introductory concepts - New Age International
... The quantity ml, referred to as the magnetic quantum number, specifies the splitting of energies with a given n and l in a magnetic field. The number ms is called the spin quantum number; it shows that the spin of the electron about its own axis is quantised. The values of the four quantum numbers a ...
... The quantity ml, referred to as the magnetic quantum number, specifies the splitting of energies with a given n and l in a magnetic field. The number ms is called the spin quantum number; it shows that the spin of the electron about its own axis is quantised. The values of the four quantum numbers a ...
elastic - NUCLEAR REACTIONS VIDEO Project
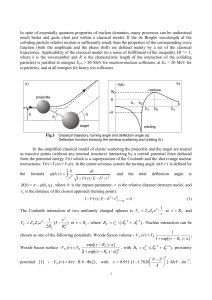
... where k (b, r ) k 1 V (r ) / E b 2 / r 2 is the local wavenumber, r0 (b) is the turning point of the trajectory with the impact parameter b (l 1 / 2) / k . In the general case there are several complex solutions of Eq. (1) for the turning points. Imaginary part of r0 (b) arises due to a po ...
... where k (b, r ) k 1 V (r ) / E b 2 / r 2 is the local wavenumber, r0 (b) is the turning point of the trajectory with the impact parameter b (l 1 / 2) / k . In the general case there are several complex solutions of Eq. (1) for the turning points. Imaginary part of r0 (b) arises due to a po ...
Chemistry Important Questions Collection
... 16. State and explain Avogadro’s hypothesis. How this theory can be used to determine the molecular weight of gas? 1. What is limiting reactants? Why is it essential in stoichiometric calculations? 2. 10.6gm of pure Na2CO3 if treated with 7.9gm of HCl to produce NaCl, H2O and CO2, a) Find the limiti ...
... 16. State and explain Avogadro’s hypothesis. How this theory can be used to determine the molecular weight of gas? 1. What is limiting reactants? Why is it essential in stoichiometric calculations? 2. 10.6gm of pure Na2CO3 if treated with 7.9gm of HCl to produce NaCl, H2O and CO2, a) Find the limiti ...
Easy Problems in Physics 130B
... if both electrons have principal quantum number n = 1? What are the states if one has n = 1 and the other n = 2? If an electron is in an n = 1 state, it can only have ` = 0 since ` < n for hydrogen states. So the only angular momenta we can add is the two spins. Adding spin one-half to spin one-half ...
... if both electrons have principal quantum number n = 1? What are the states if one has n = 1 and the other n = 2? If an electron is in an n = 1 state, it can only have ` = 0 since ` < n for hydrogen states. So the only angular momenta we can add is the two spins. Adding spin one-half to spin one-half ...
Document
... To be able to do this: the orbitals involved must have the same energy there must not be an electron in the second orbital with the same spin as that in the first orbital. If there is, the electron cannot orbit without breaking the Pauli principle. ...
... To be able to do this: the orbitals involved must have the same energy there must not be an electron in the second orbital with the same spin as that in the first orbital. If there is, the electron cannot orbit without breaking the Pauli principle. ...
Thermochemistry (4 lectures)
... To be able to do this: the orbitals involved must have the same energy there must not be an electron in the second orbital with the same spin as that in the first orbital. If there is, the electron cannot orbit without breaking the Pauli principle. ...
... To be able to do this: the orbitals involved must have the same energy there must not be an electron in the second orbital with the same spin as that in the first orbital. If there is, the electron cannot orbit without breaking the Pauli principle. ...
Chapter 2
... 5. Calculate the density of states of 1 m3 of copper at the Fermi level (m* = m0, EF = 7 eV). Note: Take 1 eV as energy interval. (Why?) 6. The density of states at the Fermi level (7 eV) was calculated for 1 cm3 of a certain metal to be about 1021 energy states per electron volt. Someone is asked t ...
... 5. Calculate the density of states of 1 m3 of copper at the Fermi level (m* = m0, EF = 7 eV). Note: Take 1 eV as energy interval. (Why?) 6. The density of states at the Fermi level (7 eV) was calculated for 1 cm3 of a certain metal to be about 1021 energy states per electron volt. Someone is asked t ...
Sodium D Line Data
... Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 27 May 2000 (revision 1.6, 14 October 2003) ...
... Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 27 May 2000 (revision 1.6, 14 October 2003) ...
File - SPHS Devil Physics
... The Photoelectric Effect All three of these observations are in violation of the standard laws of physics A more intense beam of light should produce ...
... The Photoelectric Effect All three of these observations are in violation of the standard laws of physics A more intense beam of light should produce ...
Strongly perturbed Stark states and electron correlation in Ba F. Robicheaux,
... Rydberg states in static electric fields. Because the Hamiltonian of a hydrogen atom in a static field separates in parabolic coordinates, the behavior of Rydberg states of nonhydrogenic systems may be described within a multichannel formalism. In this formalism, even a simple alkali-metal atom like ...
... Rydberg states in static electric fields. Because the Hamiltonian of a hydrogen atom in a static field separates in parabolic coordinates, the behavior of Rydberg states of nonhydrogenic systems may be described within a multichannel formalism. In this formalism, even a simple alkali-metal atom like ...
Prediction of a quantum anomalous Hall state in Co decorated silicene
... in the irreducible Brillouin zone is used. Silicene has been demonstrated to exist on various substrates. While we do not take into account a specific substrate in our calculations, our results are valid not only for a suspended sample but also in the case that the interaction with the substrate is ...
... in the irreducible Brillouin zone is used. Silicene has been demonstrated to exist on various substrates. While we do not take into account a specific substrate in our calculations, our results are valid not only for a suspended sample but also in the case that the interaction with the substrate is ...
ppt - UCSB Physics
... • Local constraint changes the nature of the “paramagnetic”=“classical spin liquid” state - Youngblood+Axe (81): dipolar correlations in “ice-like” models • Landau-theory assumes paramagnetic state is disordered - Local constraint in many models implies non-Landau classical criticality ...
... • Local constraint changes the nature of the “paramagnetic”=“classical spin liquid” state - Youngblood+Axe (81): dipolar correlations in “ice-like” models • Landau-theory assumes paramagnetic state is disordered - Local constraint in many models implies non-Landau classical criticality ...
Chap. 7 - Quantum Chemistry
... mechanics which suggested that an electron (or any other particle) exhibiting wavelike properties should be described by a mathematical equation called a wavefunction (denoted by the Greek letter psi, ). Specifically, he developed a mathematical formalism to describe the hydrogen atom as a wave. Th ...
... mechanics which suggested that an electron (or any other particle) exhibiting wavelike properties should be described by a mathematical equation called a wavefunction (denoted by the Greek letter psi, ). Specifically, he developed a mathematical formalism to describe the hydrogen atom as a wave. Th ...
File
... Alloy: A mixture of a metal and at least one other element. Balanced chemical equation: A written model for a reaction that shows the formulae and number of units for all the substances involved. Boiling point: The temperature at which a substance changes from the liquid state to the gas state. Carr ...
... Alloy: A mixture of a metal and at least one other element. Balanced chemical equation: A written model for a reaction that shows the formulae and number of units for all the substances involved. Boiling point: The temperature at which a substance changes from the liquid state to the gas state. Carr ...