The Ear: Hearing and Balance
... – Coils around a bony pillar – Contains the organ of Corti (hearing receptor) ...
... – Coils around a bony pillar – Contains the organ of Corti (hearing receptor) ...
our Student Guide - Cleveland Hearing and Speech Center
... loud sounds/noises as opposed to other causes. NIHL is permanent and cannot be fixed, but it can be prevented. Pinna – This is the outer part of your ear that everyone can see; also called the auricle. It helps to ‘collect’ sound waves and funnels them into the ear canal. ...
... loud sounds/noises as opposed to other causes. NIHL is permanent and cannot be fixed, but it can be prevented. Pinna – This is the outer part of your ear that everyone can see; also called the auricle. It helps to ‘collect’ sound waves and funnels them into the ear canal. ...
Sound - Safety Executives of New York
... Human ears attenuate sounds below 1 kHz We perceive high frequency sounds to be louder ...
... Human ears attenuate sounds below 1 kHz We perceive high frequency sounds to be louder ...
The Basics, the Science, and the Future Potential of Otoacoustic
... The ear canal sound pressure waveform from a healthy adult ear following the presentation of a click stimulus of intensity 84 dB SPL peak equivalent (approximately 60 dB SL, sensation level) presented at a rate of 50 per second. The small panel inset shows the waveform of the stimulus in the ear can ...
... The ear canal sound pressure waveform from a healthy adult ear following the presentation of a click stimulus of intensity 84 dB SPL peak equivalent (approximately 60 dB SL, sensation level) presented at a rate of 50 per second. The small panel inset shows the waveform of the stimulus in the ear can ...
The Ear - Downey Unified School District
... window and pass through the cochlea • In the cochlea, the waves trigger the hair receptor cells from the organ of corti • The organ of corti passes the signal onto the cochlear nerve which goes all the way up into the auditory cortex, where it’s processed. • The waves continue on, out the round wind ...
... window and pass through the cochlea • In the cochlea, the waves trigger the hair receptor cells from the organ of corti • The organ of corti passes the signal onto the cochlear nerve which goes all the way up into the auditory cortex, where it’s processed. • The waves continue on, out the round wind ...
Hearing with Our Brains - Brainvolts
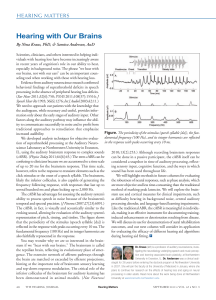
... the audiogram, while necessary and useful, provides information only about the early stages of auditory input. Other factors along the auditory pathway may influence the ability to communicate successfully in noise and to profit from traditional approaches to remediation that emphasize Figure. The p ...
... the audiogram, while necessary and useful, provides information only about the early stages of auditory input. Other factors along the auditory pathway may influence the ability to communicate successfully in noise and to profit from traditional approaches to remediation that emphasize Figure. The p ...
How Does the Ear Work? - Deaf Children Australia
... The Inner Ear The vibrations from the small bones in the middle ear causes small waves in the fluid inside the cochlear. The cochlear is shaped like a snail's shell, is very intricate and complex and has about 24,000 very tiny hair cells. In the cochlear, the hair cells are arranged so that high fre ...
... The Inner Ear The vibrations from the small bones in the middle ear causes small waves in the fluid inside the cochlear. The cochlear is shaped like a snail's shell, is very intricate and complex and has about 24,000 very tiny hair cells. In the cochlear, the hair cells are arranged so that high fre ...
Hearing
... threshold of detectability is elevated ⇒ signal must be > threshold to detect signal ...
... threshold of detectability is elevated ⇒ signal must be > threshold to detect signal ...
Facts About Noise- Induced Hearing Loss
... Approximately 36 million Americans have hearing loss. One in three developed their hearing loss as a result of exposure to noise. ...
... Approximately 36 million Americans have hearing loss. One in three developed their hearing loss as a result of exposure to noise. ...
Answer Key: Hearing (Grades 9 to 12)
... a. auditory processing disorder b. otitis media c. noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) Congenital ...
... a. auditory processing disorder b. otitis media c. noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) Congenital ...
The anatomy of the hearing process involves the external, middle
... sound aid and residual hearing to develop oral communication skills. The oral approach emphasizes the use of amplified sound and residual hearing but also may employ lipreading, reading and writing, motokinesthetic speech training (feeling an individual’s face and reproducing breath and voice patter ...
... sound aid and residual hearing to develop oral communication skills. The oral approach emphasizes the use of amplified sound and residual hearing but also may employ lipreading, reading and writing, motokinesthetic speech training (feeling an individual’s face and reproducing breath and voice patter ...
Sensory_systems
... 8) From medulla impulses travel to superior olivary nucleus then to the inferior colliculus 9) From inferior colliculus impulses go to medial geniculate bodies in the thalamus and then to auditory cortex - inferior colliculus also sends impulses to superior colliculus for reflex action ...
... 8) From medulla impulses travel to superior olivary nucleus then to the inferior colliculus 9) From inferior colliculus impulses go to medial geniculate bodies in the thalamus and then to auditory cortex - inferior colliculus also sends impulses to superior colliculus for reflex action ...
psychoacoustics and the effects of hearing loss
... Assessment of the audibility and clarity of the speech that children hear via their hearing aids is usually determined using at least three methods – observing reactions and spoken responses to spoken messages, formal speech perception tests and listening to their voluntary speech. It is important t ...
... Assessment of the audibility and clarity of the speech that children hear via their hearing aids is usually determined using at least three methods – observing reactions and spoken responses to spoken messages, formal speech perception tests and listening to their voluntary speech. It is important t ...
HOW IS HEARING TESTED? - Boys Town National Research Hospital
... used commonly during newborn and early childhood hearing screenings. It does not require sedation. With Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR), the patient sleeps or rests quietly while sounds are played to the ear through a small earphone. Recording electrodes on the head send the brain wave response to ...
... used commonly during newborn and early childhood hearing screenings. It does not require sedation. With Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR), the patient sleeps or rests quietly while sounds are played to the ear through a small earphone. Recording electrodes on the head send the brain wave response to ...
What is an audiogram?
... masking to find out which ear (cochlea) is hearing the test sound. Sound heard in a room reaches both ears at very similar levels. When very young children are tested with sounds played out of a loudspeaker, the sound is assumed to be heard by the “better ear”, regardless of which ear is nearest the ...
... masking to find out which ear (cochlea) is hearing the test sound. Sound heard in a room reaches both ears at very similar levels. When very young children are tested with sounds played out of a loudspeaker, the sound is assumed to be heard by the “better ear”, regardless of which ear is nearest the ...
Cochlear Implants - Electrical, Computer & Biomedical Engineering
... Fluid movement stimulates hair cells Hairs move back and forth sending electrical signals to auditory nerve Carried to the brain ...
... Fluid movement stimulates hair cells Hairs move back and forth sending electrical signals to auditory nerve Carried to the brain ...
HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE
... – Filled with fluid and tiny hair cells – Depending on which way your head is tilted, the fluid moves the hair cells, an they send a signal to your brain ...
... – Filled with fluid and tiny hair cells – Depending on which way your head is tilted, the fluid moves the hair cells, an they send a signal to your brain ...
скачати - ua
... does all of the work. The outer ear works as a reverse megaphone, which collects the sounds that we hear and brings them into the inner part of the ear. Ears are located on either side of the head to help with sound localization. Sound localization is how we determine where the different sounds are ...
... does all of the work. The outer ear works as a reverse megaphone, which collects the sounds that we hear and brings them into the inner part of the ear. Ears are located on either side of the head to help with sound localization. Sound localization is how we determine where the different sounds are ...
Olivocochlear system

The olivocochlear system is a component of the auditory system involved with the descending control of the cochlea. Its nerve fibres, the olivocochlear bundle (OCB), form part of the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIIIth cranial nerve, also known as the auditory-vestibular nerve), and project from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem (pons) to the cochlea.