View Commentary - Journal Club for Condensed Matter Physics
... and C. M. Varma, Phys. Rev. B 26, 4883 (1982)). The recent condensed matter realizations of the Higgs mode are associated with quantum phase transitions which are fully described by relativistic Lagrangians like those in (1) in both the ordered and disordered phases, and at the quantum critical poin ...
... and C. M. Varma, Phys. Rev. B 26, 4883 (1982)). The recent condensed matter realizations of the Higgs mode are associated with quantum phase transitions which are fully described by relativistic Lagrangians like those in (1) in both the ordered and disordered phases, and at the quantum critical poin ...
AP_Electrostatics_Ho.. - Jaclyn Kuspiel Murray
... (a) 5.89 106 electrons and 7.23 106 protons C (b) 241 electrons and 161 protons C ...
... (a) 5.89 106 electrons and 7.23 106 protons C (b) 241 electrons and 161 protons C ...
Contest
... 39. An ideal gas is enclosed in a container. The volume of the container is reduced to half the original volume at constant temperature. According to kinetic theory, what is the best explanation for the increase in pressure created by the gas? (A) The average speed of the gas particles decreases, bu ...
... 39. An ideal gas is enclosed in a container. The volume of the container is reduced to half the original volume at constant temperature. According to kinetic theory, what is the best explanation for the increase in pressure created by the gas? (A) The average speed of the gas particles decreases, bu ...
This is the magnitude of the potential energy of the electron. This
... The electron and proton of the hydrogen atom are said to be equally and oppositely charged. They carry the fundamental constant called electric charge with them. The magnitude of this value appears empirically to be the same for both. The current explanation of electric charge is given by electric f ...
... The electron and proton of the hydrogen atom are said to be equally and oppositely charged. They carry the fundamental constant called electric charge with them. The magnitude of this value appears empirically to be the same for both. The current explanation of electric charge is given by electric f ...
Masterclass spreads the word for physics
... much as possible like real scientists in an authentic environment at a particle-physics institute, not only to feel the excitement of dealing with real data, but also to experience the difficulties of validating the scientific results. After lectures from practising scientists they performed measure ...
... much as possible like real scientists in an authentic environment at a particle-physics institute, not only to feel the excitement of dealing with real data, but also to experience the difficulties of validating the scientific results. After lectures from practising scientists they performed measure ...
Inertial mass and the quantum vacuum fields
... known as quantum field theory, is both conceptually rich and quantitatively successful: witness the agreement between theory and experiment of the magnetic moment of the electron to thirteen significant figures. Although the technique that has been used so far to develop the hypothesis connecting in ...
... known as quantum field theory, is both conceptually rich and quantitatively successful: witness the agreement between theory and experiment of the magnetic moment of the electron to thirteen significant figures. Although the technique that has been used so far to develop the hypothesis connecting in ...
Paper
... localization and edge states. And it has found generalizations in the spin quantum Hall effect and topological insulators. In the field of ultracold atoms, many-body phenomena are now explored at a scale a thousand times enlarged and at atomic densities a billion times smaller than electron densitie ...
... localization and edge states. And it has found generalizations in the spin quantum Hall effect and topological insulators. In the field of ultracold atoms, many-body phenomena are now explored at a scale a thousand times enlarged and at atomic densities a billion times smaller than electron densitie ...
problems - Physics
... (e) When we set up an integral to find the electric field at the observation location due to the entire rod, what will be the integration variable? ...
... (e) When we set up an integral to find the electric field at the observation location due to the entire rod, what will be the integration variable? ...
Student Pages - Quarknet
... What do we do? Students work in pairs. Your teacher will assign you events to examine, which analyses to do, and how to incorporate our results into results for the entire team. The goal, as stated in the introduction, is to state and support the assertion that we can use these experimental data to ...
... What do we do? Students work in pairs. Your teacher will assign you events to examine, which analyses to do, and how to incorporate our results into results for the entire team. The goal, as stated in the introduction, is to state and support the assertion that we can use these experimental data to ...
ARE THERE REALLY ELECTRONS? EXPERIMENT AND REALITY
... cathode rays carried negative charge. That had presum- electrostatic field. Thomson proceeded to answer that ably been shown earlier by Jean Perrin. Perrin had placed objection with the apparatus shown in figure 3. Cathode two coaxial metal cylinders, insulated from one another, rays from the cathod ...
... cathode rays carried negative charge. That had presum- electrostatic field. Thomson proceeded to answer that ably been shown earlier by Jean Perrin. Perrin had placed objection with the apparatus shown in figure 3. Cathode two coaxial metal cylinders, insulated from one another, rays from the cathod ...
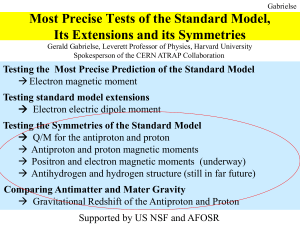
Most Precise Tests of the Standard Model, Its
... ever have envisioned, is correct. As one of the inventors, I remember that we thought of QED in 1949 as a temporary and jerry-built structure, with mathematical inconsistencies and renormalized infinities swept under the rug. We did not expect it to last more than ten years before some more solidly ...
... ever have envisioned, is correct. As one of the inventors, I remember that we thought of QED in 1949 as a temporary and jerry-built structure, with mathematical inconsistencies and renormalized infinities swept under the rug. We did not expect it to last more than ten years before some more solidly ...
Pdf
... cluster integrals which themselves depend upon Z, unlike their classical analogs. The definition of these cluster integrals follows in a natural fashion using techniques illustrated by construction (in closed form) of the successive Z derivatives of the Bose and Fermi ideal gas grand partition funct ...
... cluster integrals which themselves depend upon Z, unlike their classical analogs. The definition of these cluster integrals follows in a natural fashion using techniques illustrated by construction (in closed form) of the successive Z derivatives of the Bose and Fermi ideal gas grand partition funct ...
Wave mechanics and the Schrödinger equation
... was a mature, complete, and predictive science. Nowehere was confidence expressed more clearly than in the famous quote made at the time by Lord Kelvin: There is nothing new to be discovered in physics now. All that remains is more and more precise measurement. However, there were a number of seemin ...
... was a mature, complete, and predictive science. Nowehere was confidence expressed more clearly than in the famous quote made at the time by Lord Kelvin: There is nothing new to be discovered in physics now. All that remains is more and more precise measurement. However, there were a number of seemin ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.