
... Relativistic Quantum Mechanics: Klein-Gordon equations, charge & current densities, physical interpretations and short comings of K-G equation, Dirac equation and its derivation, Dirac matrices and their properties, constant of motion for Dirac equation (spin of Dirac particle), electron in electrom ...
Publication : Relativistic Coupled Cluster Calculations with
... level, namely at the DCB-FSCCSD level. The individual QED contributions are presented in Table III. To test the validity of these results, we also carried out perturbative QED calculations using the Uehling and Källén–Sabry [25,56] terms (as implemented in GRASP) for the VP, and the effective nonloc ...
... level, namely at the DCB-FSCCSD level. The individual QED contributions are presented in Table III. To test the validity of these results, we also carried out perturbative QED calculations using the Uehling and Källén–Sabry [25,56] terms (as implemented in GRASP) for the VP, and the effective nonloc ...
Selective field ionization in Li and Rb: Theory and experiment
... that lead to ionization at field F, with nearly randomly varying phases on the different paths; the differing phases essentially guarantee that the interference between different paths will average to zero. In the model of Ref. 关13兴, the phases need to be retained because all of the phase difference ...
... that lead to ionization at field F, with nearly randomly varying phases on the different paths; the differing phases essentially guarantee that the interference between different paths will average to zero. In the model of Ref. 关13兴, the phases need to be retained because all of the phase difference ...
shp_05 - Columbia University
... Observation tells us that physical quantities are not continuous down to the smallest scales, but tend to be discrete. O.K., we can live with that. But QM has another surprise: if you look small enough, matter – that is, “particles” –start to exhibit wavelike behavior. We have already seen hints of ...
... Observation tells us that physical quantities are not continuous down to the smallest scales, but tend to be discrete. O.K., we can live with that. But QM has another surprise: if you look small enough, matter – that is, “particles” –start to exhibit wavelike behavior. We have already seen hints of ...
Atoms and Nuclei PA 322
... Terms for non-equivalent electrons in many-electron atoms • Non-equivalent electrons: those which belong to different (n,l) subshells (e.g. orthohelium 1s2s) • Any (s, l) combination allowed without violating Pauli Exclusion ...
... Terms for non-equivalent electrons in many-electron atoms • Non-equivalent electrons: those which belong to different (n,l) subshells (e.g. orthohelium 1s2s) • Any (s, l) combination allowed without violating Pauli Exclusion ...
True Nature of Potential Energy of a Hydrogen Atom
... reduction comes from potential energy. However, potential energy has no fundamental substance and is considered a concept introduced by classical mechanics to maintain the law of energy conservation. Meanwhile, the energy gained by the hydrogen atom, as obtained using the Dirac equation, includes t ...
... reduction comes from potential energy. However, potential energy has no fundamental substance and is considered a concept introduced by classical mechanics to maintain the law of energy conservation. Meanwhile, the energy gained by the hydrogen atom, as obtained using the Dirac equation, includes t ...
Applications of the Schrodinger Wave Equation The free particle
... reflected particles. In zone II, they are only moving in one direction so the probability is constant. (remember the free particle with no ...
... reflected particles. In zone II, they are only moving in one direction so the probability is constant. (remember the free particle with no ...
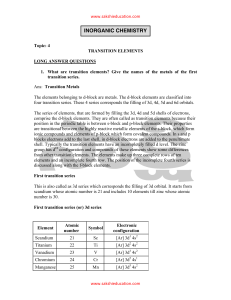
inorganic chemistry - Sakshieducation.com
... Alloys are homogenous solid solutions of two or more metals obtained by melting the components and then cooling the melt. These are formed by metals whose atomic radii differ by not more than 15% so that the atoms of one metal can easily take up the positions in the crystal lattice of the other. Sin ...
... Alloys are homogenous solid solutions of two or more metals obtained by melting the components and then cooling the melt. These are formed by metals whose atomic radii differ by not more than 15% so that the atoms of one metal can easily take up the positions in the crystal lattice of the other. Sin ...
Document
... Each photon has an energy hν, so the total # of photons needed to produce energy E is E/hν. The frequency of the radiation (ν = c/λ=?) and the total energy (?) emitted by the lamp E =?. E = P∆t, P - the power (in watts), ∆t - the time interval for which the lamp is turned on. • Answer: The number of ...
... Each photon has an energy hν, so the total # of photons needed to produce energy E is E/hν. The frequency of the radiation (ν = c/λ=?) and the total energy (?) emitted by the lamp E =?. E = P∆t, P - the power (in watts), ∆t - the time interval for which the lamp is turned on. • Answer: The number of ...
6. Molecular vibrations
... The force constant of a typical X-H chemical bond is around 500 N/m. Mass of the proton is about 1.7x10-27 kg w=5.4 x 1014 1/s ...
... The force constant of a typical X-H chemical bond is around 500 N/m. Mass of the proton is about 1.7x10-27 kg w=5.4 x 1014 1/s ...
RANDOM MATRIX THEORY IN PHYSICS
... U = [u1 u2 · · · uN ] are these eigenvectors. The probability density of the components unm of the eigenvector un can be calculated rather easily. For large N it approaches a Gaussian. This is equivalent to the Porter– Thomas distribution. While wavefunctions are often not accessible in an experimen ...
... U = [u1 u2 · · · uN ] are these eigenvectors. The probability density of the components unm of the eigenvector un can be calculated rather easily. For large N it approaches a Gaussian. This is equivalent to the Porter– Thomas distribution. While wavefunctions are often not accessible in an experimen ...
Spin-polarized transport through two quantum dots Interference and Coulomb correlation effects P.
... calculate the higher order Green functions from the corresponding equations of motion. The average values of the occupation numbers (which enter the expressions for the Green functions) and the Green functions have been calculated self-consistently. In section 2, we briefly describe the model as wel ...
... calculate the higher order Green functions from the corresponding equations of motion. The average values of the occupation numbers (which enter the expressions for the Green functions) and the Green functions have been calculated self-consistently. In section 2, we briefly describe the model as wel ...