Chapter 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS
... PREVIEW Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material through which charge can easily flow due to a large ...
... PREVIEW Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material through which charge can easily flow due to a large ...
Electric Forces
... PREVIEW Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material through which charge can easily flow due to a large ...
... PREVIEW Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material through which charge can easily flow due to a large ...
Visualizing cardiac blood flow using Lagrangian Coherent Structures
... The dynamics of cardiac blood flow is highly complex and not yet fully understood. Using threedimensional, three-component, time-resolved phase contrast MRI (4D PC-MRI), new understanding of flow dynamics can be obtained. However, the three-dimensional time-resolved flow is too complex to visualize ...
... The dynamics of cardiac blood flow is highly complex and not yet fully understood. Using threedimensional, three-component, time-resolved phase contrast MRI (4D PC-MRI), new understanding of flow dynamics can be obtained. However, the three-dimensional time-resolved flow is too complex to visualize ...
Microscopic Realization of 2-Dimensional Bosonic Topological
... where Jij = α,β (−ib†α,i bβ,j + h.c.) is the current operator of the condensate, and g > D. Under above interaction, the vortex/anti-vortex tends to increase/decrease the spin momentum at its core and as a consequence vortex (anti-vortex) will change its sign under time reversal. According to our pr ...
... where Jij = α,β (−ib†α,i bβ,j + h.c.) is the current operator of the condensate, and g > D. Under above interaction, the vortex/anti-vortex tends to increase/decrease the spin momentum at its core and as a consequence vortex (anti-vortex) will change its sign under time reversal. According to our pr ...
Lecture Notes
... Good question. One thing we know about Alexei Kitaev, is that he always has an answer. In this case it was the Kitaev model. Today I would like to start with explaining a bit my perspective on majoranas. Then move on to show a model the Kitaev model - that allows the exposed formation of Majoranas. ...
... Good question. One thing we know about Alexei Kitaev, is that he always has an answer. In this case it was the Kitaev model. Today I would like to start with explaining a bit my perspective on majoranas. Then move on to show a model the Kitaev model - that allows the exposed formation of Majoranas. ...
CIRCULAR MOTION
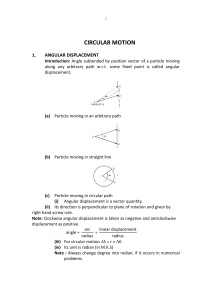
... Because Fc is always perpendicular to velocity or displacement, hence the work done by this force will always be zero. (ii) Circular motion in horizontal plane is usually uniform circular motion. (iii) There is an important difference between the projectile motion and circular motion. In projectile ...
... Because Fc is always perpendicular to velocity or displacement, hence the work done by this force will always be zero. (ii) Circular motion in horizontal plane is usually uniform circular motion. (iii) There is an important difference between the projectile motion and circular motion. In projectile ...
Charges and Electric Fields - University of Colorado Boulder
... Most materials can be classified as conductor or insulator. A conductor is also called a metal; an insulator also called a dielectric. Metals (Cu, Al, Au, Ag, Fe…) conduct electricity. In metals, some of the electrons (conduction electrons) can move freely through the metal. If there is an E-field, ...
... Most materials can be classified as conductor or insulator. A conductor is also called a metal; an insulator also called a dielectric. Metals (Cu, Al, Au, Ag, Fe…) conduct electricity. In metals, some of the electrons (conduction electrons) can move freely through the metal. If there is an E-field, ...
Quantum Mechanics in Three Dimensions
... long as both L 2 and L 3 are not equal to L 1, the first excited level is nondegenerate, that is, there is no other state with this energy. If L 2 or L 3 equals L 1, the level is doubly degenerate; if all three are equal, the level will be triply degenerate. Thus, the higher the symmetry, the more d ...
... long as both L 2 and L 3 are not equal to L 1, the first excited level is nondegenerate, that is, there is no other state with this energy. If L 2 or L 3 equals L 1, the level is doubly degenerate; if all three are equal, the level will be triply degenerate. Thus, the higher the symmetry, the more d ...
- Spiral - Imperial College London
... The College’s submission checklist informs me that I “must include a short statement in [my] own words, that the work is [my] own and that all else is appropriately referenced”, and that this statement “should appear at the beginning of the thesis” [1]. It adds that the copyright declaration should ...
... The College’s submission checklist informs me that I “must include a short statement in [my] own words, that the work is [my] own and that all else is appropriately referenced”, and that this statement “should appear at the beginning of the thesis” [1]. It adds that the copyright declaration should ...
Chapter 6 Work and Kinetic Energy
... True or false: (a) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its speed must have changed. (b) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its velocity must have changed. (c) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its direction of motion ...
... True or false: (a) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its speed must have changed. (b) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its velocity must have changed. (c) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its direction of motion ...
Introduction to ”Topological Geometrodynamics: an Overview
... Standard model describes rather successfully both electroweak and strong interactions but sees them as totally separate and contains a large number of parameters which it is not able to predict. For about four decades ago unified theories known as Grand Unified Theories (GUTs) trying to understand e ...
... Standard model describes rather successfully both electroweak and strong interactions but sees them as totally separate and contains a large number of parameters which it is not able to predict. For about four decades ago unified theories known as Grand Unified Theories (GUTs) trying to understand e ...
"Low-order longitudinal modes of single-component plasmas" Physics of Plasmas 2 (1995), pp. 2880-2894. M. D. Tinkle, R. G. Greaves, and C. M. Surko (PDF)
... probesused for neutral plasmasnor the destructivediagnostics used for electron plasmasare desirable.The sametechniques could also be used to monitor antiproton plasmas30*31 or as an adjunct to the usual techniquesfor electron plasma experiments.The propertiesof positron plasmasare the same as those ...
... probesused for neutral plasmasnor the destructivediagnostics used for electron plasmasare desirable.The sametechniques could also be used to monitor antiproton plasmas30*31 or as an adjunct to the usual techniquesfor electron plasma experiments.The propertiesof positron plasmasare the same as those ...
Kinetic Theory of the Alfvén Wave Acceleration of
... 1975; Borovsky, 1984, 1993a; Koskinen and Mälkki, 1993; Berthomier et al., 1998). While these steady-state solutions show that such structures can exist, they do not describe how they form. The time evolution of these structures has been studied through particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations (e.g., Goe ...
... 1975; Borovsky, 1984, 1993a; Koskinen and Mälkki, 1993; Berthomier et al., 1998). While these steady-state solutions show that such structures can exist, they do not describe how they form. The time evolution of these structures has been studied through particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations (e.g., Goe ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.