Lecture 10 - Eunil Won
... A shell of uniform charge attracts or repels a charged particle that is outside the shell as if all the shell’s charge were concentrated at its center If a charged particle is located inside a shell of uniform charge, there is no net electrostatic force on the particle from the shell ...
... A shell of uniform charge attracts or repels a charged particle that is outside the shell as if all the shell’s charge were concentrated at its center If a charged particle is located inside a shell of uniform charge, there is no net electrostatic force on the particle from the shell ...
Snímek 1
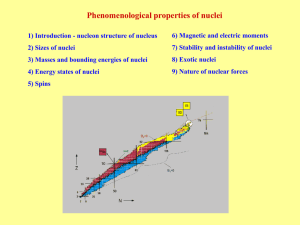
... Magic numbers – observed values of N and Z with increased stability. At 1896 H. Becquerel observed first sign of instability of nuclei – radioactivity. Instable nuclei irradiate: Alpha decay → nucleus transformation by 4He irradiation Beta decay → nucleus transformation by e-, e+ irradiation or capt ...
... Magic numbers – observed values of N and Z with increased stability. At 1896 H. Becquerel observed first sign of instability of nuclei – radioactivity. Instable nuclei irradiate: Alpha decay → nucleus transformation by 4He irradiation Beta decay → nucleus transformation by e-, e+ irradiation or capt ...
Magnetic effect of electric current Sources of
... Let a charge particle moves with velocity ~v . We also assume that there is no electric and gravitational fields. Experiments on the motion of the charge particles give the following results. (i) The magnetic force (Fm ) is proportional to the charge (q), speed (~v ) of the particle ~ i.e. and the m ...
... Let a charge particle moves with velocity ~v . We also assume that there is no electric and gravitational fields. Experiments on the motion of the charge particles give the following results. (i) The magnetic force (Fm ) is proportional to the charge (q), speed (~v ) of the particle ~ i.e. and the m ...
Solution
... page; see Fig. 2. (ii) Gravitational force: Fg = mg = 9.11 × 10−31 kg · 9.80 m/s2 = 8.93 × 10−30 N, downward. Electric force: Fe = qE = (−1.60 × 10−19 C) · (−100 N/C) = 1.60 × 10−17 N, upward. Magnetic force: Fm = qvB sin θ = (−1.60 × 10−19 C) · 6.00 × 106 m/s · 50.0 × 10−6 T · sin(π/2) = 4.80 × 10− ...
... page; see Fig. 2. (ii) Gravitational force: Fg = mg = 9.11 × 10−31 kg · 9.80 m/s2 = 8.93 × 10−30 N, downward. Electric force: Fe = qE = (−1.60 × 10−19 C) · (−100 N/C) = 1.60 × 10−17 N, upward. Magnetic force: Fm = qvB sin θ = (−1.60 × 10−19 C) · 6.00 × 106 m/s · 50.0 × 10−6 T · sin(π/2) = 4.80 × 10− ...
P1elec1
... E from1 = k q1 / r122 for a point charge, and g = G M / r2 for a mass. Why do both have an inverse square of distance (1/r2) ? If we consider that the field consists of a bunch of “moving particles” that make up the field, the density of particles, and hence the strength of the field, will decrease ...
... E from1 = k q1 / r122 for a point charge, and g = G M / r2 for a mass. Why do both have an inverse square of distance (1/r2) ? If we consider that the field consists of a bunch of “moving particles” that make up the field, the density of particles, and hence the strength of the field, will decrease ...
Static
... • Similar to Newton’s law of gravitation for masses • Underlies the bonding forces between molecules ...
... • Similar to Newton’s law of gravitation for masses • Underlies the bonding forces between molecules ...
The Cloud Chamber Experiment - University of Toronto Physics
... may want to determine whether this is true, and justify this assumption. This equation governs the deposit of energy as a charged particle travels through the sensitive medium, which in turn gives rise to the formation of droplets. The mechanism behind this interaction is that the charged particle a ...
... may want to determine whether this is true, and justify this assumption. This equation governs the deposit of energy as a charged particle travels through the sensitive medium, which in turn gives rise to the formation of droplets. The mechanism behind this interaction is that the charged particle a ...
STRUCTURE OF A TURE OF A TURE OF ATOM STRUCTURE OF A
... possess to eject an electron from a metal. It is different for different metals. When a photon of frequency 1.0×1015 s–1 was allowed to hit a metal surface, an electron having 1.988 × 10–19 J of kinetic energy was emitted. Calculate the threshold frequency of this metal. Show that an electron will n ...
... possess to eject an electron from a metal. It is different for different metals. When a photon of frequency 1.0×1015 s–1 was allowed to hit a metal surface, an electron having 1.988 × 10–19 J of kinetic energy was emitted. Calculate the threshold frequency of this metal. Show that an electron will n ...
Theory of (strongly coupled) quark
... • The falling membrane is created which separate two regions of two different metrics: it is becoming a b.h. horizon Now linearized version in progress (field from a static Maldacena string recently done Lin,ES ...
... • The falling membrane is created which separate two regions of two different metrics: it is becoming a b.h. horizon Now linearized version in progress (field from a static Maldacena string recently done Lin,ES ...
UNCHARGED PARTICLE TUNNELING FROM NON
... of quantum gravity or string/ M-theory , it is argued that the information could come out if the outgoing radiation were not exactly thermal but had subtle corrections[2]. There is some degree of mystery remains in the mechanism of blackhole radiation. In the original derivation of blackhole evapora ...
... of quantum gravity or string/ M-theory , it is argued that the information could come out if the outgoing radiation were not exactly thermal but had subtle corrections[2]. There is some degree of mystery remains in the mechanism of blackhole radiation. In the original derivation of blackhole evapora ...
Higgs Colliquium, U of South Carolina - Physics
... Cannot predict the mass of the Higgs or how many Higgs particles. The minimum is one, but there can be more! Does not contain dark matter or dark energy. Magnitude of CP violation for baryon asymmetry (CKM CPV too small) • Second level No gravity Neutrino mass ? ...
... Cannot predict the mass of the Higgs or how many Higgs particles. The minimum is one, but there can be more! Does not contain dark matter or dark energy. Magnitude of CP violation for baryon asymmetry (CKM CPV too small) • Second level No gravity Neutrino mass ? ...
Electric Potential
... C. The potential difference between two points is thus the negative of the work done by the electrostatic force to move a unit charge from one point to the other. D. If we set Ui =0 at infinity as our reference potential energy, then the electric potential V must also be zero there. Therefore, t ...
... C. The potential difference between two points is thus the negative of the work done by the electrostatic force to move a unit charge from one point to the other. D. If we set Ui =0 at infinity as our reference potential energy, then the electric potential V must also be zero there. Therefore, t ...
Coulomb`s Law - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ► He was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1923 for his 1917 research that led to the elementary charge of 1.60x10-19C ► Today, the accepted value of the elementary charge is 1.60217733x10-19C ...
... ► He was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1923 for his 1917 research that led to the elementary charge of 1.60x10-19C ► Today, the accepted value of the elementary charge is 1.60217733x10-19C ...
physics/9902034 PDF
... A new formulation of special relativity is described. It is based on a postulate that the universe is a vast Cellular Automata (CA), (ref. 2,3,4). It is also based on a new theory of inertia (ref. 5) proposed by R. Haisch, A. Rueda, and H. Puthoff, which we modified, and called Quantum Inertia (QI). ...
... A new formulation of special relativity is described. It is based on a postulate that the universe is a vast Cellular Automata (CA), (ref. 2,3,4). It is also based on a new theory of inertia (ref. 5) proposed by R. Haisch, A. Rueda, and H. Puthoff, which we modified, and called Quantum Inertia (QI). ...
PH203 exam 1 2014
... _____1) Two nuclei each contain two protons and exert a force 4 N on each other. If we transfer a proton from one of these nuclei to the other, the force on each nucleus is now reduced to 3 N. _____2) Two neutral objects cannot attract each other electrically because they have no excess charge. ____ ...
... _____1) Two nuclei each contain two protons and exert a force 4 N on each other. If we transfer a proton from one of these nuclei to the other, the force on each nucleus is now reduced to 3 N. _____2) Two neutral objects cannot attract each other electrically because they have no excess charge. ____ ...
Systems of Particles - UCF College of Sciences
... Two blocks are free to slide along the frictionless wooden track ABC shown in Figure. A block of mass m1 = 5.00 kg is released from A. Protruding from its front end is the north pole of a strong magnet, repelling the north pole of an identical magnet embedded in the back end of the block of mass m2 ...
... Two blocks are free to slide along the frictionless wooden track ABC shown in Figure. A block of mass m1 = 5.00 kg is released from A. Protruding from its front end is the north pole of a strong magnet, repelling the north pole of an identical magnet embedded in the back end of the block of mass m2 ...
Student ______ AP PHYSICS 2 Date ______ Magnetostatics
... a. Determine the spring constant k of each spring in terms of the other given quantities and fundamental constants. ...
... a. Determine the spring constant k of each spring in terms of the other given quantities and fundamental constants. ...
Magnetic dynamics of weakly and strongly interacting
... ⫽570⫾100 K and the preexponential factor 0 ⫽1.3⫺0.8 ⫻10⫺10 s for a rotation of the sublattice magnetization directions in the rhombohedral 共111兲 plane. The corresponding median superparamagnetic blocking temperature is about 150 K. The dynamics of the second, dry sample, in which the particles are ...
... ⫽570⫾100 K and the preexponential factor 0 ⫽1.3⫺0.8 ⫻10⫺10 s for a rotation of the sublattice magnetization directions in the rhombohedral 共111兲 plane. The corresponding median superparamagnetic blocking temperature is about 150 K. The dynamics of the second, dry sample, in which the particles are ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.