16-3 NV pages mx - Quantum Optics and Spectroscopy
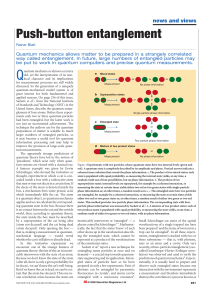
... In contrast, entangling states of many subsystems turns out to be a useful tool for quantum information processing. It has been shown that, by coherent manipulation of quantum states, quantum computers could solve certain problems much faster than conventional (classical) computers. This speed incre ...
... In contrast, entangling states of many subsystems turns out to be a useful tool for quantum information processing. It has been shown that, by coherent manipulation of quantum states, quantum computers could solve certain problems much faster than conventional (classical) computers. This speed incre ...
Quarterly 1 Review Trupia - Trupia
... approximately 1 atomic mass unit each? (1) proton and electron (2) proton and neutron (3) neutron and positron (4) electron and positron ...
... approximately 1 atomic mass unit each? (1) proton and electron (2) proton and neutron (3) neutron and positron (4) electron and positron ...
File
... • If the other person does the wrong action, he/she has to give everyone in the group the correct amount. • Be the highest chip holder at the end of the class period. ...
... • If the other person does the wrong action, he/she has to give everyone in the group the correct amount. • Be the highest chip holder at the end of the class period. ...
Fall/Winter 1994, Vol. 24, No. 3 - SLAC
... now been extended to cover other databases including experiments in HEP, conferences, software, institutions, and information from the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Particle Data Group. There are now over 9000 publications available with full text, and more than 40,000 accesses per week to the SPIRES ...
... now been extended to cover other databases including experiments in HEP, conferences, software, institutions, and information from the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Particle Data Group. There are now over 9000 publications available with full text, and more than 40,000 accesses per week to the SPIRES ...
Thixotropic Phenomena in Water
... The energy associated with the increment at 10 nm was calculated to be ~1.5 × 10−20 J. This was an important value for several reasons [7]. First, it is consistent with Woutersen and Bakker’s [8] measurements of the resonant intermolecular transfer of excitations from distention of OH excitations ov ...
... The energy associated with the increment at 10 nm was calculated to be ~1.5 × 10−20 J. This was an important value for several reasons [7]. First, it is consistent with Woutersen and Bakker’s [8] measurements of the resonant intermolecular transfer of excitations from distention of OH excitations ov ...
Particle Accelerators for High Energy Physics A Short History
... applies in the other transverse degree of freedom, with reversal of lens focusing character. Stability requires that M n remain finite for arbitrarily large n, and an eigenvalue analysis quickly shows that this will be so provided F < `/2. For ` small compared with the circumference of the orbit, th ...
... applies in the other transverse degree of freedom, with reversal of lens focusing character. Stability requires that M n remain finite for arbitrarily large n, and an eigenvalue analysis quickly shows that this will be so provided F < `/2. For ` small compared with the circumference of the orbit, th ...
Chemistry Review
... Capillary Action - the attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid Condensation- change in state from a gas to a liquid Deposition – change in state directly from a gas to a solid Diffusion – mixing of 2 or more gases Effusion – movement of a gas through a small opening Evaporati ...
... Capillary Action - the attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid Condensation- change in state from a gas to a liquid Deposition – change in state directly from a gas to a solid Diffusion – mixing of 2 or more gases Effusion – movement of a gas through a small opening Evaporati ...
Motors and Generators
... plan, choose equipment or resources for, and perform a first-hand investigation to predict and verify the effect on a generated electric current when: the distance between the coil and magnet is varied the strength of the magnet is varied the relative motion between the coil and magnet is varied ...
... plan, choose equipment or resources for, and perform a first-hand investigation to predict and verify the effect on a generated electric current when: the distance between the coil and magnet is varied the strength of the magnet is varied the relative motion between the coil and magnet is varied ...
Subtle is the Gravity - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... charge must be the same, which would mean all particles irrespective of their mass, shape and substance would fall with the same acceleration under gravity. This was what for the first time experimentally tested by Galileo. In Einstein’s words, gravity could be removed by letting oneself fall alongw ...
... charge must be the same, which would mean all particles irrespective of their mass, shape and substance would fall with the same acceleration under gravity. This was what for the first time experimentally tested by Galileo. In Einstein’s words, gravity could be removed by letting oneself fall alongw ...
Dimensionless Physical Constant Mysteries
... (7) There are many π and e combinations which are not unique solutions to this important unique physical number.4 (8) The α math formula must be useful for solving physical mysteries, mere arithmetic is not appreciated. (9) There may be an unique mysterious theoretical number J for the unique physic ...
... (7) There are many π and e combinations which are not unique solutions to this important unique physical number.4 (8) The α math formula must be useful for solving physical mysteries, mere arithmetic is not appreciated. (9) There may be an unique mysterious theoretical number J for the unique physic ...
Atomic Emission Spectra, Electron Configuration, Periodicity
... 2. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle: we cannot know where an electron is at any given moment in time - the best we can hope for is a probability picture of where the electron is likely to be. The possible positions of an electron are spread out in space in the same way that a wave is spread across ...
... 2. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle: we cannot know where an electron is at any given moment in time - the best we can hope for is a probability picture of where the electron is likely to be. The possible positions of an electron are spread out in space in the same way that a wave is spread across ...
Note
... material will be useful when analysing the motion of gears, cams and planar mechanisms (e.g. the crank-slider in an engine). Following determination of the motion, the forces and moments causing (or resulting) from the motion can be evaluated. Planar motion - all particles of a rigid body move along ...
... material will be useful when analysing the motion of gears, cams and planar mechanisms (e.g. the crank-slider in an engine). Following determination of the motion, the forces and moments causing (or resulting) from the motion can be evaluated. Planar motion - all particles of a rigid body move along ...
Complete the following statement: When a glass rod is rubbed with
... b) The net electrostatic force on the particle will be larger than that which would be exerted if the particle was at the center of the sphere. c) The net electrostatic force on the particle will be smaller than that which would be exerted if the particle was at the center of the sphere. d) The net ...
... b) The net electrostatic force on the particle will be larger than that which would be exerted if the particle was at the center of the sphere. c) The net electrostatic force on the particle will be smaller than that which would be exerted if the particle was at the center of the sphere. d) The net ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.