Introduction to elementary quantum mechanics
... In both cases the Schrödinger equation depends only on one variable x. As differential equation it requires imposition of two boundary conditions to get its unique solution. In case of infinite potential barrier we have to require that the wave function vanishes at x=0 and x=L and also beyond the se ...
... In both cases the Schrödinger equation depends only on one variable x. As differential equation it requires imposition of two boundary conditions to get its unique solution. In case of infinite potential barrier we have to require that the wave function vanishes at x=0 and x=L and also beyond the se ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... • The wave equation is designated with a lower case Greek psi (). • The square of the wave equation, 2, gives a probability density map of where an electron has a certain statistical likelihood of being at any given instant in time. ...
... • The wave equation is designated with a lower case Greek psi (). • The square of the wave equation, 2, gives a probability density map of where an electron has a certain statistical likelihood of being at any given instant in time. ...
Full Text PDF
... In calculations we used two ab initio codes: OpenMx [4] and Quantum Espresso [5]. The first one uses atomic orbitals, the second one uses plane waves as the basis set for wave functions. The fully relativistic pseudopotentials are distributed only with OpenMx package. However, due to a very large nu ...
... In calculations we used two ab initio codes: OpenMx [4] and Quantum Espresso [5]. The first one uses atomic orbitals, the second one uses plane waves as the basis set for wave functions. The fully relativistic pseudopotentials are distributed only with OpenMx package. However, due to a very large nu ...
Atomic configuration guide
... Just a visualisation of what an atom plus its orbitals might be like. ...
... Just a visualisation of what an atom plus its orbitals might be like. ...
Calculating particle properties of a wave
... Quantum computing requires that quantum effects are dominant. Three approaches to quantum computing are pursued in the Physics Department ( silicon quantum dots , superconducting junctions , and cold atoms in traps). All of them use very low temperatures to keep the quantum effects undisturbed by th ...
... Quantum computing requires that quantum effects are dominant. Three approaches to quantum computing are pursued in the Physics Department ( silicon quantum dots , superconducting junctions , and cold atoms in traps). All of them use very low temperatures to keep the quantum effects undisturbed by th ...
REVISION CLASS SHEET - SEM - 2 CHEM
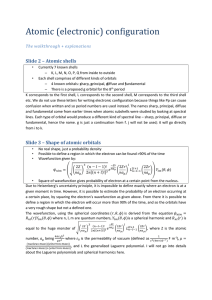
... moving small body like an electron. 68. How are the quantum numbers related to each other ? 69. Define pauli exclusion principle. Why it is called exclusion principle ? 70. In an atom, the first shell may contain upto 2 electrons, the second shell upto 8 the third upto 18 and the fourth shell upto 3 ...
... moving small body like an electron. 68. How are the quantum numbers related to each other ? 69. Define pauli exclusion principle. Why it is called exclusion principle ? 70. In an atom, the first shell may contain upto 2 electrons, the second shell upto 8 the third upto 18 and the fourth shell upto 3 ...
PowerPoint
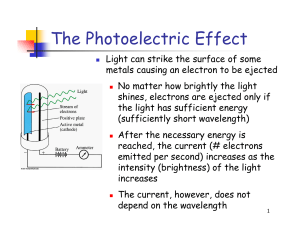
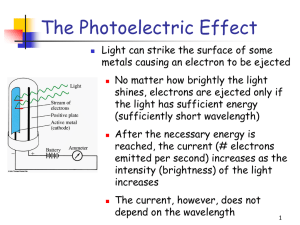
... particular amount of energy, called a quantum of energy Upon collision, each photon can transfer its energy to a single electron The more photons strike the surface of the metal, the more electrons are liberated and the higher is the current ...
... particular amount of energy, called a quantum of energy Upon collision, each photon can transfer its energy to a single electron The more photons strike the surface of the metal, the more electrons are liberated and the higher is the current ...
quantum mechanical model
... All moving objects have wavelike behavior. Louis de Broglie (1892-1987) derived an equation to find the wavelength of the associated matter wave for a moving object. ...
... All moving objects have wavelike behavior. Louis de Broglie (1892-1987) derived an equation to find the wavelength of the associated matter wave for a moving object. ...
Prof. Darrick Chang - Lecures - ICFO Schools on the Frontiers of Light
... • Tightly trap atoms to linearize the displacement • Numbers are not especially unique • Can we find physics more unique to atoms? ...
... • Tightly trap atoms to linearize the displacement • Numbers are not especially unique • Can we find physics more unique to atoms? ...
Parts of Unit 4 and 5Chp 5-6 – Electrons and
... Remember to start at the beginning of each arrow, and then follow it all of the way to the end, filling in the sublevels that it passes through. In other words, the order for filling in the sublevels becomes 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d,7p ...
... Remember to start at the beginning of each arrow, and then follow it all of the way to the end, filling in the sublevels that it passes through. In other words, the order for filling in the sublevels becomes 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d,7p ...
Lecture 30: Molecular interactions
... high spin complex, in the left figure, has all the spins unpaired hence the Fe in this state exhibits strong paramagnetism, which is directly related to the number of unpaired electron present in a molecule. ...
... high spin complex, in the left figure, has all the spins unpaired hence the Fe in this state exhibits strong paramagnetism, which is directly related to the number of unpaired electron present in a molecule. ...
Exercise 1, from the final exam in AST4220, 2005 Exercise 2
... This is a Schrödinger-like equation for the wave function of the Universe. The wave function of the Universe gives the probability density for observing different metrics. If we restrict the space of possible metrics to those of the Robertson-Walker form with a given spatial curvature k, the wave f ...
... This is a Schrödinger-like equation for the wave function of the Universe. The wave function of the Universe gives the probability density for observing different metrics. If we restrict the space of possible metrics to those of the Robertson-Walker form with a given spatial curvature k, the wave f ...