Trapped particles and asymmetry-induced transport
... below the plasma E⫻B rotation frequency, i.e., f ⱗm f E . The mode consists of trapped particles on either side of an electrostatic potential barrier which execute E⫻B drift oscillations that are 180° out of phase, while passing particles move along field lines to Debye shield the potential from t ...
... below the plasma E⫻B rotation frequency, i.e., f ⱗm f E . The mode consists of trapped particles on either side of an electrostatic potential barrier which execute E⫻B drift oscillations that are 180° out of phase, while passing particles move along field lines to Debye shield the potential from t ...
Superluminal Quantum Models of the Photon and Electron
... In 1925, Werner Heisenberg introduced matrix mechanics to describe what is observable about radiation from atoms – light frequencies and intensities. In 1926, Erwin Schrodinger in introduced wave mechanics to predict the observed energy levels of atoms based on electron wave properties. The two theo ...
... In 1925, Werner Heisenberg introduced matrix mechanics to describe what is observable about radiation from atoms – light frequencies and intensities. In 1926, Erwin Schrodinger in introduced wave mechanics to predict the observed energy levels of atoms based on electron wave properties. The two theo ...
Document
... • The wave functions for the hydrogen atom contain three parameters that must have specific integral values called quantum numbers. • A wave function with a given set of these three quantum numbers is called an atomic orbital. • These orbitals allow us to visualize the region in which there is a pro ...
... • The wave functions for the hydrogen atom contain three parameters that must have specific integral values called quantum numbers. • A wave function with a given set of these three quantum numbers is called an atomic orbital. • These orbitals allow us to visualize the region in which there is a pro ...
a ∇ µ
... Here we will consider N = 3 case of the Yang – Mills equations. Equations (3) are nonlinear generalizations of Maxwell equations. The spherally symmetric static solution in electrodynamics is Coulomb potential. Well known spherically symmetric static solution for the SU(2) Yang – Mills equations are ...
... Here we will consider N = 3 case of the Yang – Mills equations. Equations (3) are nonlinear generalizations of Maxwell equations. The spherally symmetric static solution in electrodynamics is Coulomb potential. Well known spherically symmetric static solution for the SU(2) Yang – Mills equations are ...
ISWTalmadge1
... than for the mirror configuration. However, at the reduced power and field strength of the present experiments, the effect of the radial electric field for the mirror configuration is to lower the neoclassical transport for the mirror configuration so that the anomalous contribution dominates for bo ...
... than for the mirror configuration. However, at the reduced power and field strength of the present experiments, the effect of the radial electric field for the mirror configuration is to lower the neoclassical transport for the mirror configuration so that the anomalous contribution dominates for bo ...
CYC69H07
... In order to get a quantitative estimate of the amplitude build up by this process a series of computations were made. The motion was followed from an energy slightly above 100 keV for 800 particle turns. The acceleration occurred in a narrow, straight acceleration gap with a voltage of 25 kV. In Fig ...
... In order to get a quantitative estimate of the amplitude build up by this process a series of computations were made. The motion was followed from an energy slightly above 100 keV for 800 particle turns. The acceleration occurred in a narrow, straight acceleration gap with a voltage of 25 kV. In Fig ...
DR8_Circular_Colliders_2
... The beam-beam interaction at large amplitudes is highly nonlinear For small amplitude particles it is characterized by a quadrupole-like force with focal ...
... The beam-beam interaction at large amplitudes is highly nonlinear For small amplitude particles it is characterized by a quadrupole-like force with focal ...
P.def.g.1. The first particle is in equilibrium.
... that initial avaliable information is used as an input, this information evokes the rules from long term memory, and judgements are produced as an output by the rules. Judgements resulting from reasoning is a new information. There are two main operations in the process: the first is evoking the rul ...
... that initial avaliable information is used as an input, this information evokes the rules from long term memory, and judgements are produced as an output by the rules. Judgements resulting from reasoning is a new information. There are two main operations in the process: the first is evoking the rul ...
Nanowire dye-sensitized solar cells
... • These excess electrons have a broad and featureless absorption spectrum in the range 400-800 nm Study of the electron injection rate • Comparison between the nanoparticles and the nanowires • Particle and wire films have dissimilar surfaces onto which the sensitizing dyes adsorbs - ZnO particles ...
... • These excess electrons have a broad and featureless absorption spectrum in the range 400-800 nm Study of the electron injection rate • Comparison between the nanoparticles and the nanowires • Particle and wire films have dissimilar surfaces onto which the sensitizing dyes adsorbs - ZnO particles ...
Ground-state properties of the attractive one
... The results we find from the study of incremental groundstate wave-function overlaps give overwhelmimg support to the mean-field results, viz. the general existence of two transitional couplings. Within the context of mean-field theory the system exhibits a broken symmetry phase. Our meanfield resul ...
... The results we find from the study of incremental groundstate wave-function overlaps give overwhelmimg support to the mean-field results, viz. the general existence of two transitional couplings. Within the context of mean-field theory the system exhibits a broken symmetry phase. Our meanfield resul ...
CH20-revision - University of Southampton
... Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
... Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
Beta Decay
... theory of beta decay and establishing the small mass of the neutrino. Toward that end, your reports should include a counts vs. momentum and a counts vs. energy plot for both Cs137 and Na22 for the full energy range of the spectrometer. For Na22 you should show the Fermi-Kurie plot, from which the v ...
... theory of beta decay and establishing the small mass of the neutrino. Toward that end, your reports should include a counts vs. momentum and a counts vs. energy plot for both Cs137 and Na22 for the full energy range of the spectrometer. For Na22 you should show the Fermi-Kurie plot, from which the v ...
6.8 Mb - Todd Satogata
... § It’s a much much better approximation, but again only an approximation! § Superceded by Einstein’s general theory of relativity (1916) § But this equation works well enough to pretty much all everyday phenomena ...
... § It’s a much much better approximation, but again only an approximation! § Superceded by Einstein’s general theory of relativity (1916) § But this equation works well enough to pretty much all everyday phenomena ...
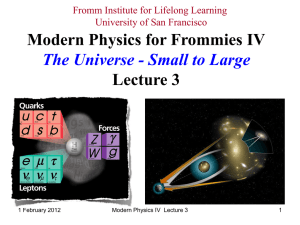
ModPhys IV Lecture 3
... The solutions are characterized by a single quantum number (n) in the 1-D case and by three numbers (nx, ny and nz) in 3-D. These quantum numbers arise from the imposition of boundary conditions on the solutions. We might expect that in the 3-D problem of the hydrogen atom the solutions will be char ...
... The solutions are characterized by a single quantum number (n) in the 1-D case and by three numbers (nx, ny and nz) in 3-D. These quantum numbers arise from the imposition of boundary conditions on the solutions. We might expect that in the 3-D problem of the hydrogen atom the solutions will be char ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.